FIGURE 1. Posterior skull schematic (above) and photograph (below) of OMNH 58340. The schematic was reconstructed by digitally mirroring the left side of the suspensorium in order to approximate the actual appearance of the skull. The two images are set to the same scale, demonstrating the amount of displacement in the right side. Anterior is into the page. Abbreviations: bp - basipterygoid process; fm - foramen magnum; ptf - posterior temporal foramen (obscured); sb - squamosal boss.
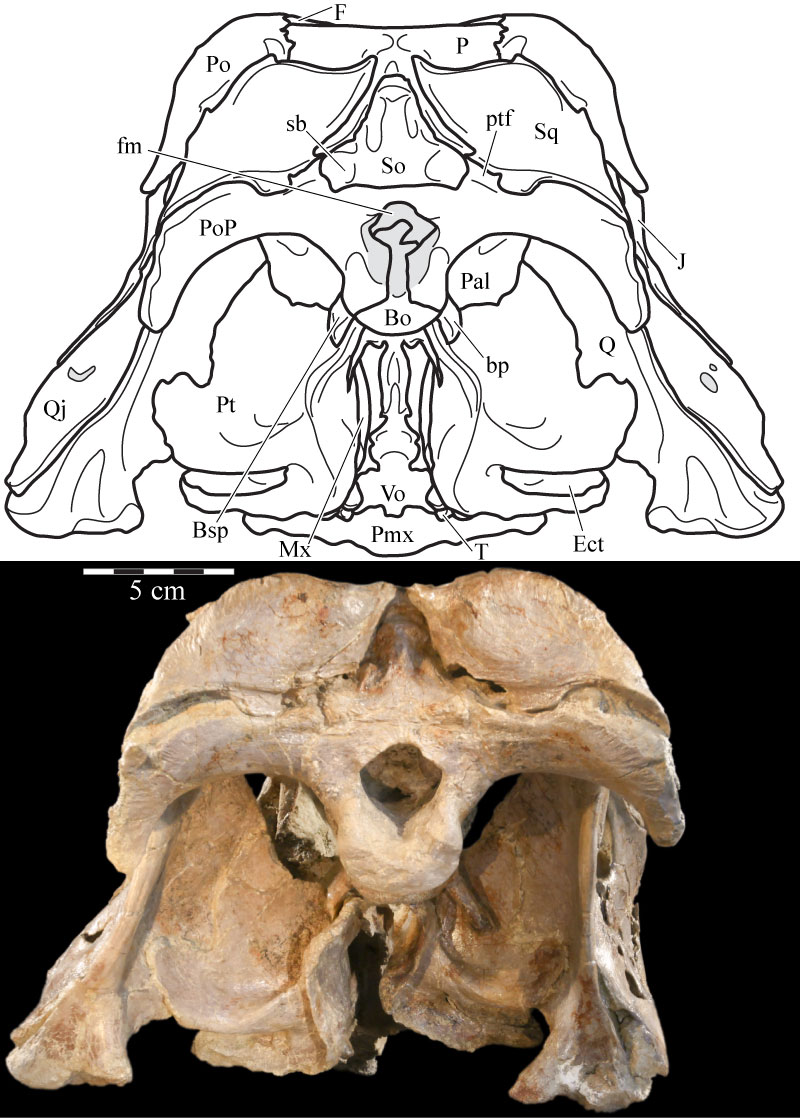
FIGURE 2. Left lateral skull schematic (above) and left skull photograph (below) of OMNH 58340. The skull is angled at the ‘alert position’ indicated by the horizontal semicircular canal. Natural fenestrae are shaded gray. Dashed outline denotes conjectural sclerotic ring. Anterior is to the left. Abbreviation: mf - maxillary foramen.
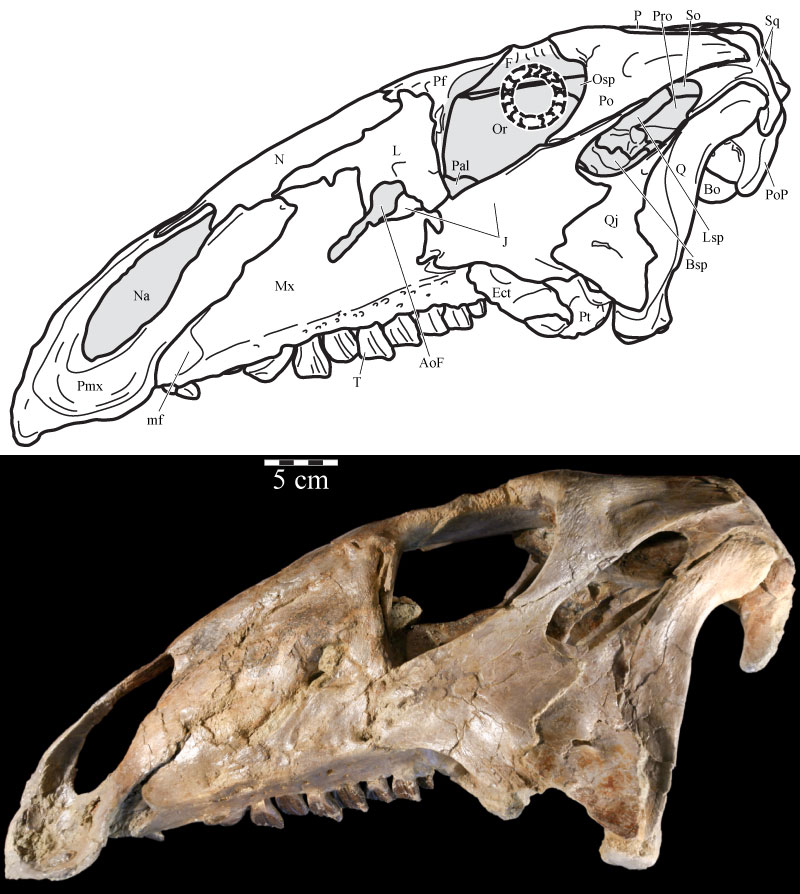
FIGURE 3. Photograph of the lateral side of the disarticulated right maxilla and other associated elements of OMNH 58340. The exclusion of the maxilla from contact with the nasal is apparent, although there is some separation, probably taphonomic, of the premaxilla and lacrimal. Dotted line indicates uncertain sutural placement between the nasal and maxilla.
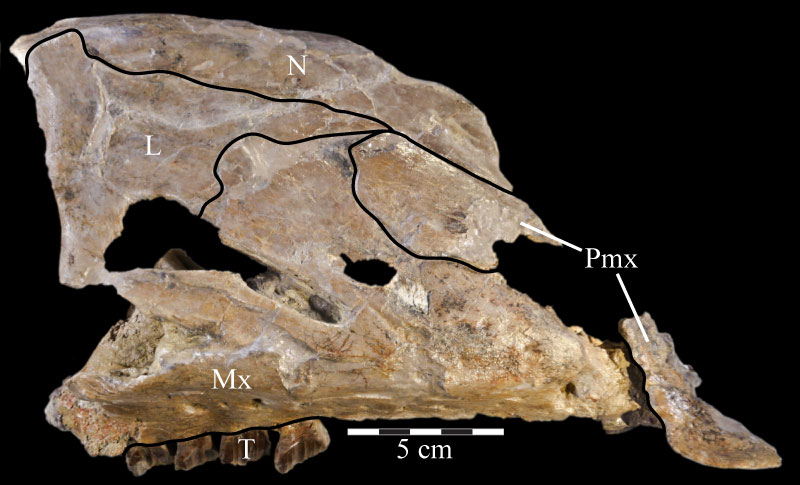
FIGURE 4. Ventral (4.1) and anterior (4.2) photographs of the right premaxilla of OMNH 34191. In 4.1, anterior is out of the page and lateral is left. In 4.2, lateral is to the left and anterior is up.
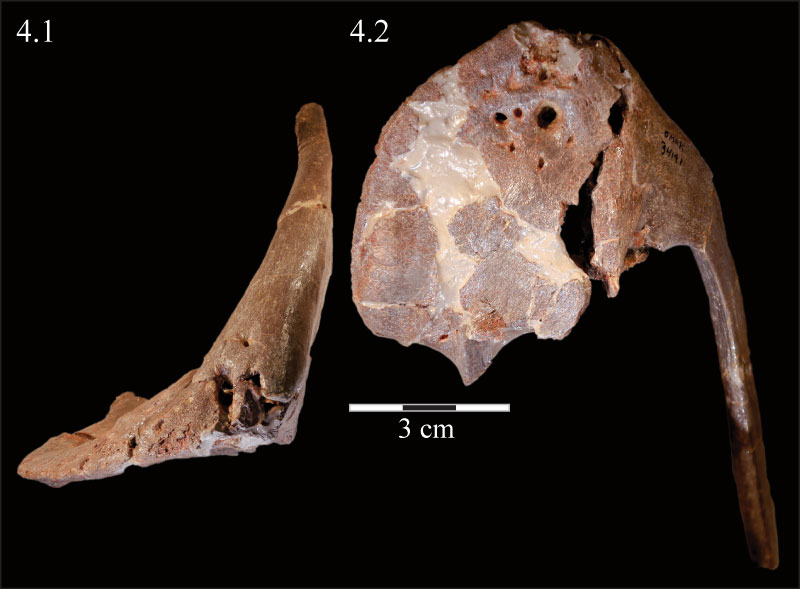
FIGURE 5. Dorsal skull schematic (above) and photograph (below) of OMNH 58340. The schematic was reconstructed by digitally mirroring the left side of the rostrum and suspensorium in order to approximate the actual appearance of the skull. Dotted line at the anterior edge of the frontals indicates uncertain sutural placement. Natural fenestrae are shaded gray. Anterior is to the right.
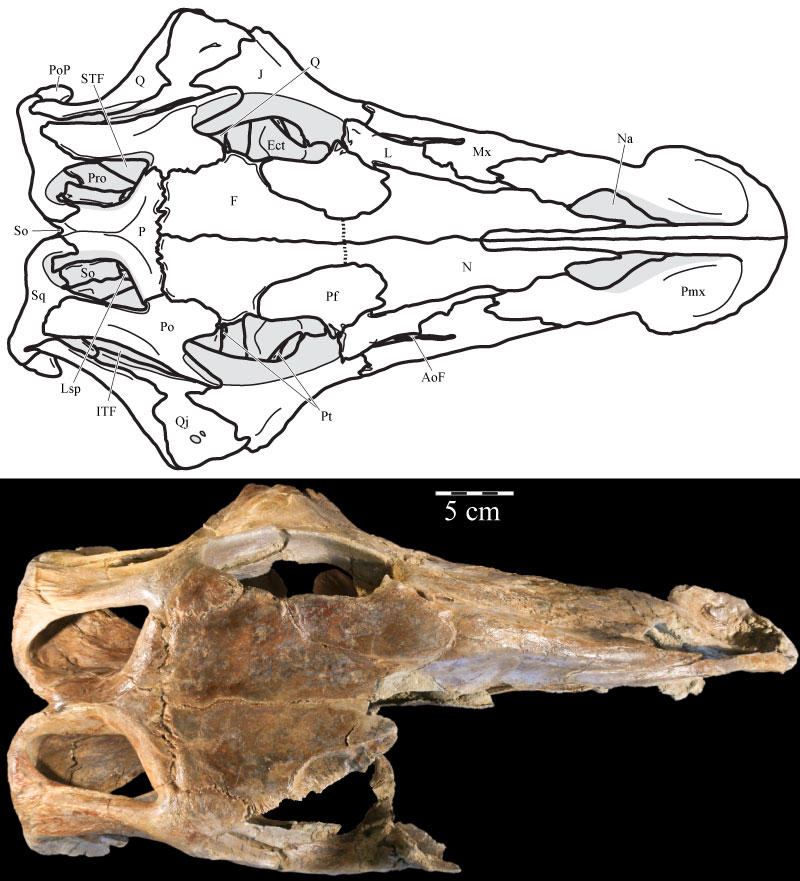
FIGURE 6. Ventral skull schematic (above) and photograph (below) of OMNH 58340. The schematic was reconstructed by digitally mirroring the left side of the rostrum and suspensorium in order to approximate the actual appearance of the skull. Natural fenestrae are shaded gray. Anterior is to the right. Abbreviations: bt - basal tubera of the basisphenoid; lt - lateral tubercle of the basioccipital; mt - median tubercle of the basioccipital; ? - possible second lateral tubercle of the basioccipital.
