APPENDIX 1. List of characters
Note that the zero state is primitive unless otherwise stated. Multistate characters are ordered unless stated to be unordered or a stepmatrix.
Teeth
1. Upper incisors: more than 3, simple structure, similar-sized (0); 3, simple structure, similar sized (1); 2, simple structure, similar-sized (2); 3 or 2, similar-sized, spatulate (3); 3 or 2, the first enlarged without heel (posterocone) (4); 2, both enlarged, simple (5); 3, the first enlarged with heel (posterocone) but only one terminal cusp (6); 3 or 2, the first enlarged, with heel (posterocone) and 2 or 3 terminal cusps (7); 3 or 2, similar-sized, serrated/denticulate (8); 1 or none (9). Primitive state based on Eomaia and Vincelestes. STEPMATRIX.
2. Mesial gap between mesialmost upper teeth: absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on Eomaia and Vincelestes. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 9.
3. Lower incisors: 4, simple structure, similar-sized (0); 4, first enlarged (1); 3, simple structure, similar-sized (2); 3 or 2, similar-sized, spatulate (3); 3 or 2, first enlarged, simple (4); 3, first two enlarged, simple (5); first incisor of 3 or 2, or sole if one, enlarged and serrated (6); 3 or 2, similar-sized, serrated/denticulate (7); absent (8). Primitive state based on Eomaia and Prokennalestes. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | - | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | - | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| 6 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | - | 1 | 2 |
| 7 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 |
| 8 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | - |
4. DI2 /2 simple, small, fully enamelled, rooted (if unknown, inferred from state of I2 /2 or form of the dentary), or absent (0); hypselodont, chisel-shaped with buccally restricted enamel (1). Primitive state based on ingroup commonality.
5. Upper canine: large, two-rooted (0); large, single-rooted (1); small, single rooted (2); small, two-rooted (3); absent (4). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) characters 23-24. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 |
| 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | - |
6. Lower canine: large, two-rooted (0); large, single-rooted (1); small, single rooted, without talonid cusp (2); small, single rooted, with talonid cusp (3); small, two-rooted (4); absent (5). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) characters 25-26. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - |
7. P3 /3 present (0); absent (1). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
8. P1 root number: 2 (0); 1 (1); tooth absent (2). Primitive state based on Juramaia. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 33.
9. P1 root number: 2 (0); 1 (1); tooth absent (2). Primitive state based on Juramaia. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 48.
10. P2 root number: 2 or more (0); 2 upper, one lower (1); 1 (2); 2 or one upper, P2 absent (3); P2 absent (4). Primitive state based on Juramaia. Those only known from P2 are assumed to have same P2 root number.
11. P4 root number: 1 (0); 2 (1) PRIMITIVE; 3 (2). Primitive state based on Juramaia.
12. P4 metacone absent (0); small, close to paracone (1); large, distant from paracone (2); no cusp structure (3). Primitive state based on Juramaia and Prokennalestes. Modified from Hooker and Russell (2012) character 2. STEPMATRIX
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - |
13. P4 protocone lobe essentially absent (0); small, short with small protocone (1); relatively long with small protocone (2); relatively long with large protocone (3). Primitive state based on Juramaia and Prokennalestes. Modified from Hooker and Russell (2012) character 3. STEPMATRIX
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 |
| 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | - |
14. P4 parastyle mesially projecting (0); poorly developed (1). Primitive state based on Juramaia and Prokennalestes. Modified from Hooker and Russell (2012) character 4.
15. P5 metacone small to absent (0); prominent but smaller than paracone (1); as large as paracone (2). Primitive state based on Juramaia and Prokennalestes. Modified from Hooker and Russell (2012) character 5.
16. P5 preparacrista: strong (0); weak (1); absent (2). Primitive state based on Juramaia and Prokennalestes. Modified from Hooker and Russell (2012) character 6.
17. P5 parastyle large, mesially projecting (0); medium (1); small (2). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes. Modified from Hooker and Russell (2012) character 7.
18. P5 metastylar wing (homologue of postmetacrista or, when metacone is absent, of postparacrista): continuous (0); cleft (1) PRIMITIVE; deeply notched, short (2); deeply notched, long (3). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
19. P5 preprotocrista-paracingulum complex without paraconule (0); paraconule present on preprotocrista-paracingulum complex (1); paraconule present with postparaconule crista (2); preprotocrista not linked to parastyle and without paraconule or postparaconule crista, precingulum (if present) joining paracingulum (3); preprotocrista linked to paracone and without paraconule or postparaconule crista, precingulum joining paracingulum (4). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes and Juramaia. Modified from Hooker and Russell (2012) character 9. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 3 | 3 |
| 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | - | 1 |
| 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | - |
20. (see 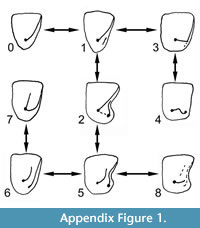 Appendix Figure 1). P5 with: undifferentiated postprotocrista + metacingulum from protocone to metastyle (0); undifferentiated postprotocrista + metacingulum, with weak, short postcingulum (1); confluent postprotocrista + metacingulum, orientated distobuccally, postcingulum strong, long, with incipient to small hypocone (2); postprotocrista orientated nearly distally, joining long distal cingulum (3); postprotocrista short, distally orientated, joining prehypocrista, with hypocone (4); postprotocrista orientated buccally to distobuccally towards metacone or (where metacone absent) towards postparacrista, independent of distal cingulum (composed of postcingulum + metacingulum), with postflexus (5); as (5), but with no postflexus (6); as (6), but with lingual end of distal cingulum joind to protocone as postprotocingulum (7); postprotocrista deflected distally with buccal part weak to absent, distal cingulum present or absent (8). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes and Juramaia. Modified from Hooker and Russell (2012) character 10. STEPMATRIX.
Appendix Figure 1). P5 with: undifferentiated postprotocrista + metacingulum from protocone to metastyle (0); undifferentiated postprotocrista + metacingulum, with weak, short postcingulum (1); confluent postprotocrista + metacingulum, orientated distobuccally, postcingulum strong, long, with incipient to small hypocone (2); postprotocrista orientated nearly distally, joining long distal cingulum (3); postprotocrista short, distally orientated, joining prehypocrista, with hypocone (4); postprotocrista orientated buccally to distobuccally towards metacone or (where metacone absent) towards postparacrista, independent of distal cingulum (composed of postcingulum + metacingulum), with postflexus (5); as (5), but with no postflexus (6); as (6), but with lingual end of distal cingulum joind to protocone as postprotocingulum (7); postprotocrista deflected distally with buccal part weak to absent, distal cingulum present or absent (8). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes and Juramaia. Modified from Hooker and Russell (2012) character 10. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 3 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | - | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 |
| 4 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | - | 4 | 5 | 6 | 5 |
| 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 4 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 6 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 1 | - | 1 | 2 |
| 7 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 2 | 1 | - | 3 |
| 8 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | - |
21. P5 metaconule +/- premetaconule crista: absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
22. P5 : without talon shelf (0); with talon shelf (1). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes and Juramaia.
23. P5 : without precingulum (0); with precingulum (1). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes and Juramaia. Wible et al. (2009) character 43.