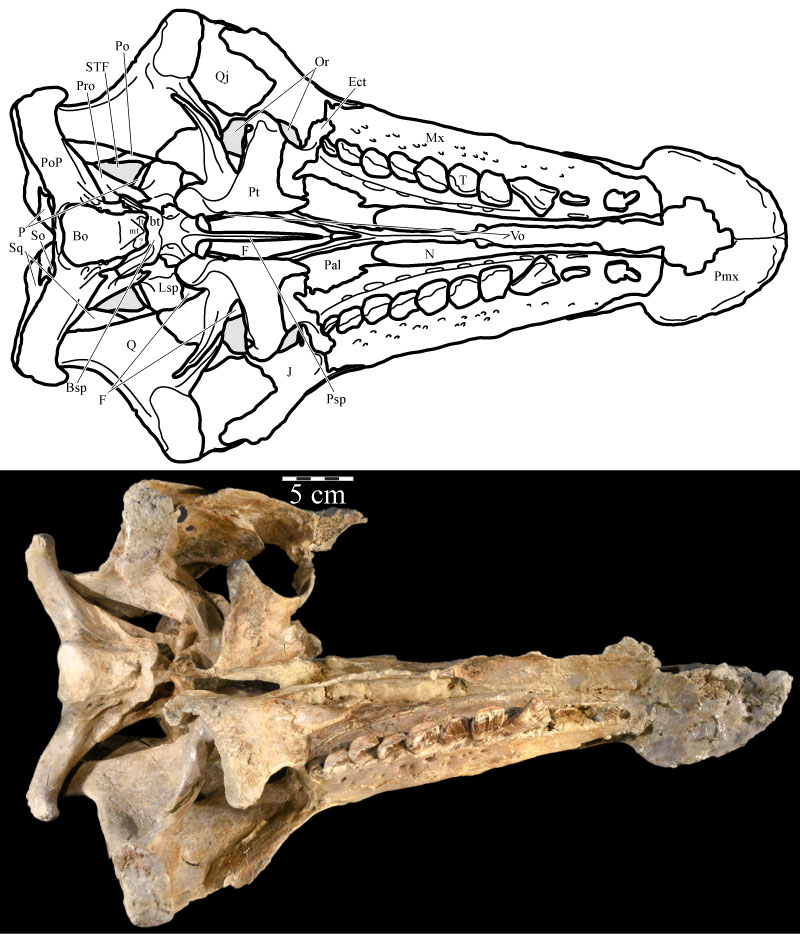
FIGURE 7. Strict component consensus tree of selected members of Ornithopoda included in this analysis. Lesothosaurus diagnosticus is the outgroup. Bremer support values are located below, while Bootstrap and Group Present/Contradicted (GC) support values are located above the branches immediately preceding the node to which they refer. GC values are in bold. Certain nodes are noted with letters referenced in the text. Optimization was performed in PAUP* version 4.0b10 (Swofford, 2002) and checked in TNT (Goloboff et al., 2008).
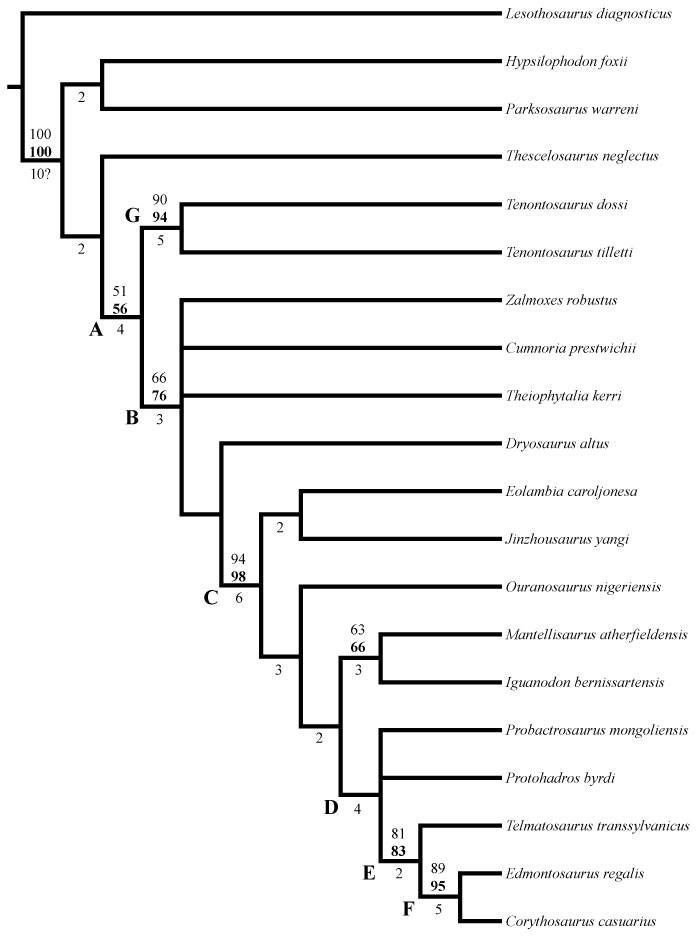
FIGURE 8. Coronal CT image, taken at the level of the open naris, of the left premaxilla (green, left), maxilla (pink, middle), and the vomer (cream, bottom) of OMNH 58340 showing the nature of their articulation. The maxilla likely fitted in closer articulation with the premaxilla. Faint green lines are an artifact of the program used to define the element on each image. Anterior is into the page.
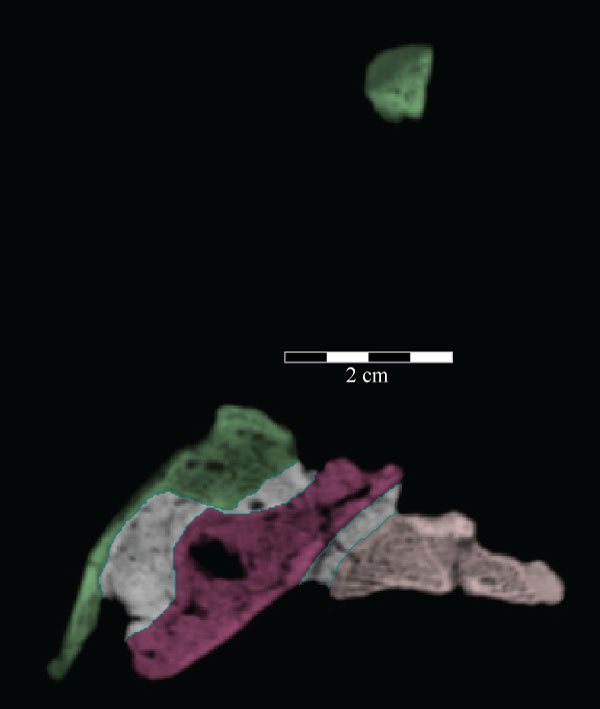
FIGURE 9. Medial skull schematic (above), right skull photograph (middle), and right skull schematic (below) of OMNH 58340. Parts of the vomer, frontal, parietal, laterosphenoid, squamosal, supraoccipital, exoccipital/opisthotic, and prootic, as well as the entirety of the right quadrate, quadratojugal, and jugal, have been removed from the medial skull schematic in order to show the structure of the braincase and its orientation with the rest of the skull. The broken texture in gray in the upper schematic indicates the sectioning of elements necessary to view the endocranium. The skull is angled at the ‘alert position’ indicated by the horizontal semicircular canal. Natural fenestrae are shaded gray. Anterior is to the right. Abbreviations: ap - alveolar parapet; s - sulcus.
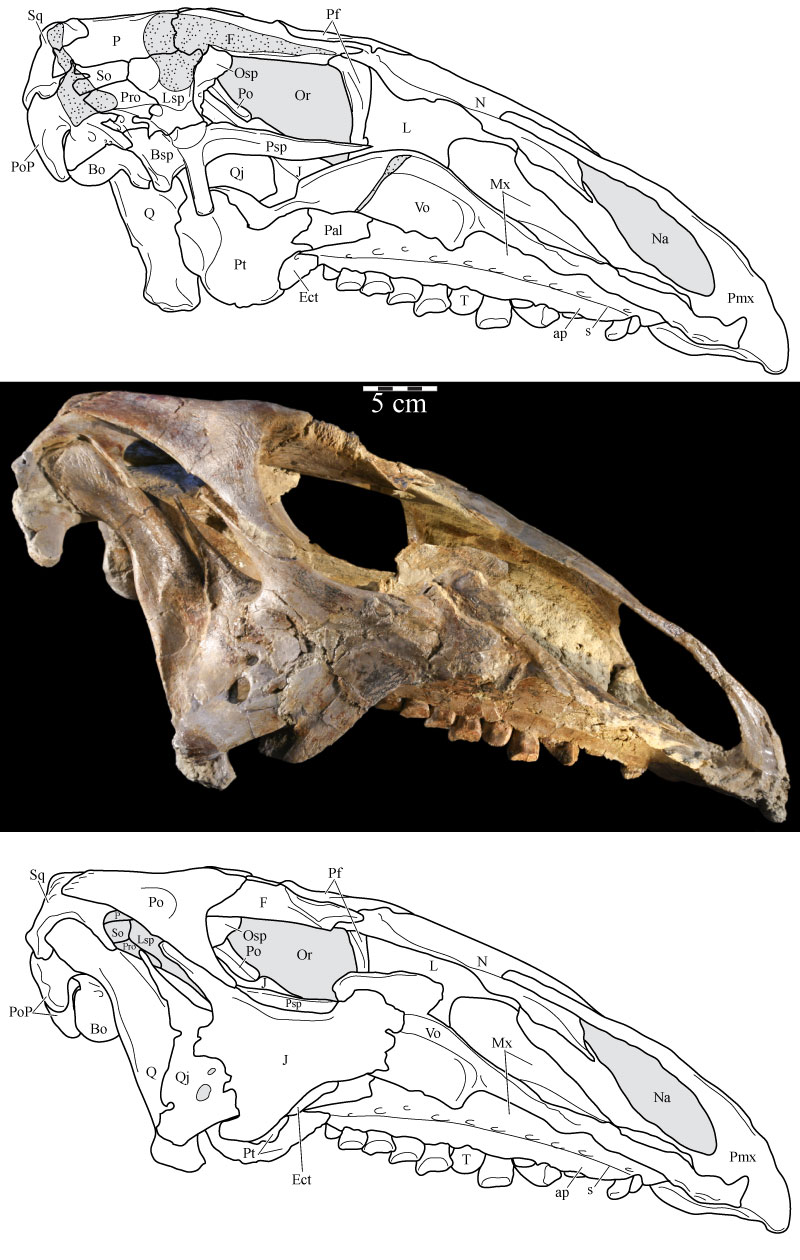
FIGURE 10. Medial view of the left side of the virtual skull of OMNH 58340 with the vomer present (10.1), allowing a view of the articulation of the vomer with the pterygoid, and with the palatine and vomer removed (10.2), allowing a view of the joints between the maxilla, lacrimal, prefrontal, jugal, ectopterygoid, and pterygoid. The vertically striated texture present on the visible surfaces of many elements, notably the lacrimal, maxilla, and premaxilla, is an artifact of the process used to isolate CT images of each element from the remainder of the data set. Abbreviations: f - flange; pp - posterior processes; tp - triangular processes.
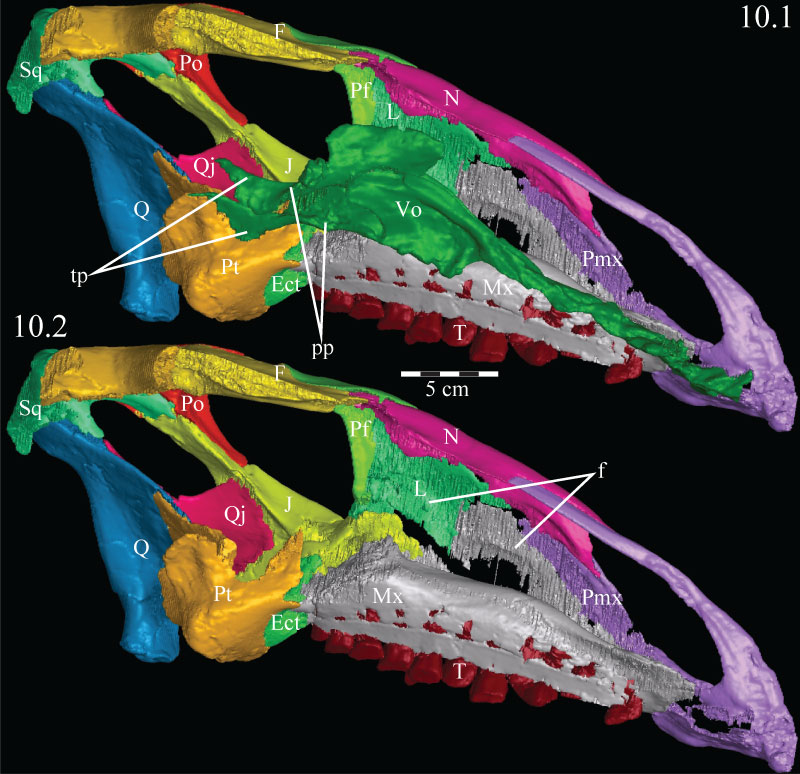
FIGURE 11. Photographs of the medial aspect of the vomer (foreground) and dental ridge of the maxilla (background, just below matrix) of OMNH 58340 (11.1) and showing the fine grain on the dorsal surface of the maxilla (11.2). Single headed arrow indicates the median ridge of the vomer. Double headed arrows indicate the paired sharp ridges of the same element. The area figured in 11.2 is indicated by the shaded area in 11.1. Anterior is to the right.
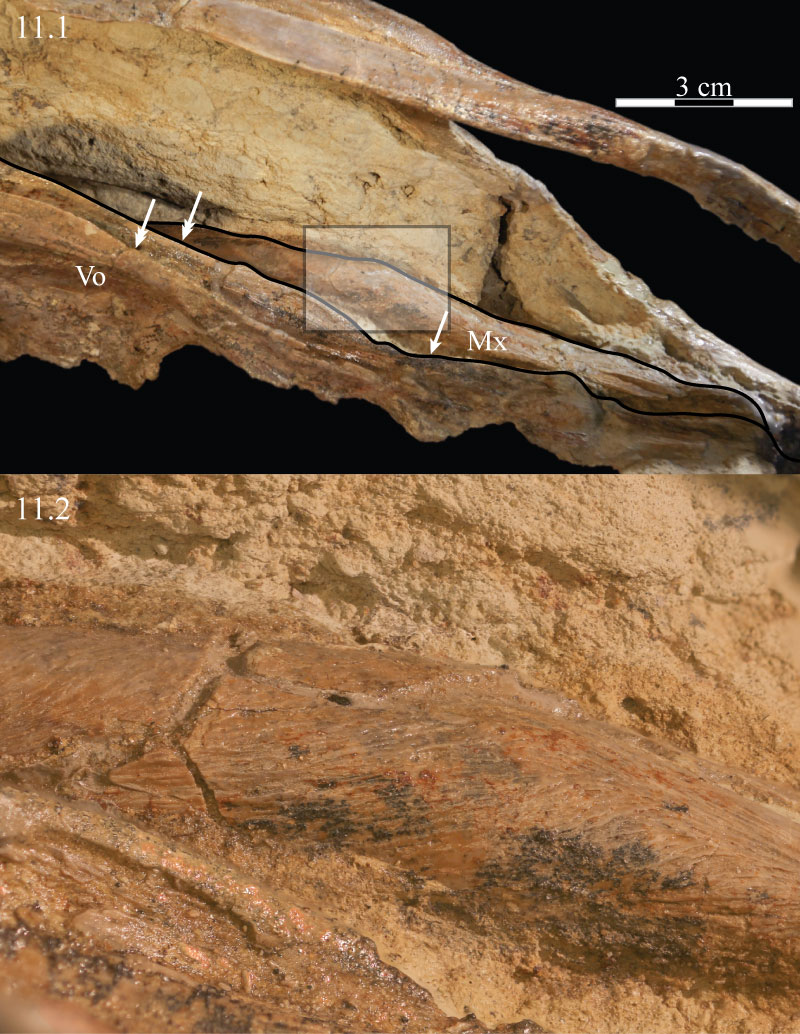

FIGURE 12. Coronal CT image, taken at the level of the posterior termination of the antorbital fenestra, of the paired posterior processes of the vomer of OMNH 58340. This image shows the disarticulated nature of the two halves of the posterior part of the element, as well as their shape just anterior to the opening of the orbit, between the paired palatines. Faint green lines are an artifact of the program used to define the element on each image. Anterior is into the page.
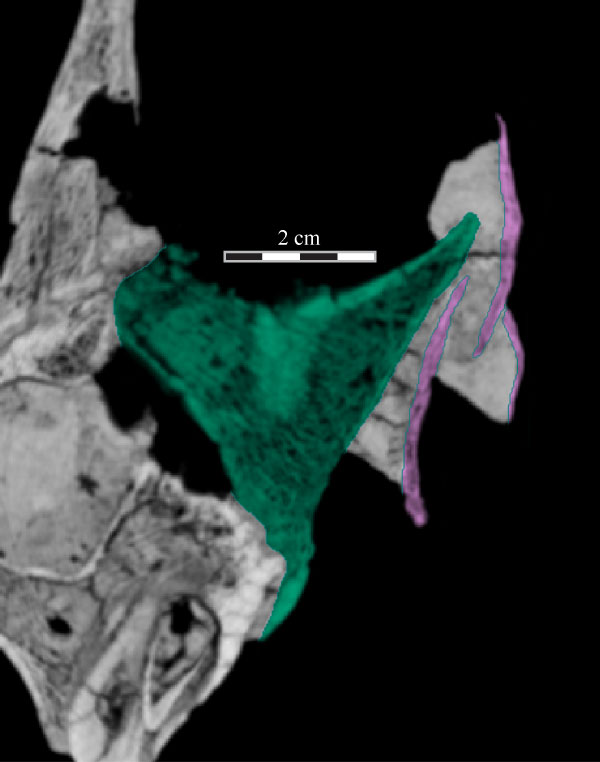
FIGURE 13. Medial (13.1) and ventral (13.2) photographs of the disarticulated right palatine of OMNH 58340. Anterior is to the left. Abbreviations: ap - anterior process; apt - articulation with pterygoid; l - lamina; lp - lateral process.

FIGURE 14. Dorsal view of the elements of the virtual palate of OMNH 58340, including the palatine, maxilla, pterygoid, and ectopterygoid, as well as the jugal, detailing the means of articulation between the various elements. Anterior is to the right.
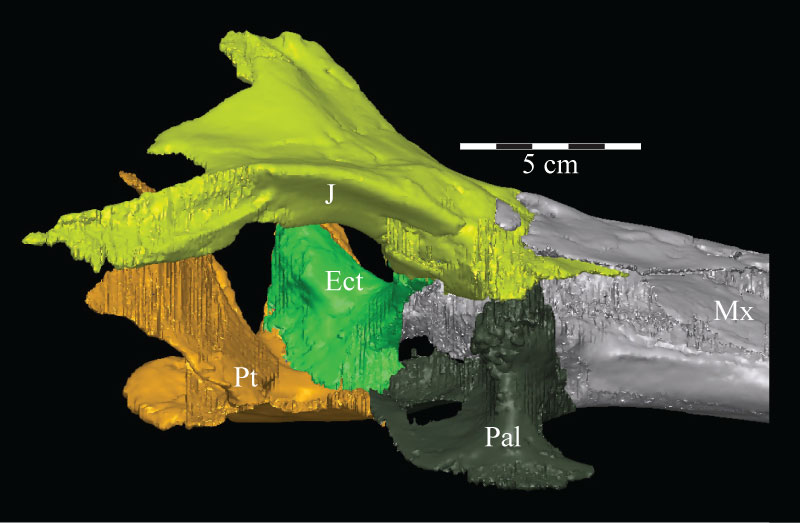
FIGURE 15. Posterolaterodorsal view of the left orbit of the virtual skull of OMNH 58340, presenting a view of the joint between the prefrontal, lacrimal, jugal, and palatine. The parallel contour lines on the posterior surfaces of the parietal, prefrontal, quadrate, and squamosal, are an artifact of the CT scanning process, and represent the faces of individual slice images. These lines occur on any surface angled near parallel with the scanner. Anterior is into the page, toward the top left. Abbreviation: lt - lateral tubercle; pg - pterygoid groove.