24. P5 distinct ectoflexus: present (0); absent (1). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
25. P5 buccal protocone crest (central crista of Archibald et al., 2011) absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
26. P5 protocone lobe transversely orientated (0); twisted mesially, making protocone tilt distally (1). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
27. P4 /4 subequal in size to P5 /5 (0); much smaller (1). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes and Juramaia.
28. P4 paraconid height: low (0); nearly half the height of the protoconid (1); more than half the height of the protoconid (2). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
29. P4 paraconid strength: weak (0); medium (1); strong (2). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
30. P4 metaconid: absent (0); about half the height of the protoconid, lingually placed (1); of subequal height to the protoconid, part of widely open trigonid (2); about half the height of the protoconid, distally placed (3). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 2 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | - |
31. P4 talonid: single-cusped, no basin (0); single-cusped, tiny basin (1) PRIMITIVE; prominent hypoconid (the single cusp), small basin (2); basined with hypoconid and hypoconulid (3); basined with hypoconid, hypoconulid and entoconid (4); basined with hypoconid and entoconid (5). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 3 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | 2 |
| 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 |
| 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | - |
32. P5 : not exodaenodont (0); exodaenodont (1). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
33. P5 paraconid height: low (0); about a third of the height of the protoconid (1) PRIMITIVE; about half the height of the protoconid (2); more than half the height of the protoconid (3). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
34. P5 paraconid strength: weak (0); medium (1) PRIMITIVE; strong (2). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
35. P5 metaconid: absent or negligeably developed (0); about half the height of the protoconid, lingually placed (1); of subequal height to the protoconid, part of widely open trigonid (2); of subequal height to the protoconid, part of fully formed short trigonid (3). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
36. P5 talonid: single-cusped, basin tiny or absent (0); prominent hypoconid (the single cusp), small basin (1); basined with hypoconid and hypoconulid (2); basined with hypoconid, hypoconulid and entoconid (3); basined with hypoconid and entoconid (4); basined with hypoconid, entoconid and doubled entoconid (also lower molars) (5). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 4 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | 2 |
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | - |
37. M1 transverse axis: buccolingual (0); slightly distobuccal-mesiolingual (1). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes. Hooker and Russell (2012) character 28.
38. M1 metacone: smaller than paracone (0); equal sized or slightly larger (1). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes. Hooker and Russell (2012) character 29.
39. M1 preparacrista: nearly transverse, joining stylocone (0); directed mesiobuccally, joining parastyle (possibly including a reduced, mesially shifted stylocone) (1); distinct, directed mesially (2); indistinct, directed mesially (3). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes. Modified from Hooker and Russell (2012) character 30.
40. M1 parastyle: massive and shelf-like (0); large, cuspate (1); small (2). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes. Modified from Hooker and Russell (2012) character 31.
41. Preultimate upper molar centrocrista: straight or slightly lingually deflected (0); buccally deflected, but not reaching buccal margin (1); buccally deflected, meeting buccal margin at single mesostyle (2); buccally deflected, meeting buccal margin at double mesostyle (3). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes. Modified from Hooker and Russell (2012) character 33.
42. Preultimate upper molar postmetacrista: strong, cleft or notched (0); strong, continuous (1); weak, cleft (2). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes. UNORDERED.
43. M1 postmetacrista: distinct, long, nearly buccally directed (0); distinct, long, curved or angled distobuccally then buccally (1) PRIMITIVE; distinct, short distobuccally directed (2); distinct, short, distally directed (3); indistinct, short, distally directed (4). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes. Modified from Hooker and Russell (2012) character 34.
44. M1 : paraconule and metaconule situated close to protocone (0); paraconule closer to protocone than is metacone (1); paraconule and metaconule equally more distant from protocone (2); paraconule close to protocone, metaconule absent (3). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes. Modified from Hooker and Russell (2012) character 35. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 2 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | - |
45. Preultimate upper molar(s): preprotocrista +/- paracingulum (incorporating preparaconule crista) without precingulum (0); Preultimate upper molar(s): preprotocrista + paracingulum with precingulum (1); precingulum and paracingulum joined, from which preprotocrista (including preparaconule crista) is isolated and which may join paracone (2). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
46. Preultimate upper molar paraconule and postparaconule crista absent (0); paraconule present, postparaconule crista absent (1) PRIMITIVE; paraconule and postparaconule crista present (2). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
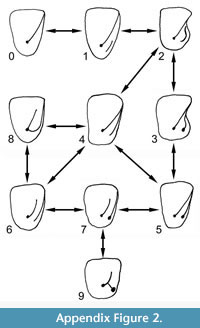 47. (see Appendix Figure 2). Preultimate upper molar: postprotocrista +/- metacingulum present, postcingulum absent (0); postprotocrista + metacingulum present, postcingulum present (1); postprotocrista + metacingulum present, postcingulum expanded into a short hypocone shelf (2); postprotocrista +/- metacingulum present, short hypocone shelf bearing hypocone (3); postprotocrista + metacingulum present, postcingulum expanded into a long hypocone shelf (4); postprotocrista + metacingulum present, long hypocone shelf bearing hypocone (5); postcingulum confluent with metacingulum, bypassing postprotocrista (6); postcingulum confluent with metacingulum, bypassing postprotocrista and bearing hypocone (7); as (6) but with postprotocingulum (Nannopithex fold) joining or nearly joining hypocone shelf (8); as (7) but with prehypocrista (erinaceid crest) (9). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes. STEPMATRIX.
47. (see Appendix Figure 2). Preultimate upper molar: postprotocrista +/- metacingulum present, postcingulum absent (0); postprotocrista + metacingulum present, postcingulum present (1); postprotocrista + metacingulum present, postcingulum expanded into a short hypocone shelf (2); postprotocrista +/- metacingulum present, short hypocone shelf bearing hypocone (3); postprotocrista + metacingulum present, postcingulum expanded into a long hypocone shelf (4); postprotocrista + metacingulum present, long hypocone shelf bearing hypocone (5); postcingulum confluent with metacingulum, bypassing postprotocrista (6); postcingulum confluent with metacingulum, bypassing postprotocrista and bearing hypocone (7); as (6) but with postprotocingulum (Nannopithex fold) joining or nearly joining hypocone shelf (8); as (7) but with prehypocrista (erinaceid crest) (9). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes. STEPMATRIX.