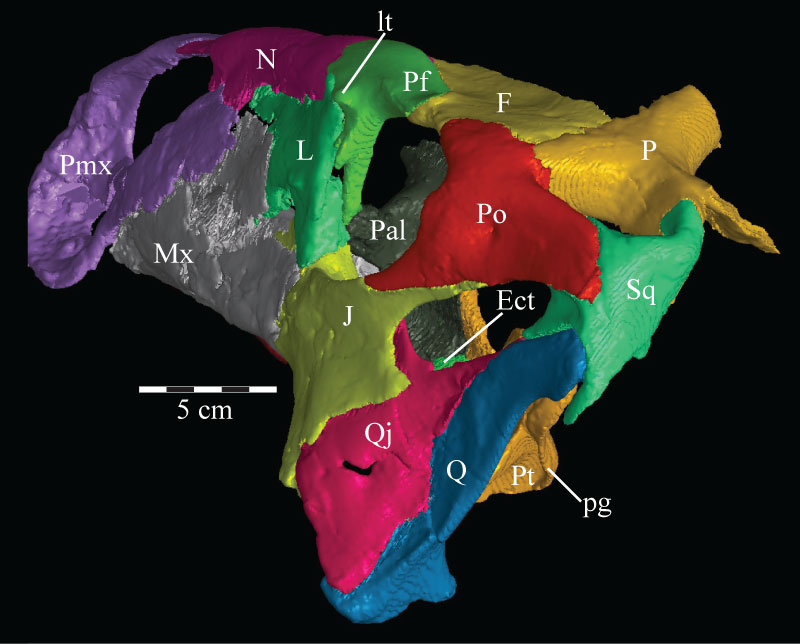
FIGURE 16. Lateral view (16.1) of the virtual ectopterygoid (green) and pterygoid (yellow) of OMNH 58340. Dorsal view (16.2) of the virtual pterygoid only. Anterior is to the left. Abbreviations: ep - ectopterygoid process; lf - lateral fossa; pf - pterygoid flange; pp - palatine process; mp - medial process; qp - quadratic process.
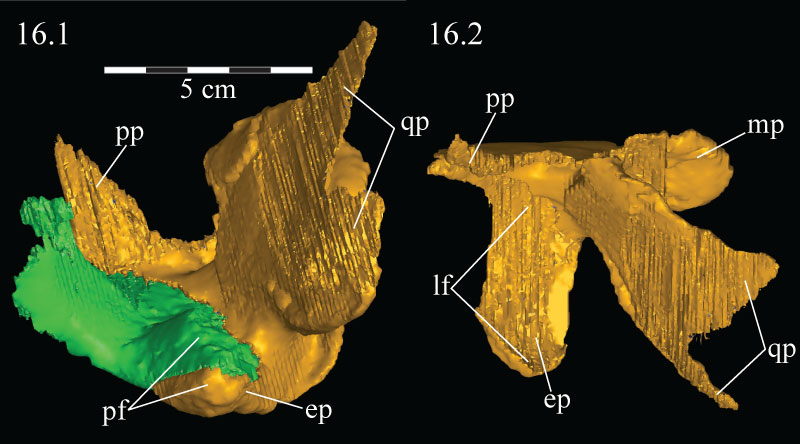
FIGURE 17. Anteromediodorsal view of the virtual skull of OMNH 58340, showing the features surrounding the maxillary groove of the maxilla, including the dental ridge and the possibility of a soft-tissue roof covering it in life. Abbreviations: dr - dental ridge of the maxilla; la - lamina of the maxilla; mf - medial flange of the lacrimal; mg - maxillary groove; mp - maxillary projection.
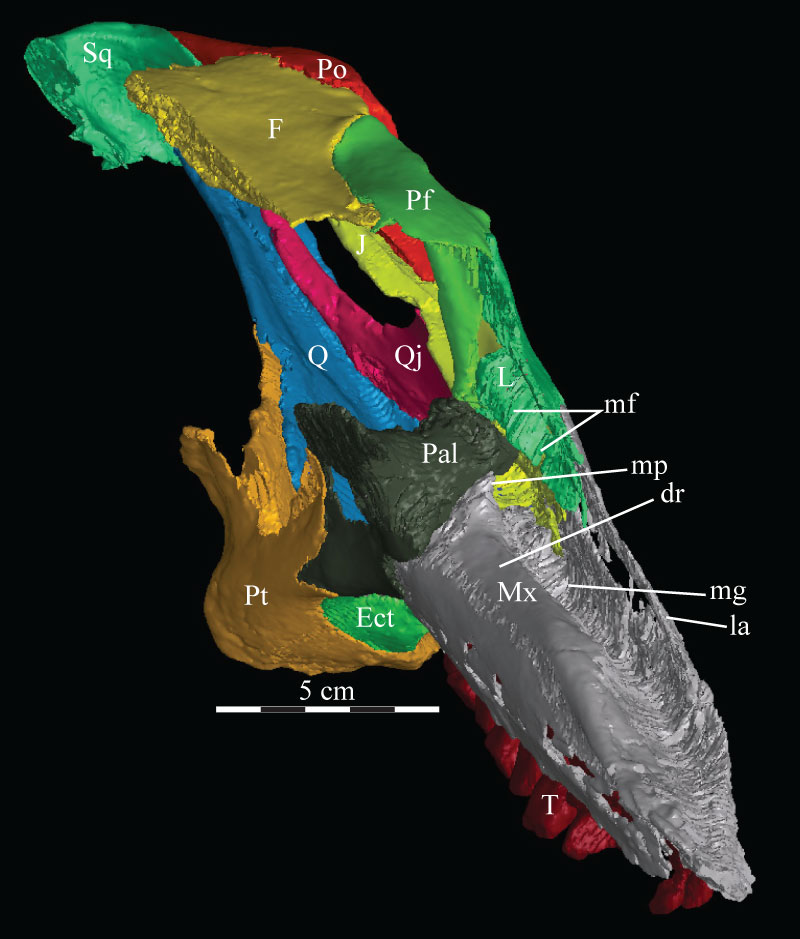
FIGURE 18. Anterior skull schematic (above) and photograph (below) of OMNH 58340. The two images are set to the same scale, demonstrating the amount of displacement in the right side of the skull. The schematic was reconstructed by digitally mirroring the left side of the rostrum and suspensorium in order to approximate the actual appearance of the skull. Natural fenestrae are shaded gray. Anterior is out of the page.
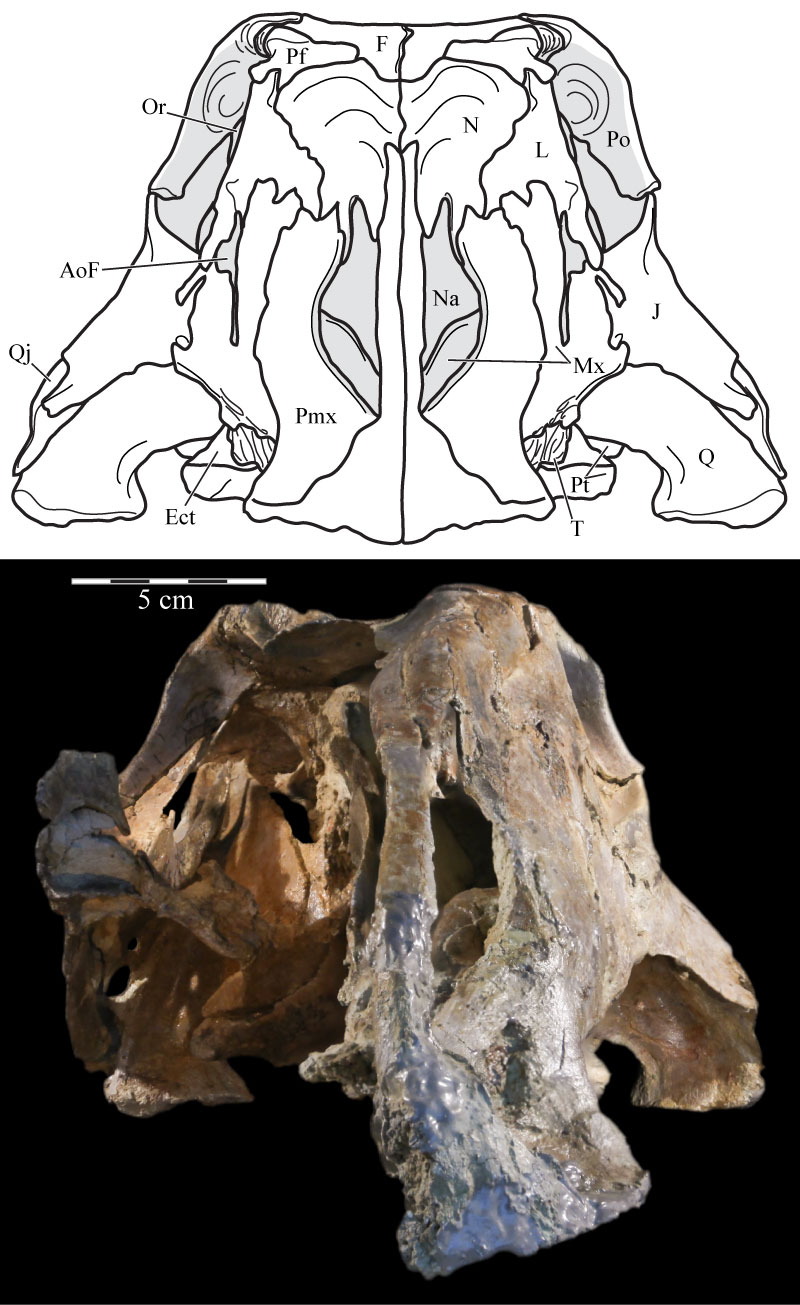
FIGURE 19. Medial view of the virtual left premaxilla, nasal, lacrimal, and maxilla of OMNH 58340 showing the nasal arch of the nasal just below its articulation with the nasal process of the premaxilla. Anterior is to the right. Abbreviation: na - nasal arch.
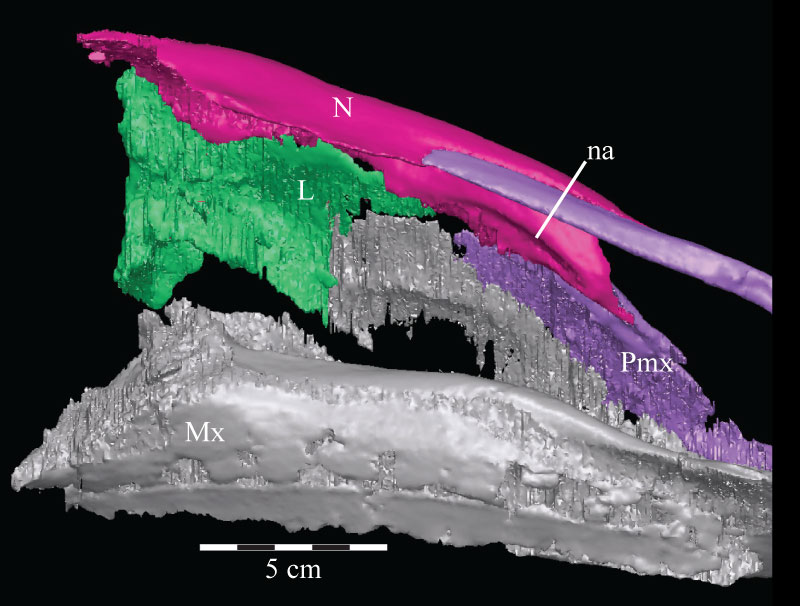
FIGURE 20. Coronal CT image, taken at the anterior edge of the left orbit, of the prefrontal (violet), nasal (dark green), and frontal (yellow) of OMNH 58340 showing their articulation. Faint green lines are an artifact of the program used to define the element on each image. Anterior is into the page.
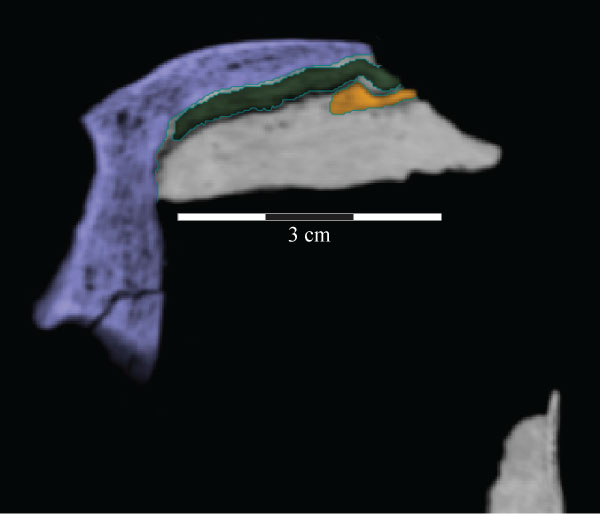
FIGURE 21. Ventral view of the skull roof of OMNH 58340. The palate and the lateral facial elements have been removed to allow for the viewing of the associations of the elements depicted. Location of endocast indicated by black outline. Note the nasal and prefrontal ending at nearly the same point posteriorly. Anterior is to the right. Abbreviations: la - area of articulation with capitate process of laterosphenoid; pp - pedicles of partietal; ar - arcuate ridge; sa - area of articulation with supraoccipital.
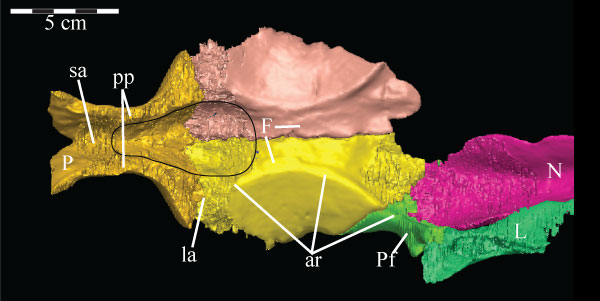
FIGURE 22. Coronal CT image of the left maxilla (pink) of OMNH 58340, taken midway along the axial length of the element, showing its facial lamina (left) and dental ridge (right, surrounding two teeth, lighter, due to higher density). Faint green lines are an artifact of the program used to define the element on each image. Abbreviations: a - alveolus; c - canal; lg - lamellar gap.
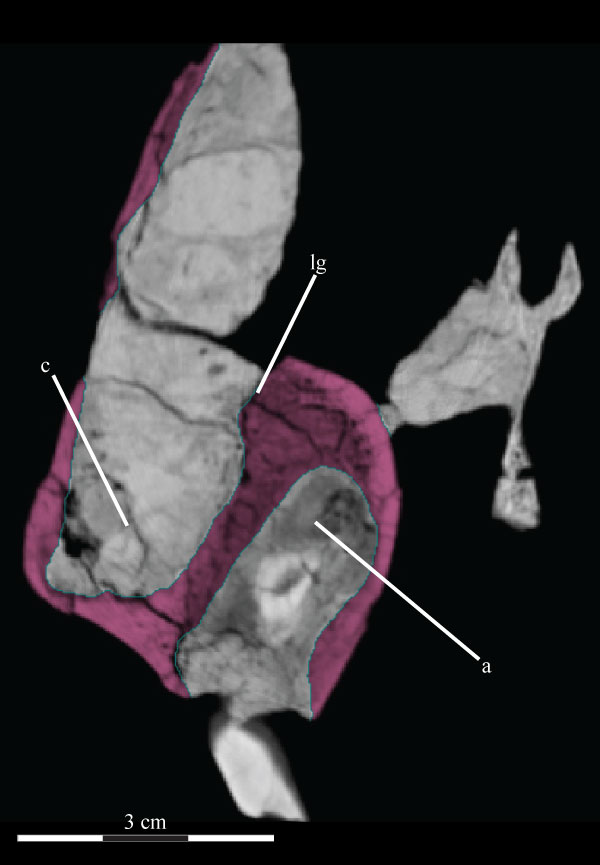
FIGURE 23. Labial photograph of the left maxillary dentition (23.1) and lingual photograph of the left dentary dentition (23.2) of OMNH 58340. Note the finely ornamented surface of the alveolar parapet of the dentary between the lower exposed surfaces of the teeth and the dorsally arched sulcus.
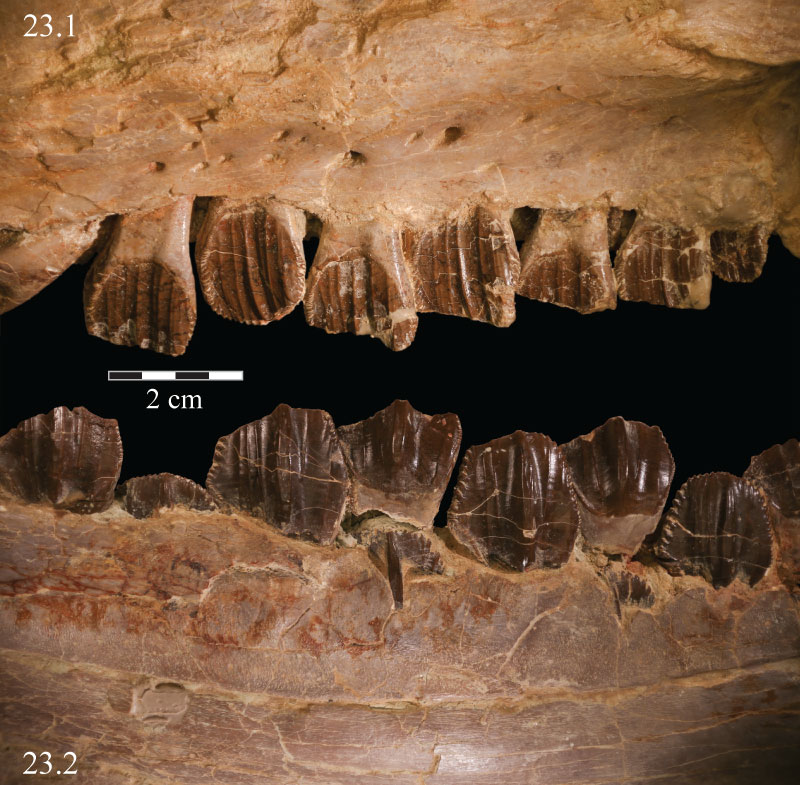
FIGURE 24. Coronal CT image, taken just anterior of the left orbit, of the lacrimal (light blue) and its shelf (lower right) of OMNH 58340. Faint green lines are an artifact of the program used to define the element on each image. Anterior is into the page.
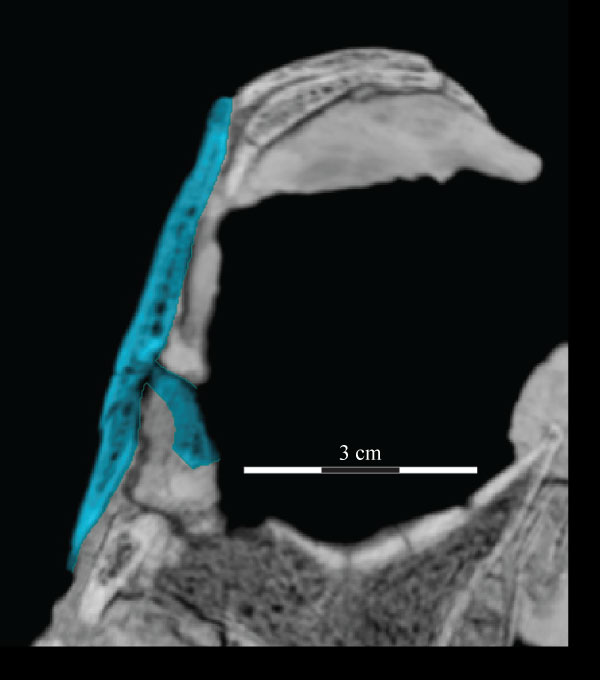
FIGURE 25. Ventral (25.1) and medial (25.2) photographs of the disarticulated right prefrontal of OMNH 58340. Anterior is left. Arrows indicate undulating texture on the ventral and medial surfaces of the element, which indicate the area of articulation with the frontal. The space between two broken ends of the ventral process in 25.2 is indicated by a dashed gray line. Abbreviation: vp - ventral process.
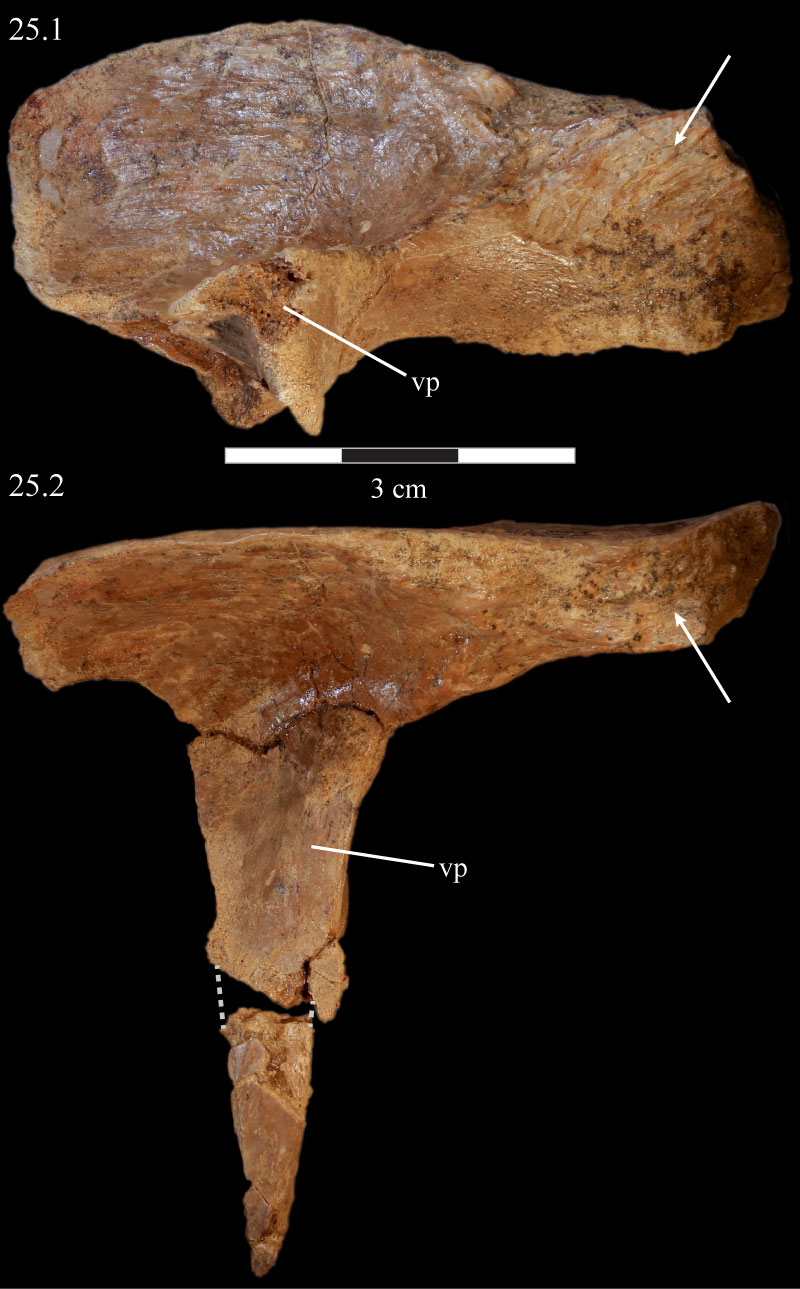
FIGURE 26. Photograph of the left prefrontal, frontal, and postorbital of OMNH 58340, showing the high degree of rugosity above the orbit. Anterior is to the left.