48. Preultimate upper molar: metaconule and premetaconule crista absent (0); metaconule present, premetaconule crista absent (1) PRIMITIVE; metaconule and premetaconule crista present (2). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
49. Preultimate upper molar inflated talon shelf: absent (0); present, restricted lingually (1); present, extending buccally (2). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
50. Preultimate upper molar ectoflexus: deep on M2 , shallow on M1 (0); shallow on M2 and shallow or absent on M1 (1); absent (2). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
51. Upper molar buccal margin with: stylar shelf nearly a third of the tooth width (0); stylar shelf narrow (1); no stylar shelf, strong ectocingulum (2); no stylar shelf, ectocingulum weak or incomplete (3); stylar shelf and ectocingulum absent (4). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
52. Preultimate upper molar stylar cusp D present (0); absent (1). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
53. Upper molar protocone tilt: lingual (0); more or less vertically orientated from crown base (1); buccal (2). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
54. M1 paraconid height from lingual side: about a third the height of the protoconid (0); about half the height of the protoconid (1) PRIMITIVE; about two thirds the height of the protoconid (2); nearly as tall as protoconid (3). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
55. Transverse position of M1 paraconid tip with respect to that of metaconid: lingual (0); sublingual (1) PRIMITIVE; median (2). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
56. M1 paraconid strength: weak (0); medium (1) PRIMITIVE; strong (2). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
57. M1 paraconid shape: cuspate (0); crestiform (1). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
58. Lower molar paracristid notch: absent (0); present as cleft or angle (1) PRIMITIVE; present as deep (carnassial) notch (2). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
59. Shape of M1 trigonid: very narrow mesiodistally (0); approximately an equilateral triangle (1) PRIMITIVE; elongate mesially (2). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
60. M2 paraconid: cuspate (0); crestiform (1). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
61. M2 paraconid: separate from metaconid (0); the two cusps connate (1). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
62. M1 hypoconid height: half or less than half height of protoconid (0); about two thirds the height of protoconid (1); subequal (2). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
63. M1 entoconid: less than half height of metaconid (0); about half height of metaconid (1); about two thirds height of metaconid (2); the two cusps subequal (3). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
64. Lower molar hypoconulid buccal of midline (0); central (1) PRIMITIVE; lingual of midline (2); at or near lingual margin, nyctalodont condition (3). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
65. Lower molar cristid obliqua meets trigonid: lingually, rising up distolingual edge of metaconid (0); at about midpoint, rising obliquely up the back of the metaconid (1); at about midpoint, not or scarcely rising up back of trigonid (2); slightly buccal of midpoint, not or scarcely rising up back of trigonid (3); nearly at buccal margin, not or scarcely rising up back of trigonid (4); from a buccally convex trajectory, rising up the buccal side of the metaconid (5). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
66. Lower molar cristid obliqua: unnotched (0); notched (1). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
67. M1 talonid: narrower than trigonid (0); equal in width to trigonid (1); wider than trigonid (2). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
68. Lower molar posthypocristid: complete or only narrowly notched (0); broken (1). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
69. Lower molar protocristid: fissured with carnassial notch (0); angled/cleft (1) PRIMITIVE; a smooth continuous crest (2). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
70. Lower molar precingulid: strong (0); weak (1); absent (2). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
71. Preultimate lower molar postcingulid: absent (0); present basally (1); rising to join hypoconulid (2); present basally, extended mesially to join precingulid, i.e., forming ectocingulid (3). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 2 |
| 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | - |
72. M3 hypoconulid: distally protruding, inflated to enclose a basin (0); distally protruding, a distinct cusp (1) PRIMITIVE; contracted, not protruding significantly from talonid, entoconid present (2); contracted, not protruding significantly from talonid, entoconid absent (3); absent together with talonid or entire tooth (4). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
73. M3 hypoconulid: overhangs distal tooth margin (0); distally extensive basally beyond tip (1); absent together with talonid or entire tooth (2). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
74. Relative height of molar cusps judged from height of M1/2 protoconid as % of tooth length: more than 95% (0); between 75 and 95% (1); less than 75% (2). Primitive state based on Prokennalestes.
Dentary
75. Anterior mental foramen below P2 (0); between P1 and P2 (1); below P1 (2); between P4 and P5 (3); at extreme anterior position (4); absent (5). Primitive state based on Juramaia. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 129. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | - | 2 | 1 |
| 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | - | 1 |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - |
76. Posterior mental foramen: below P2 (0); between P2 and P4 (1); below P4 (2); between P4 and P5 (3) PRIMITIVE; below P5 (4); between P5 and M1 or below M1 (5). Primitive state based on Juramaia. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 130.
77. Height of condyle above alveolar line: one molar length (0); two molar lengths (1); three molar lengths (2); four molar lengths or more (3). Primitive state based on Juramaia. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 150.
78. Tilting of coronoid process; angle of anterior border to alveolar line: 120-130 degrees (0); 110 degrees (1); 100 degrees (2); 90 degrees (3). Primitive state based on Juramaia and Prokennalestes. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 135.
79. Height of coronoid process above alveolar line: two to three molar lengths (0); four molar lengths (1); five molar lengths or more (2). Primitive state based on Juramaia and Prokennalestes. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 133.
80. Lateral mandibular foramen present (0); absent (1). Primitive state based on Eomaia, Juramaia and Prokennalestes. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 139: polarity reversed.
81. Angular process directed posteroventrally (0); posteroventromedially (1); posteroventrolaterally (2); posteriorly (3); dorsally to dorsomedially inflected (4); in the form of a rounded posteroventral corner (5); rounded with dorsal hook (6). Primitive state based on Eomaia, Juramaia and Prokennalestes. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 143. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | - | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 2 | 1 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | - | 1 |
| 6 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | - |
82. Depression in ventral dentary margin anterior to angle present (0); absent (1). Primitive state based on Eomaia, Juramaia and Prokennalestes.
83. Angular process projects posteriorly less than dentary condyle (0); about equal (1); farther (2). Primitive state based on Eomaia, Juramaia and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 147.
84. Angular process vertical position: at posteroventral border (0); posterodorsal, at or near alveolar border (1). Primitive state based on Eomaia, Juramaia and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 146.
85. Dentary condyle with posteriorly directed peduncle (0); without (1). Primitive state based on Eomaia, Juramaia and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 148. Cimolestes magnus recoded 1 (Lillegraven 1969, figure 37.3); Erinaceus recoded 0 (personal obs.).
86. Vertical position of mandibular foramen: near ventral margin at root of angle (0); recessed dorsally from ventral margin, but below alveolar plane (1); recessed dorsally from ventral margin, at or above alveolar plane (2). Primitive state based on Eomaia and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 157.
Rostrum
87. Premaxilla-maxilla suture on face: vertically orientated, contacting nasals (0); projecting posterodorsally no further than canine, but without contacting frontal (1) PRIMITIVE; projecting posterodorsally further than canine, but without contacting frontal (2); projecting posterodorsally and contacting frontal (3); premaxilla lacking facial process (4). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) characters 160-162. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - |
88. Infraorbital foramen dorsal to: P4 or more anterior (0); dorsal to P5 (1); Dorsal to M1 or more posterior (2). Primitive state based on Eomaia and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 165, with changed state numbering.
89. Vertical position of anterior margin of orbit with respect to tooth loci. Above P5 or more anterior (0); M1 (1) PRIMITIVE; M2 or more posterior (2). Primitive state based on Eomaia. This, together with character 15, approximates length of infraorbital canal (Wible et al., 2009, character 166).
90. Nasal widest posteriorly (0); with sides subparallel (1); widest anteriorly (2). Primitive state based on Eomaia. Wible et al. (2009) character 168.
91. Nasal overhangs external nasal aperture (0); does not overhang (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 169.
92. Nasofrontal suture with medial process of frontals wedged between nasals (0); not wedged between nasals (1). Primitive state based on Eomaia. Wible et al. (2009) character 170.
93. Posterior margin of nasals posterior to or even with anterior orbital rim (0); anterior to anterior orbital rim (1). Primitive state based on Eomaia. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 171.
94. Anterior process of frontal weak/absent (0); elongate/thin (1). Primitive state based on Eomaia. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 174.
95. No frontal maxillary contact on rostrum (0); contact (1). Primitive state based on Eomaia. Wible et al. (2009) character 173.