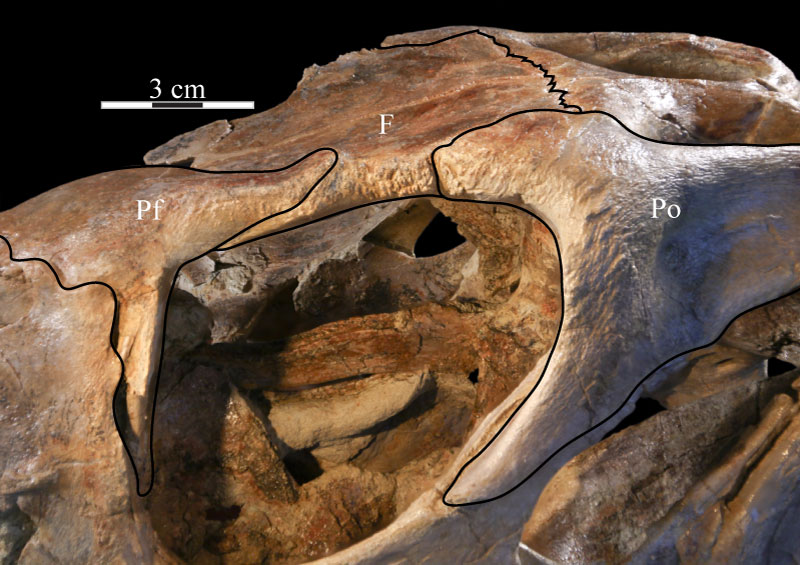
FIGURE 27. Photograph of the prefrontal fossa (indicated by arrows) of the right frontal of OMNH 58340. The pyramidal corner of the disarticulated prefrontal fits into this fossa. Anterior is to the right and out of the page.
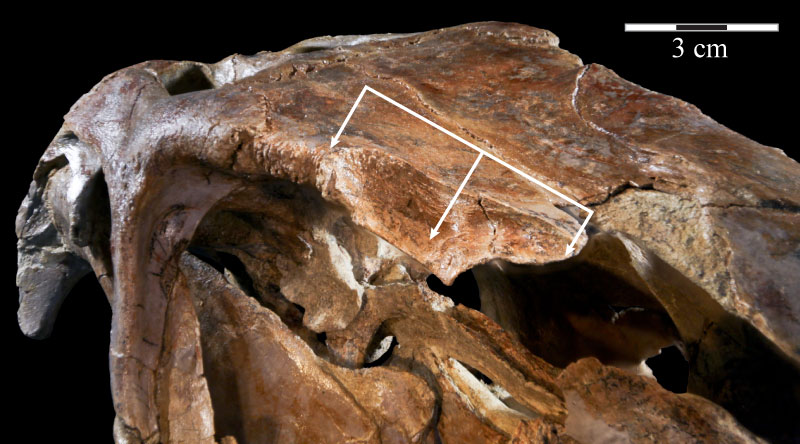

FIGURE 28. Coronal CT image, taken just anterior of the orbit, of the left prefrontal and its ventral process (violet), lacrimal (light blue), and palatine and its lateral process (brown) of OMNH 58340 showing the nature of their articulation. Faint green lines are an artifact of the program used to define the element on each image. Anterior is into the page.
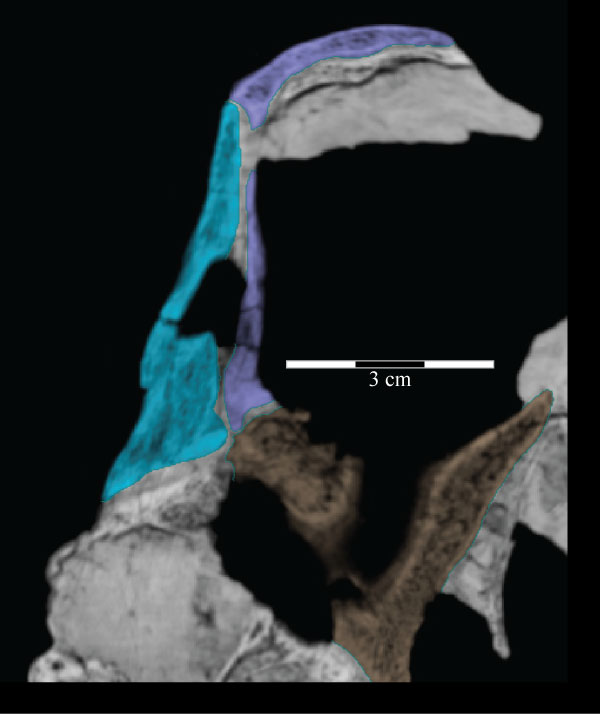
FIGURE 29. Photograph of the left squamosal of OMNH 58340, showing the deep texture on the lateral surface of the body of the bone, continued forward onto the lateral surface of the squamosal process of the postorbital. Anterior is to the upper left and into the page. Abbreviations: vt - ventral tab of the squamosal.
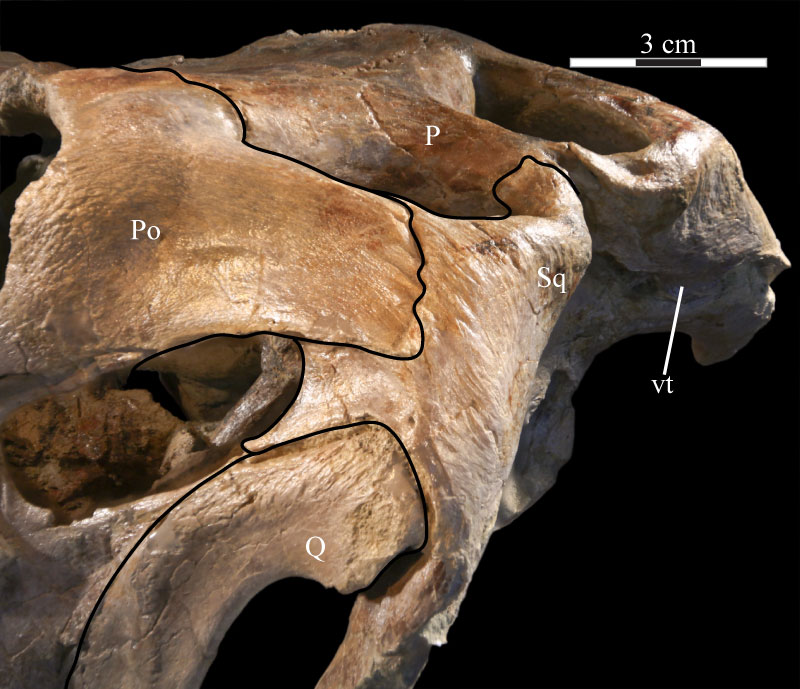
FIGURE 30. Lateral view of the virtual left squamosal of OMNH 58340 showing the deep articular fossae and the processes of the element. Anterior is to the left. Abbreviations: ap - anterior process; ah - articulation for head of quadrate; apo - articulation for postorbital; poq - postquadratic process; preq - prequadratic process.
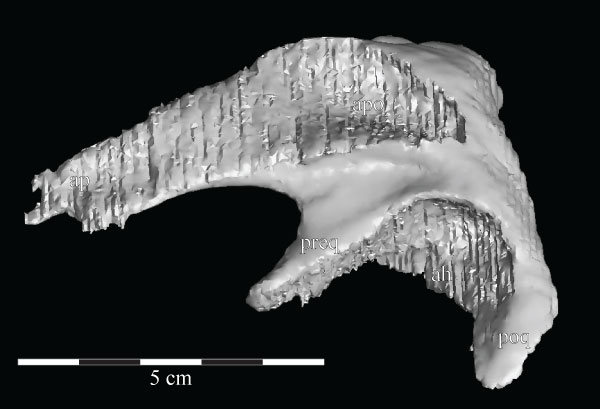

FIGURE 31. Lateral view of the virtual left quadratojugal of OMNH 58340 showing the rhomboidal shape of the element. The corrugated area on the left half of the element (outlined in black) is an artifact of the sectioning process and represents the articular surface for the jugal. Anterior is to the left.
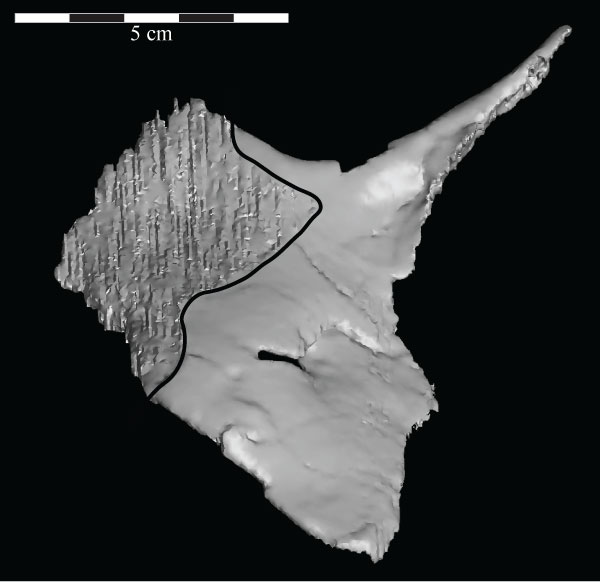

FIGURE 32. A lateral view of the virtual skull (lower left) and braincase (inlay, upper right) of OMNH 58340 with a high transparency, making the endocast (blue), cranial nerves (yellow), and semicircular canals (magenta) visible. The skull is at the ‘alert position’ indicated by the horizontal semicircular canals. Abbreviations: bt - basal tubera; bpt - basipterygoid process; oc - occipital condyle.
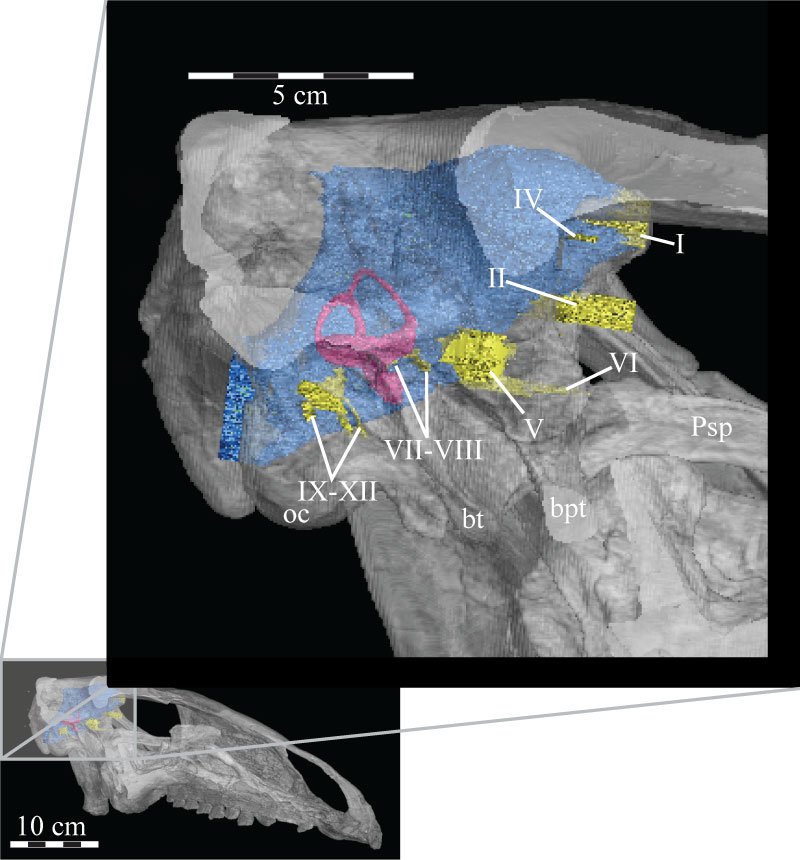
FIGURE 33. Photograph of the posterior portion of the dorsal surface of the skull of OMNH 58340, showing the small waist of the parietal (indicated by arrow). This groove may have been for the passage of an artery or may mark the separation between two muscles. There is an identical feature on the opposite side of the skull. Anterior is to the left.
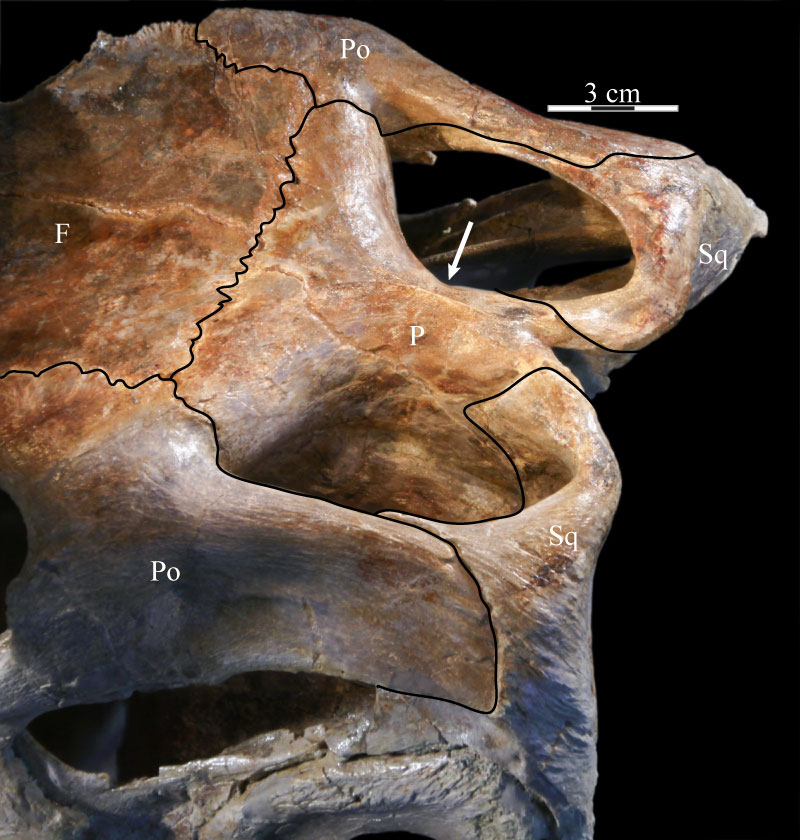
FIGURE 34. Anterior view of the virtual braincase of OMNH 58340. The supraoccipital is indicated by the pink that shows through the foramina for CN I–III. The smooth area across the front of the parasphenoid and the left basipterygoid process, as well as the regular curvature of the outer edge of the right laterosphenoid, prootic, and opisthotic (to the left), are artifacts of CT scanning and represent the limits of the data set. Note the irregular anterior surface of the parietal, showing the interdigitate nature of the suture of that element with the frontals. Black lines are used to denote particular features. Anterior is out of the page and ventral is down. Abbreviations: bt - basal tubera; bpt - basipterygoid process; ct - crista terminalis; eV - excavation for trigeminal nerve (CN V); hf - hypophysial fossa; pp - preotic pendant; st - sella turcica; vt - ventral tubercle of the orbitosphenoid.
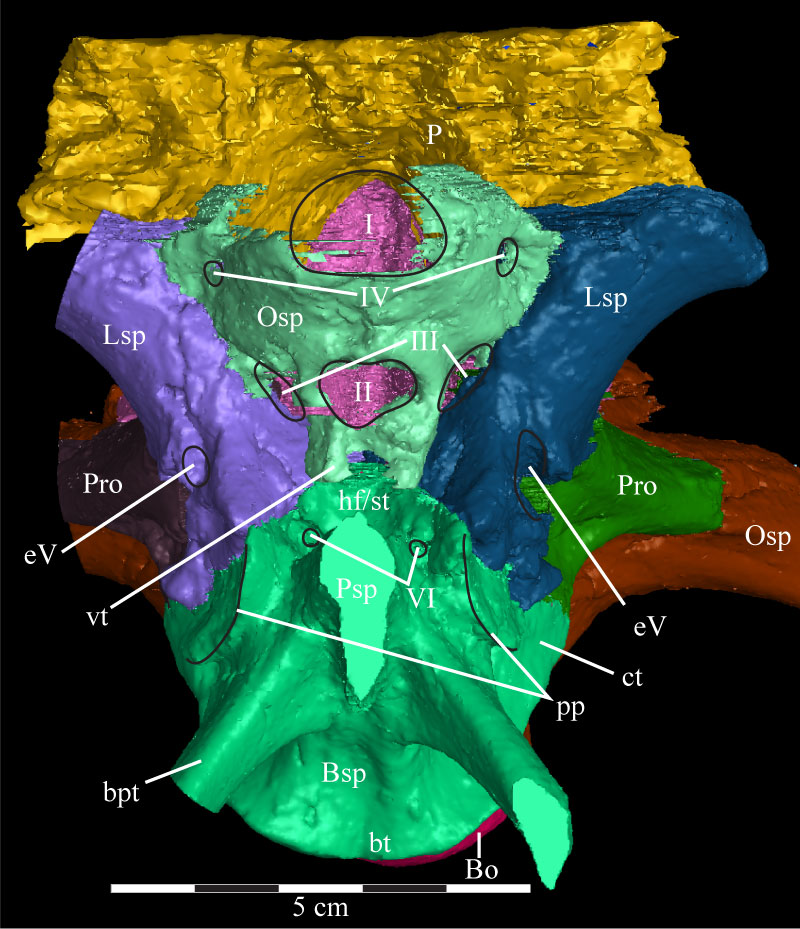
FIGURE 35. Lateral view of the virtual braincase of OMNH 58340. Black lines are used to denote particular features. The straight lines at the front of the basisphenoid to the left and the exoccipital/opisthotic to the right are artifacts of the CT scanning and represent the limits of the data set. The frontal and parietal extend beyond these levels because they were transplanted from the full cranial scan. Note that the basioccipital is visible in two locations. Anterior is to the left. Abbreviations: bt - basal tubera; bpt - basipterygoid process; cc - internal carotid canal (obscured); ci - crista interfenestralis; cm - crista metotica; cp - crista prootica; ct - crista tuberalis; eV - excavation for trigeminal nerve (Cranial Nerve V); fm - fenestra metotica; fo - fenestra ovalis; g - groove of crista tuberalis; pp - preotic pendant; sr - stapedial recess; ? - unnamed ridge.
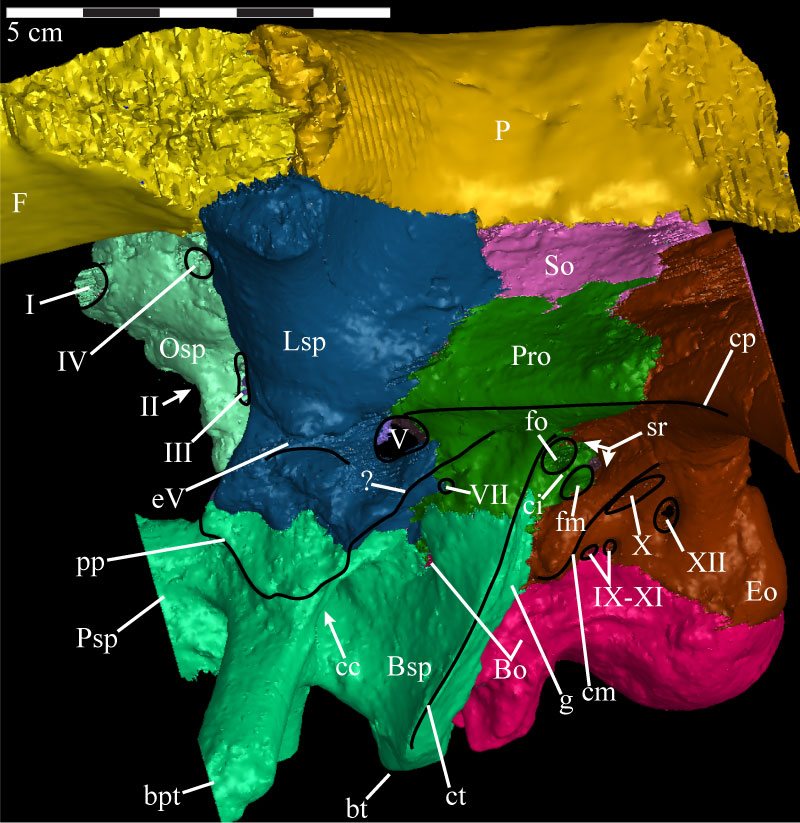
FIGURE 36. Dorsolateral view of the virtual braincase of OMNH 58340 with the parietal, left laterosphenoid, left prootic, and left sections of the supraoccipital and exoccipital/opisthotic removed. The flat edges of the parasphenoid and of the supraoccipital and exoccipital to the left and right, respectively, are artifacts of the CT scanning, and represent the limits of the data set. The supraoccipital (pink), exoccipital (brown), and orbitosphenoid (light green) were sectioned to allow for viewing of structures that would normally be covered by these elements. The computer program used to do this randomly assigns interior colors to the models, hunter green in the case of the supraoccipital, light blue in the case of the exoccipital, and maroon for the orbitosphenoid. Anterior is to the left. Abbreviations: bpt - basipterygoid process; dVIII - dorsal ramus of the acoustic nerve; ed - endolymphatic duct; mp - median process of the basioccipital; pf - area of the pontine flexure; vp - ventral process of the supraoccipital; vVIII - ventral ramus of the acoustic nerve.