96. Facial process of lacrymal large, triangular and pointed anteriorly (0); small and rectangular or crescentic (1). Primitive state based on Eomaia. Wible et al. (2009) character 177. Erinaceus rescored 1 as, although fused to maxilla in adult, its extent can be judged from juveniles (Butler, 1948).
97. Lacrymal tubercle present (0); absent (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 178.
98. Lacrymal foramen not exposed on face (0); exposed on face (1). Primitive state based on Eomaia. Wible et al. (2009) character 179, but with reversed state numbering.
99. Number of lacrymal foramina: two (0); one (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 180.
100. Lacrymal foramen within lacrymal (0); with maxillary contribution (1); with jugal contribution (2). UNORDERED. Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 181.
Palate
101. Premaxillary-maxillary suture on palate wedge-shaped, pointing anteriorly (0); transverse (1) PRIMITIVE; wedge-shaped, pointing posteriorly (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 184, with states 0 and 1 reversed.
102. Incisive foramina small, length of one or two incisors (0); length of three or four incisors (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 185.
103. Palatal vacuities absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 187.
104. Major (anterior) palatal foramen single within palatine (0); single between palatine and maxilla (1); single within maxilla (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 188.
105. Palatal expansion posterior to last molar (0); even with last molar (1) PRIMITIVE; anterior to last molar (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 190, with states 0 and 1 reversed.
106. Postpalatine torus absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 191.
107. Posterior nasal spine weak or absent (0); prominent (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 192. Ptilocercus rescored as 0 (pers. obs.).
108. Minor (posterior) palatal foramen small, single or multiple within palatine or between maxilla and palatine (0); large with thin posterior bony bridge, within palatine or between maxilla and palatine (1); large, with thin posterior bony bridge between palatine and pterygoid (2); absent (3). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Combined from Wible et al. (2009) characters 193 and 194. Ptilocercus rescored as 0 (personal obs.). STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - |
109. Maxilla without large shelf-like expansion posterior to last molar (0); with (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 195.
Zygoma
110. Posterior edge of anterior zygomatic root aligned with last molar (0); with anterior molars (1). Primitive state based on Eomaia. Wible et al. (2009) character 196.
111. Zygomatic process of maxilla: not bifurcated, jugal contribution to anteroventral orbit and zygoma, and jugal-lacrymal contact (0); bifurcated, jugal contribution to anteroventral orbit and zygoma, and jugal-lacrymal contact (1); bifurcated, jugal contribution to anteroventral orbit and zygoma, but no jugal-lacrymal contact (2); absent/vestigial, jugal contribution to anteroventral orbit and zygoma, and jugal-lacrymal contact (3); not bifurcated, jugal contribution to anteroventral orbit and zygoma, but no jugal-lacrymal contact (4); not bifurcated, jugal contribution only to zygoma and no jugal-lacrymal contact (5); present but no jugal (6). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) characters 197-201. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | - | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | - | 1 | 2 |
| 5 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | - | 1 |
| 6 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 | - |
112. Zygomatic arch: stout, without malar foramen (0); delicate, without malar foramen (1) PRIMITIVE; delicate, with malar foramen (2); absent (3). Primitive state based on Eomaia. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 202. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - |
Orbit
113. Palatine reaches infraorbital canal (0); does not reach (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 204.
114. Lacrymal contributes to maxillary foramen (0); does not contribute (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 205.
115. No groove connecting maxillary and sphenopalatine foramina (0); groove present (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 206.
116. Sphenopalatine (orbitonasal) foramen within palatine (0); between palatine and maxilla (1); between palatine, maxilla and frontal (2); within maxilla (3). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 207. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 |
| 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | - |
117. Sphenopalatine (orbitonasal) foramen not proximal to maxillary foramen (0); proximal (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 208.
118. Maxilla excluded from medial orbital wall (0); not excluded (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 209.
119. No frontal-maxilla contact in medial orbital wall (0); contact (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 210.
120. Orbital process of palatine present (0); absent or with thin sliver in ventromedial wall (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 211.
121. Ethmoidal foramen between frontal and orbitosphenoid (0); within frontal (1); absent (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 213. UNORDERED.
122. Foramen for frontal diploic vein absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 214.
123. Frontal foramen on cranial roof absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 215.
124. Postorbital process and dorsal process of jugal absent (0); postorbital process weak, dorsal process of jugal absent (1); postorbital process strong, dorsal process of jugal absent (2) PRIMITIVE; postorbital process strong, dorsal process of jugal present (3); postorbital bar composed of postorbital process and dorsal process of jugal (4). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) characters 216, 218, 219.
125. Optic foramen narrowly separated from sphenorbital fissure (0); broadly separated (1); not visible in lateral view (2). Polarity problematic as optic foramen absent or its state unknown in potential outgroups. Wible et al. (2009) character 221. UNORDERED.
126. Orbitosphenoid expanded anteriorly from optic foramen (or with anterior process) (0); expanded dorsally from optic foramen (or with dorsal process) (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 222, with changed state numbering.
127. Suboptic foramen absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 223. N.B., presence in Leptictis shown by Butler (1956) but stated by Novacek (1986), quoting Butler (1956, p. 473) to be absent anterior to the sphenorbital fissure, but not necessarily absent per se (see Butler 1956, figure 7), thus contra Wible et al. (2009). N.B., absence in Erinaceus is shown by Butler (1948, figure 7) contra Wible et al. (2009).
128. Orbitotemporal canal (sinus canal, cranio-orbital foramen) present (0); absent (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 224.
Braincase
129. Frontal length on midline more than 50% longer than parietal (0); subequal to slightly shorter than parietal (1) PRIMITIVE; less than half length of parietal (2). Primitive state based on Eomaia. Wible et al. (2009) character 226, with state numbering changed.
130. Fronto-parietal suture: with anterior process of parietal off the midline (0); transverse (1) PRIMITIVE; with anterior process on the midline (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 227.
131. Temporal lines (crista frontalis externa) meet on midline to form sagittal crest (0); do not meet (1). Primitive state based on Eomaia. Wible et al. (2009) character 228.
132. Interparietal absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 229.
133. Nuchal crest level with or anterior to foramen magnum (0); posterior to foramen magnum (1). Primitive state based on Eomaia. Wible et al. (2009) character 230.
Mesocranium
134. Choanae as wide as posterior palate (0); narrower (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 234.
135. Vomer does not contact pterygoid (0); contacts pterygoid (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 235.
136. Pterygoids contact on midline (0); do not contact (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 236.
137. Midline crest in basipharyngeal canal present (0); absent (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 238, with state numbering reversed.
138. Entopterygoid process ends at anterior basisphenoid (0); approaches ear region (1). Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 239.
139. Midline rod-shaped eminence on basisphenoid absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 240.
140. Ectopterygoid process of alisphenoid: approaches ear region as long crest (0); ends at anterior basisphenoid as long crest (1) PRIMITIVE; ends at anterior basisphenoid as narrow process (2); approaches ear region as narrow process (3); absent (4). Wible et al. (2009) characters 241-242. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | - |
141. Exit for maxillary nerve (cranial nerve V2) relative to alisphenoid: behind (0); within (1); in front (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 244.
142. Foramen ovale in petrosal (anterior lamina) (0); in alisphenoid (1); between alisphenoid and squamosal (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 246, with changed states.
143. Alisphenoid canal absent (0); present, posterior opening separate from foramen ovale (1); present, posterior opening in common depression with foramen ovale (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) characters 248-249. UNORDERED.
Basicranium
144. Glenoid fossa on zygoma (0); partly on braincase (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 251.
145. Glenoid fossa even dorsoventrally with sphenoid on midline cranial base (0); higher (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 253.
146. Jugal contributes to glenoid with articular facet (0); contributes to glenoid without articular facet (1); does not contribute to glenoid (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 254. State 2 for Ptilocercus (Wible, 2011) contra Wible et al. (2009) (0).
147. Postglenoid process present (0); absent (1). Primitive state based on Eomaia. Wible et al. (2009) character 256.
148. Postglenoid foramen within squamosal, behind postglenoid process (0); within squamosal, medial or anterior to postglenoid process or on lateral aspect of braincase (1); behind squamosal, behind postglenoid process (2); absent (3) PRIMITIVE. Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) characters 257-259. UNORDERED.
149. Suprameatal foramen absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 260.
150. Entoglenoid process of squamosal absent (0); present, separated from postglenoid process (1); present, continuous with postglenoid process (2). Primitive state based on Eomaia. Wible et al. (2009) character 261. UNORDERED.
151. Posttympanic crest of squamosal absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 262.
152. Carotid foramen within basisphenoid (0); between basisphenoid and petrosal (1); absent (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 263. UNORDERED.
153. Cavum epiptericum floor composition: petrosal (0); petrosal and alisphenoid (1); primarily open as pyriform (piriform) fenestra (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 264. UNORDERED.
154. Alisphenoid tympanic process absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 265. Recoded 1 in Ptilocercus as shown present by Cartmill and MacPhee (1980) and Wible (2011), contra Wible et al. (2009), where coded 0.
155. Basisphenoid tympanic process absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 266.
156. Medial flange of petrosal absent (0); present (1). Polarity is equivocal as it is absent in Vincelestes, but present in Prokennalestes. 1 treated here as PRIMITIVE. Wible et al. (2009) character 268.
157. Rostral tympanic process of petrosal on posteromedial aspect of promontorium: absent or low ridge (0); moderate ridge, contributing to posterodorsomedial bulla (1); tall ridge, contributing to ventral bulla (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 269. UNORDERED.
158. Course of internal carotid artery (ICA) and of stapedial artery: ICA lateral (transpromontorial), both in sulcus (0); ICA lateral (transpromontorial), both in intratympanic vascular canal (1); medial (perbullar or extrabullar), both in sulcus (2); course indication absent (3). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Prokennalestes. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) characters 270-271, 273-274 and Bloch et al. (2007) character 87. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 2 | 2 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | - | 1 |
| 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | - |
159. Promontorium shape: flat (0); globose (1). Polarity is equivocal as it is flat in Vincelestes, but globose in Prokennalestes. 1 treated here as PRIMITIVE. Wible et al. (2009) character 278.
160. Intratympanic course of facial nerve: open in sulcus (0); open anteriorly, canal posteriorly (1); in canal (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 280.
161. Aperture of hiatus Fallopii: in tympanic roof through petrosal (0); at anterior edge of petrosal (1); through cerebral surface, via fenestra semilunaris if present (2); absent (3). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Prokennalestes. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 281. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - |
162. Prootic canal present (0); absent (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 282.
163. Length of bony shelf lateral to promontorium (lateral trough or tegmen tympani): extended anteriorly as far as promontorium (0); confined posterolaterally (1) PRIMITIVE; prolonged anterior to promontorium (2). Polarity is equivocal as Vincelestes is 0, but Prokennalestes is 1. 1 treated here as PRIMITIVE. Wible et al. (2009) character 285.
164. Width of bony shelf lateral to promontorium (lateral trough or tegmen tympani): uniform (0); expanded anteriorly (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 286.
165. Stapedial canal on bony shelf lateral to promontorium (lateral trough or tegmen tympani): absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 288.
166. Tensor tympani fossa on petrosal: shallow to absent (0); deep circular pit (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 289.
167. Cochlear width less than 20% of skull length (0); greater than 20%. Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Novacek (1987).
168. Epitympanic recess to fossa incudis relative size: subequal (0); epitympanic recess larger (1); no visible depression for epitympanic recess (2). Polarity is equivocal as Vincelestes is 0, but Prokennalestes is 1. 1 treated here as PRIMITIVE. Wible et al. (2009) character 292.
169. Epitympanic recess lateral wall: with extensive contribution to lateral wall by squamosal (0); with small contribution to posterolateral wall by squamosal (1) PRIMITIVE; no squamosal contribution (2). Polarity is equivocal as Vincelestes is 1, but Prokennalestes is 0. 1 treated here as PRIMITIVE. Wible et al. (2009) character 293, with states 0 and 1 reversed.
170. Fossa incudis continuous with epitympanic recess (0); separated from it (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 294.
171. Foramen for ramus superior of stapedial artery: posterior or lateral to fenestra vestibuli (ovalis) (0); anterior to fenestra vestibuli (1); absent (2). Polarity is equivocal as Vincelestes is 0, but Prokennalestes is 1. 1 treated here as PRIMITIVE. Wible et al. (2009) character 298. UNORDERED.
172. Ascending canal (for arteria diploëtica magna): intramural (0); intracranial (1); absent (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 299. UNORDERED.
173. Stapedius fossa twice the size of fenestra vestibuli (ovalis) (0); small and shallow (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 300.
174. Cochlear canaliculus not visible in middle ear space (0); visible (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 301.
175. Postpromontorial tympanic sinus: dorsal to cochlear fossula (0); at same level as cochlear fossula (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 302.
176. Fenestra cochleae (rotunda) position to fenestra vestibuli (ovalis): posteromedial (0); posterior (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 303.
177. Posterior septum shielding fenestra cochleae (rotunda) absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 304.
178. Paroccipital process of petrosal: vertical (0); slanted, projecting as flange towards back of promontorium (1); indistinct to absent (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 305. UNORDERED.
179. Caudal tympanic process of petrosal: not notched (0); notched (1); absent (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 306. UNORDERED.
180. Crista interfenestralis and caudal tympanic process: not connected by curved ridge (0); connected by curved ridge (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 307.
181. ‘Tympanic process’ of Kielan-Jaworowska: absent (0); present, low, composed of petrosal (1); present, low, composed of petrosal and exoccipital (2); present, high, composed of petrosal (3). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) characters 308-309. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | - | 2 |
| 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | - |
182. Jugular (posterior lacerate) foramen size relative to fenestra cochleae (rotunda): subequal (0); larger (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 312.
183. Jugular (posterior lacerate) foramen: confluent with opening for inferior petrosal sinus (0); separated from inferior petrosal sinus (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 313.
184. Hypoglossal foramen number: two or more (0); one (1); variable (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 314. UNORDERED.
185. Hypoglossal foramen not housed in opening larger than jugular (posterior lacerate) foramen (0); housed in opening larger than jugular foramen (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 315.
186. Paracondylar (paroccipital) process of exoccipital: weak or absent (0); prominent, vertical (1); prominent, posteriorly directed (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 316. UNORDERED.
187. Ectotympanic: phaneric or visible in ventral view (0); aphaneric or hidden by auditory bulla (1). Wible et al. (2009) character 317.
188. Ectotympanic: ring-like (0); fusiform (1) PRIMITIVE; expanded (2). Wible et al. (2009) character 318, but recoded (0) for Plesiadapis (Bloch and Silcox 2001, figure 7).
189. Anterior crus of ectotympanic: does not broadly contact facet on squamosal (0); does broadly contact facet on squamosal (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 319.
190. Elongate ossified external acoustic canal: absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on ingroup commonality. Wible et al. (2009) character 320.
191. Roof of external acoustic meatus: petrosal (0); petrosal and squamosal (1); squamosal (2). Polarity equivocal, as Vincelestes is 0, Prokennalestes is 1. 0 treated here as PRIMITIVE. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 321. UNORDERED.
192. Entotympanic absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes Wible et al. (2009) character 322.
193. Hyoid arch does not contribute to bulla (0); does contribute (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Prokennalestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 324.
194. Dorsum sellae tall (0); low (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 325.
195. Wall separating cavum supracochleare from cavum epiptericum: incomplete, with fenestra semilunaris (0); complete (1). Polarity equivocal, as Vincelestes is 0, Prokennalestes is 1. 0 treated here as PRIMITIVE. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 328.
196. Crista petrosa: vestigial or absent (0); a tall, thin crest (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 329.
197. Anterior (superior) semicircular canal: forms lateral wall of unconstricted subarcuate fossa aperture (0); forms lateral wall of constricted subarcuate fossa aperture (1); does not form lateral wall of constricted subarcuate fossa aperture (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) characters 330-331. UNORDERED.
198. Posttemporal canal on occiput: large, between petrosal and squamosal (0); small, between petrosal and squamosal (1); small, within petrosal (2); absent (3). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) characters 333-335. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 |
| 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | - |
Vertebrae
199. Atlantal foramen present (0); absent (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 339.
200. Atlas neural hemiarches unfused (0); fused (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 340.
201. Atlas neural arch and intercentrum unfused (0); fused (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 341.
202. Axis with suture between atlantal and axial parts (0); without (1). Wible et al. (2009) character 342.
203. Axis with extra pair of transverse processes on ventral surface (0); without (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 343.
204. Axis prezygapophyses extend ventral to dens (0); linked (1); not linked to dens (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 344.
205. Inferior lamellae present on posterior cervical vertebrae (0); absent (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 345.
206. Number of thoracic vertebrae 14 or fewer (0); 15 or more (1). Primitive state based on Eomaia. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 347.
207. Number of sacral vertebrae 2 (0); 3 (1); 4 or more (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 350.
Scapula
208. Infraspinous fossa position with respect to supraspinous fossa: different planes (in part, medial to) (0); coplanar (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 352.
209. Suprascapular incisure absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 353.
210. Acromion reaches distal to glenoid articulation (0); is proximal (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 354.
211. Metacromion weak or absent (0); a well developed process (1). Primitive state based on Eomaia. Wible et al. (2009) character 355.
Humerus
212. Greater and lesser tuberosities lower than or at same level as head (0); Greater tuberosity higher than head (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 356.
213. Proximal third of shaft curved posteriorly (0); ~ straight (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes.
214. Deltopectoral crest extending less than one third the length from the proximal end (0); between one third and one half (1) PRIMITIVE; more than a half (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes.
215. Deltopectoral crest laterally displaced (0); median (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes.
216. Deltopectoral crest strong (0); weak (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes.
217. Tuberosity for teres major muscle a crestiform or tubercular structure (0); absent or represented only by rugose surface (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes.
218. Entepicondylar foramen present (0); absent (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes, Henkelotherium and Juramaia. Wible et al. (2009) character 360).
219. Supinator crest weak and short (0); weak and long (1); strong, short, extending scarcely proximal of the flaring of the medial epicondyle (2); strong extending more proximally (3). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. STEPMATRIX
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | - | 1 |
| 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | - |
220. Medial epicondyle extends from medial trochlear ridge more than shaft width (0); less (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes.
221. Medial epicondyle projects slightly distomedially (0); medially to slightly proximomedially (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Juramaia.
222. Olecranon fossa very deep (0); moderately deep (1) (PRIMITIVE); shallow (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Modified from Goswami et al. (2011) character 413.
223. Olecranon fossa imperforate (0); perforate (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Reworded from Wible et al. (2009) character 361.
224. Trochlea concave with sharp medial keel, projecting further distally than capitulum (0); convex, without clear lateral crest, projecting farther distally than capitulum (1) PRIMITIVE; convex, without lateral crest, not projecting further distally than capitulum (2); convex, narrow, with lateral crest (3); semicylindrical, wide, with lateral crest (4). Primitive state based on Vincelestes.
225. Capitulum semi-cylindrical, confluent with trochlea (0); semi-spherical, separated from trochlea by intercondylar groove (1) PRIMITIVE; spherical, separated from trochlea by intercondylar groove (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes.
226. Capitulum with no distinct lateral flange (0); with distinct lateral flange confluent with rest of capitulum (1) PRIMITIVE; lateral flange separated from rest of capitulum by groove (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes.
227. Dorsoepitrochlear fossa absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes.
228. Radial fossa present, but coronoid fossa absent (0); both radial and coronoid fossae present (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes.
Radius
229. Capitular eminence: weak to absent (0); strong (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes.
230. Ulnar facet proximodistally shallow (0); deep (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes.
231. Facet for humeral trochlea absent (0); present (1) PRIMITIVE. Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 364.
232. Shaft strongly curved proximally with asymmetrical head (0); weakly curved with asymmetrical head (1); gently curved to straight with symmetrical head (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes.
233. Bicipital tuberosity weak to absent (0); present, simple, confluent with proximal articulation, without lateral crest (1) PRIMITIVE; confluent with proximal articulation, with lateral crest (2); separate from proximal articulation, without lateral crest (3); separate from proximal articulation, with lateral crest (4). Primitive state based on Vincelestes.STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | - | 2 | 1 |
| 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | - | 1 |
| 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | - |
234. Ulnar facet strongly rounded (0); gently rounded (1) PRIMITIVE; flat or nearly so (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes.
235. Radial articulation with carpals: a single fossa (0); two fossae (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 367.
Carpals
236. Scaphoid and lunar separate (0); partially fused, retaining surface division between the bones (1); fully fused (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 368.
237. Centrale separate (0); fused or lost (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 369.
Pelvis
238. Pubic symphysis extensive (0); narrow (1); separate (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 370.
239. Epipubic bones present (0); absent (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Eomaia. Wible et al. (2009) character 371.
Femur
240. Head spherical, not extending onto neck (0); head spherical, extending onto neck proximally (1); head more cylindrical (2). Primitive state based on Henkelotherium, Eomaia and Purbeck cladotherian femur NHMUK.PV.OR48250.
241. Head extending far round neck distally (0); not extending far round distally (1). Primitive state based on stem cladotherian NHMUK.PV.OR48250.
242. Neck distinct (0); poorly indented proximally (1). Primitive state based on Eomaia and stem cladotherian NHMUK.PV.OR48250.
243. Head and neck project medially (0); anteromedially (1); proximomedially (2); anteroproximomedially (3); UNORDERED. Primitive state based on stem cladotherian NHMUK.PV.OR48250.
244. Teres fovea central (0); posterior (1); absent (2). UNORDERED. Primitive state based on Henkelotherium. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 373.
245. Greater trochanter extends proximally less than head (0); to about level of head (1); farther (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 374.
246. Lesser trochanter posteromedial (0); medial (1). Primitive state based on Henkelotherium and stem cladotherian M13126.
247. Lesser trochanter projects as far as head or beyond (0); less than head (1). Primitive state based on Henkelotherium and stem cladotherians NHMUK.PV.OR48250, M13126. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 375.
248. Lesser trochanter near head (0); more distal (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and stem cladotherian M13126.
249. Third trochanter absent (0); small less than a third of the distance from proximal end (1); small c. one third distance from proximal end (2); small, more than a third distance from proximal end (3); large c. one third distance from proximal end (4). Primitive state based on Vincelestes, Henkelotherium and stem cladotherians NHMUK.PV.OR48250, M13126. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 376. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | - | 2 |
| 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | - |
250. Trochanteric fossa deep (0); shallow (1); essentially absent (2). Primitive state based on stem cladotherian M13126.
251. Intertrochanteric crest restricted to lateral position (0); reaches or nearly reaches the base of the lesser trochanter (1). Primitive state based on stem cladotherian M13126.
252. Shaft essentially round in cross section (0); anteroposteriorly compressed (1). Primitive state based on Henkelotherium and stem cladotherian M13126.
253. Distal femur similar in size in anteroposterior and mediolateral dimensions (0); longer anteroposteriorly (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 378.
254. Patellar groove broad and shallow (0); narrow and elevated (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 379.
255. Articulation between femur and fibula (0); no articulation (1). Primitive state based on Eomaia. Wible et al. (2009) character 381, but polarity coding reversed.
Tibia
256. Tibia separate from fibula distally (0); in contact along part of the shaft (1); co-ossified distally (2); co-ossified along much of the distal half (3). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. STEPMATRIX
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | - | 1 |
| 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | - |
257. Shaft smooth (0); with groove distally for flexor digitorum fibularis tendon (1); with groove distally for flexor digitorum tibialis and tibialis posterior tendons (2); with grooves for flexor digitorum fibularis tendon and for flexor digitorum tibialis and tibialis posterior tendons (3). UNORDERED. Primitive state based on Vincelestes.
258. Medial malleolus distally long (i.e., more than half as long as the distal width of the tibia) with articular surface for sustentaculum of calcaneum (0); Medial malleolus distally long (i.e., more than half as long as the distal width of the tibia) without articular surface (1) PRIMITIVE; length about one third of the distal width of the tibia (2); short (3); absent (4). Primitive state based on Vincelestes.
259. Posterior process absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes.
260. No tibia-fibula fusion proximally (0); fusion (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 382.
Astragalus
261. Body broader (measured proximally) than long (measured laterally) (0); approximately equidimensional (1); longer than broad (2). Primitive state based on Ukhaatherium, which, although belonging to the ingroup, is broadly primitive. Hooker (2001) character 1.
262. Lateral trochlear ridge taller than medial one (0); trochlear ridges of approximately equal height (1); medial trochlear ridge taller than lateral one (2). Primitive state based on Ukhaatherium. Hooker (2001) character 2.
263. Neck not distinct from body medially as navicular facet extends as far as body medially (0); free neck, navicular facet extending c. half way up medial side (1); free neck, navicular facet extending less than half way up medial side (2). Part of Hooker 2001, character 15. Polarity based on Vincelestes, which lacks a neck, so the more metatherian-like pattern in zalambdalestids (Szalay and Sargis, 2006) is likely to be primitive.
264. Medial and lateral walls of body (i.e., for articulation with the fibula and the medial malleolus of the tibia) converge dorsally at more than 60 degrees (0); at 60 degrees (1); essentially parallel (2). From Horovitz 2000, character 14 and description of Vincelestes.
265. Lateral tibial facet not excavated (0); gently excavated (1); deeply excavated, U-shaped (2); deeply excavated, V-shaped (3). Primitive state (0) as ‘ancestral therian’, Horovitz (2000). N.B., the deep V-shape of zalambdalestids separates two dorsally-facing facets. These were labelled ‘medial and lateral tibial facets by Szalay and Sargis (2006, figures 16-17), presumably as there is no medially facing facet on the body. However, it seems more likely that a medial tibial facet is missing, along with the medial malleolus of the tibia and that the ‘medial’ and ‘lateral’ facets are together homologous with the lateral facet of other therians. Modified from Horovitz (2000) character 11 and Hooker (2001) character 16.
266. Lateral tibial facet follows the curvature of the trochlear ridges (0); gently indented distally, into which cavity, convexity of tibial facet or anterior process of tibia fits (1); deeply indented distally for anterior process of tibia (2). Primitive state based on Ukhaatherium.
267. No extension of trochlea onto neck (0); extension of medial ridge (1); extension between ridges (2). UNORDERED. Primitive state based on Ukhaatherium. Modified from Hooker (2001) character 3.
268. Proximal foramen of astragalar canal present (0); absent (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Horovitz (2000) character 17; Hooker (2001) character 4. This structure labelled as present in the dermopteran Galeopterus variegatus by Smith et al. (2010, figure 1h) is in fact the dorsal edge of the groove for the flexor digitorum fibularis tendon (personal obs.; Beard, 1993, figure 10.12).
269. Ventral limit of trochlea on proximal surface of body at midpoint (0); more ventral (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Hooker (2001) character 5.
270. Groove for flexor digitorum fibularis tendon shallow (0); deep (1). Primitive state based on ingroup commonality. Hooker (2001) character 6.
271. Medial plantar tuberosity large (0); medium (1) PRIMITIVE; small (2). Modified from Horovitz 2000, character 15; Hooker 2001, character 7. Primitive state based on Eomaia (Luo et al., 2003, figure 3D). Deccanolestes scored incorrectly by Horovitz 2000 as having large state, probably because of distorted cast figured by Prasad and Godinot (1994), see Hooker (2001).
272. Attachment area on lateral body wall for fibuloastragalar ligament proximal (0); central (1). Primitive state based on ingroup commonality. Hooker (2001) character 8.
273. Sustentacular facet extensive, confluent with navicular facet (0); restricted distally to lateral of astragalocalcaneal ligament area, confluent with navicular facet (1); restricted distally to medial of astragalocalcaneal ligament area, confluent with navicular facet (2); extensive mediolaterally, restricted to proximal of astragalocalcaneal ligament area, not confluent with navicular facet (3); subcircular, isolated (4). Primitive state based on Eomaia (Luo et al., 2003, figure 3D). Modified from Hooker (2001) characters 9 (in part) and 10. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | - | 1 | 2 |
| 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | - |
274. Sustentacular facet strongly convex (0); flat or nearly so (1). Polarity based on Ukhaatherium being primitive. Modified from Hooker (2001) character 9 (in part).
275. Navicular facet not projecting over lateral side of neck (0); projecting over lateral side of neck (1). Primitive state based on Eomaia (Luo et al., 2003, figure 3D).
276. Head irregular or rounded in only one plane (0); evenly convex (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Hooker (2001) character 11.
277. Navicular facet in distal view: nearly circular, equidimensional (0); elongate oval, long axis 1.4-1.5 times short axis, horizontally aligned (1); elongate oval, long axis 1.6 times short axis or more, horizontally aligned (2); elongate oval, long axis 1.4-1.5 times short axis, dipping medially (3); elongate oval, long axis 1.6 times short axis or more, dipping medially (4). Primitive state based on Ukhaatherium. Modified from Hooker (2001) characters 12, 13, 14. STEPMATRIX.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 2 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | - | 1 |
| 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | - |
278. Cotylar fossa absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 388.
279. Head lacks cuboid facet (0); bears cuboid facet (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Wible et al. (2009) character 394.
Calcaneum
280. Tuber curved/twisted ventromedially and dorsoventrally compressed (0); straight, cylindrical to 1.25 times higher dorsoventrally than wide mediolaterally (1); straight, 1.3-1.6 times higher than wide (2); 1.7 or more times higher than wide (3). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and supported by more primitive mammals, fide Horovitz (2000), although Vincelestes is only medially deflected and not dorsoventrally compressed (Rougier, 1993). Modified from Horovitz (2000) characters 2 and 3; Hooker (2001) character 18.
281. Lateral edge of tuber continuous with peroneal process (0); no lateral edge (1). Polarity based on Vincelestes. Modified from Horovitz (2000) character 10.
282. Groove on lateral surface of tuber for peroneus brevis tendon absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on ingroup commonality. Hooker (2001) character 24, from Szalay and Lucas (1996).
283. Ectal facet medial of midline passing through tuber (0); essentially median or more lateral (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes.
284. Ectal facet orientation: distal end more medial than proximal end (0); proximodistal (1); proximomedial-distolateral 5-15 degrees (2); proximomedial-distolateral 25-30 degrees (3); proximomedial-distolateral 40-60 degrees (4); mediolateral with or without wrap around (5). Primitive state based on Vincelestes, backed up by Morganucodon, but no eutherian has primitive state. Modified from Horovitz (2000) character 7; Hooker (2001) character 20.
285. Ectal facet strongly evenly convex (0); gently evenly convex (1); helical (2); unevenly convex (3); sigmoidal (4). UNORDERED. Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Modified from Hooker (2001) character 19.
286. Ectal facet nearer to distal than proximal end (i.e., tuber relatively long) (0); at about midpoint along length (1) PRIMITIVE; nearer to proximal than distal end (i.e., tuber short) (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Polarity changed from Hooker (2001) character 17.
287. Fibular facet present (0); absent (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Horovitz (2000) character 4; Hooker (2001) character 21.
288. Peroneal process fully distal, its distal edge reaching level of cuboid facet (0); apex of peroneal process positioned at 10-15% of calcaneal length from the distal extremity (1); 17-25% from distal extremity (2); 35-55% from distal extremity (3). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Horovitz (2000) character 5; modified from Hooker (2001) character 26.
289. Peroneal process lateral projection as percentage of calcaneal length: 15-30% (0); 9-13% (1); 5-7% (2); no lateral projection (3). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Polarity reversed from Hooker (2001) character 27.
290. Peroneal process restricted distally (0); extending for 15-20% of calcaneal length (1); 21-27% (2); 32-46% (3) PRIMITIVE. Primitive state based on Eomaia. Hooker (2001) character 28.
291. Ectal and sustentacular facets do not overlap on long axis (0); do overlap (1) PRIMITIVE. Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Polarity changed from Hooker (2001) character 22; Wible et al. (2009) character 399.
292. Sustentacular facet reaches edge of cuboid facet (0); divided into a sustentacular facet sensu stricto and a distal sustentacular facet (1); single, but distinctly separated from edge of cuboid facet (2). UNORDERED. Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Modified from Hooker (2001) character 23, see Horovitz (2000). N.B. the 0 state is often treated as derived and an archontan synapomorphy, e.g., Hooker (2001). This change in polarity has important implications for phylogeny. The character is represented (and is interdependent) in the astragalus by a level of connection between the sustentacular facet and the navicular facet and is not treated as a separate character. However, the exact nature of this connection is a distinct character (q.v.).
293. Navicular facet absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Hooker (2001) character 25.
294. Cuboid facet faces distoventrally (0); faces distomedially at c.55-60 degrees to long axis of calcaneum (1); at c.70-75 degrees to long axis of calcaneum (2); faces essentially distally (3). STEPMATRIX. Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Horovitz (2000) character 8; modified from Hooker (2001) character 31.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | - |
295. Cuboid facet dorsoventrally concave (0); shallowly evenly concave (1); deeply evenly concave (2) PRIMITIVE; sellar (3). UNORDERED. Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Polarity and ordering changed from Hooker (2001) character 29.
296. Cuboid facet deeper dorsoventrally than wide mediolaterally (0); subequal (1) PRIMITIVE; wider mediolaterally than deep dorsoventrally (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes.Wible et al. (2009) character 407.
297. Cuboid facet without plantar pit (0); with plantar pit allowing rotation (1); with grooved plantar pit inhibiting rotation (2). UNORDERED. Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Hooker (2001) character 30.
298. Plantar groove present (0); absent (1). Primitive state based on Vincelestes and Eomaia (Luo et al. 2003, figure 3J). Modified from Horovitz (2000) character 6.
299. Distal plantar tubercle absent (0); present distal, medial (1); present distal central (2); proximal of distal edge, medial (3); proximal of distal edge, central (4). UNORDERED. Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Modified from Hooker (2001) characters 33-34.
300. Groove for tendon of flexor digitorum fibularis absent (0); shallow (1); deep (2). Primitive state based on Vincelestes. Modified from Wible et al. (2009) character 408.
301. Calcar absent (0); present (1). Primitive state based on ingroup commonality.
Navicular
302. Ectocuneiform and mesocuneiform facets not distinguished (0); the two facets of equal length (1); ectocuneiform facet longer dorsoventrally than mesocuneiform facet (2); mesocuneiform facet longer dorsoventrally than ectocuneiform facet (3). STEPMATRIX. Primitive state based on simplest form and 0 state in Zalambdalestidae).
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 2 |
| 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | - |
303. Plantar process scarcely or not projecting distally (0); projecting distinctly distally (1). Primitive state based on Eomaia (Luo et al., 2003).
304. Tuber tibialis absent (0); short (1); long (2). Primitive state based on Eomaia (Luo et al., 2003).
Cuboid
305. Edge of calcaneal facet overhangs dorsal wall, making it concave (0); not overhanging, dorsal wall essentially straight (1). Primitive state based on Asioryctes.
306. Plantar process strong (Kielan-Jaworowska, 1979, plate 9, figures 1a,1b) (0); weak (1). Primitive state based on Asioryctes (Kielan-Jaworowska, 1977, plate 18, figure 2b).
Metapodials
307. Tubercles for insertion of m. extensor carpi radialis on metacarpals absent (0); present on M/C III (1); present on M/C II-III (2). UNORDERED. Primitive state based on Henkelotherium. See Rose (1999), Rose and Lucas (2000), Rose and Koenigswald (2005).
Phalanges
308. Attachment on phalanx 1 for annular ligament absent or weak (0); present as tubercles (1) PRIMITIVE; present as long ridges (2). Primitive state based on Henkelotherium and Eomaia.
309. Manual phalanges relatively short (0); those of digits II-V greatly elongate (1). Primitive state based on ingroup commonality.
310. Unguals well developed (0); reduced to absent on manual digits III-V (1). Primitive state based on ingroup commonality.