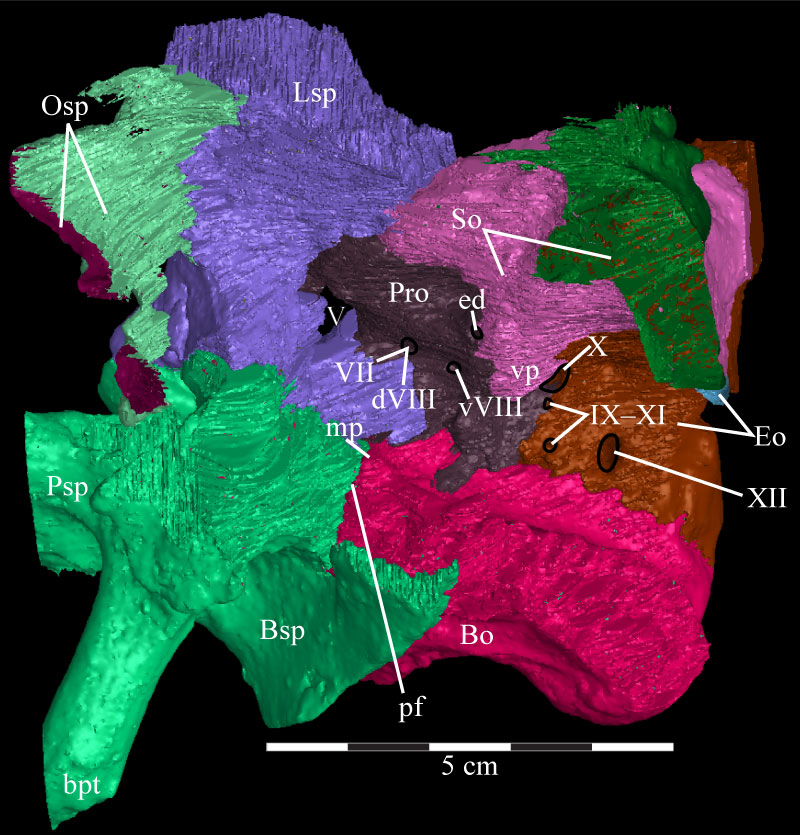
FIGURE 37. Posterior view of the virtual braincase of OMNH 58340 with the exoccipital/opisthotic removed. The regularly curved borders along the right side, as well as the flat squamosal bosses of the supraoccipital, are an artifact of the CT scanning and represent the limits of the data set. Anterior is into the page and dorsal is up. Abbreviations: ab - auditory bulla; ap - ascending process; bf - basioccipital furrow; bt - basal tubera; bpt - basipterygoid process; dt - dorsal tubercle; ns - nuchal shelf; sb - squamosal boss; ss - supraoccipital shelf; vp - ventral processes.
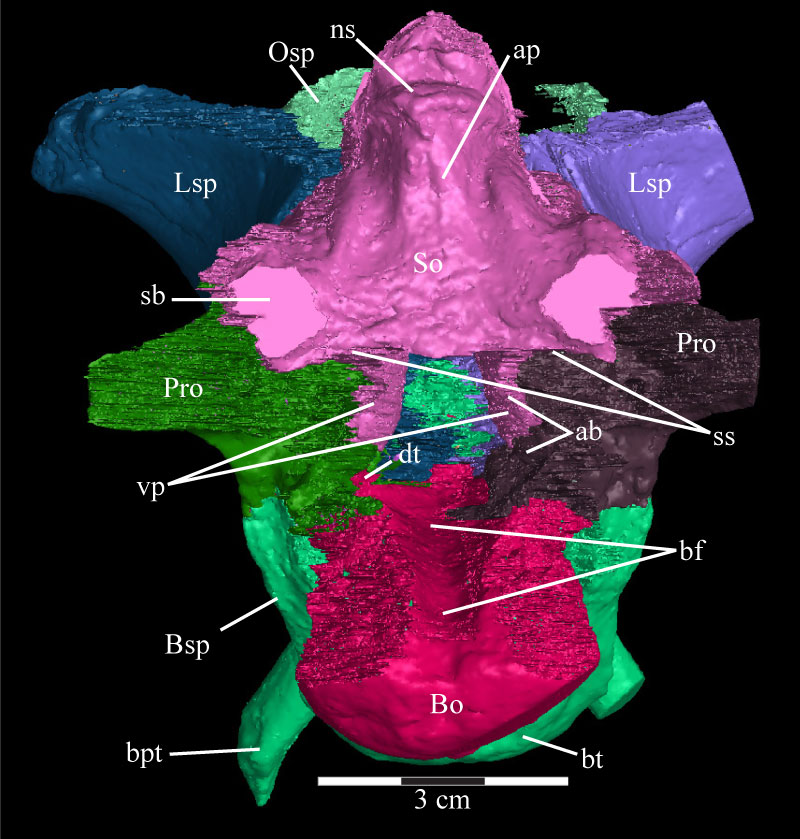
FIGURE 38. Lateral view of the virtual supraoccipital (purple) and the left endosseous labyrinth (pink) of OMNH 58340 showing the common crus of the semicircular canals entering the ventral process of the supraoccipital. Anterior is to the left. Abbreviations: asc - anterior semicircular canal; cc - common crus; nc - nuchal crest; psc - posterior semicircular canal; ss - supraoccipital shelf; vp - ventral process.
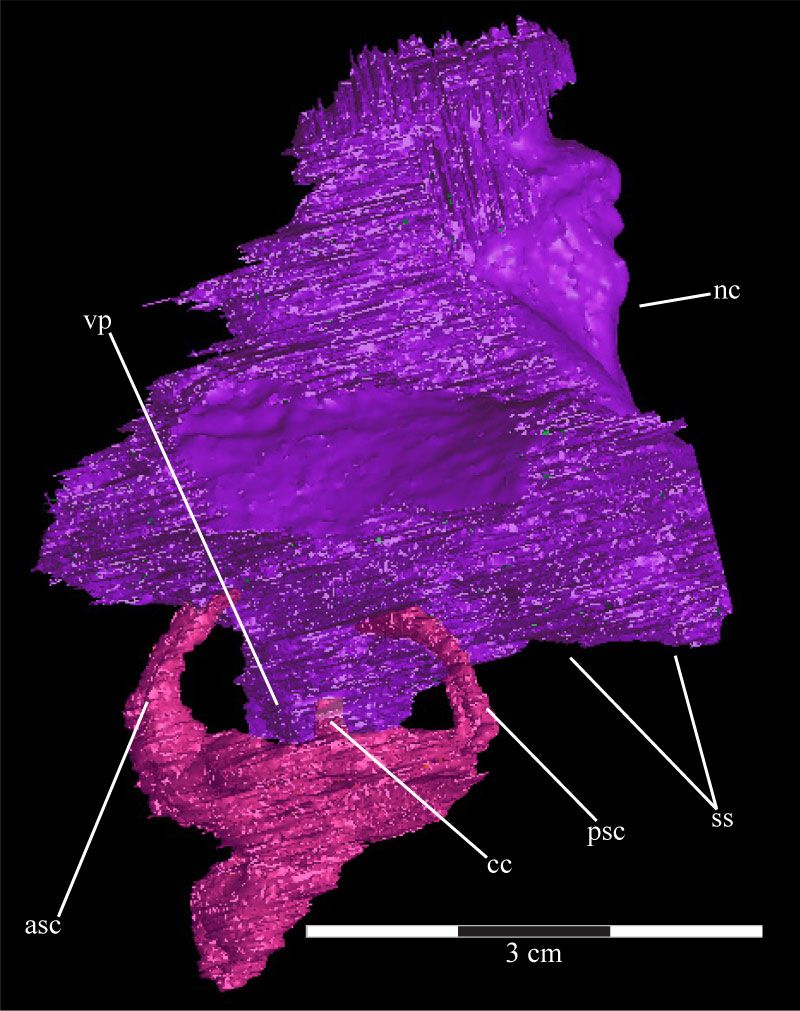
FIGURE 39. Dorsal view of the virtual braincase of OMNH 58340 with the parietal removed, showing the composition of the floor of the braincase. The straight posterior edge of the opisthotic, as well as the straight anterior edge of the basisphenoid and lateral edge of the laterosphenoid, are artifacts of the CT scanning and represent the limits of the data set. Anterior is down. Abbreviations: ap - area of articulation with parietal; i - infundibular canal; pp - posterior process of the orbitosphenoid.
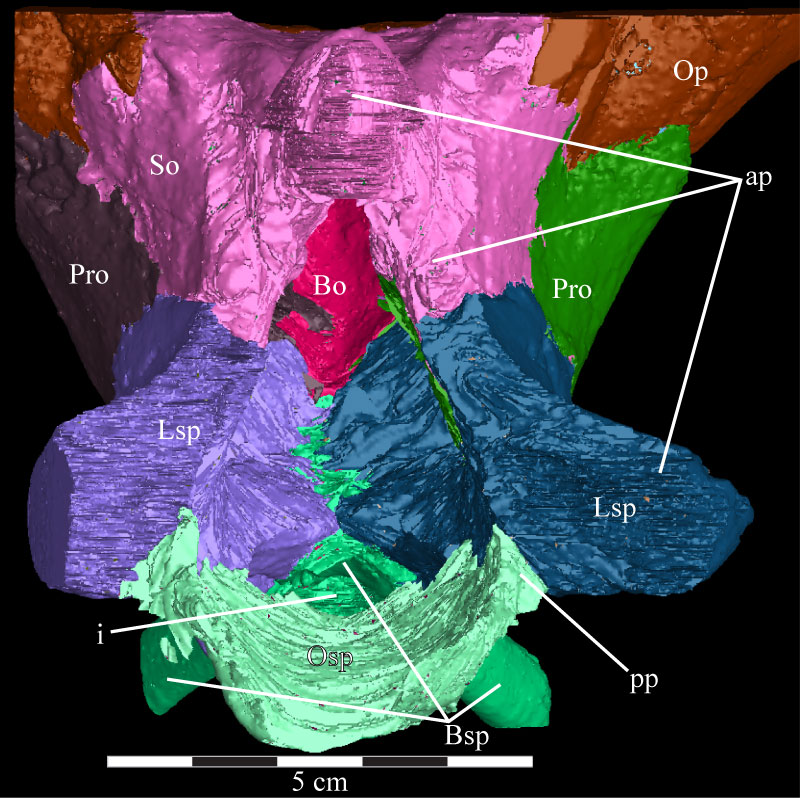
FIGURE 40. Horizontal CT image, taken at the level of the trigeminal foramina, of the basisphenoid and parasphenoid (orange), laterosphenoids (pink and light blue), trigeminal nerve foramina (yellow), prootics (teal and red), horizontal semicircular canals (purple), and exoccipital/opisthotic (green) of OMNH 58340. The endocast is the black and gray area in the middle of the image. The ventral processes of the supraoccipital can also be seen, as well as their peculiar density. Faint green lines are an artifact of the program used to define the element on each image. Anterior is down. Abbreviations: sc - horizontal semicircular canals; vp - ventral processes.
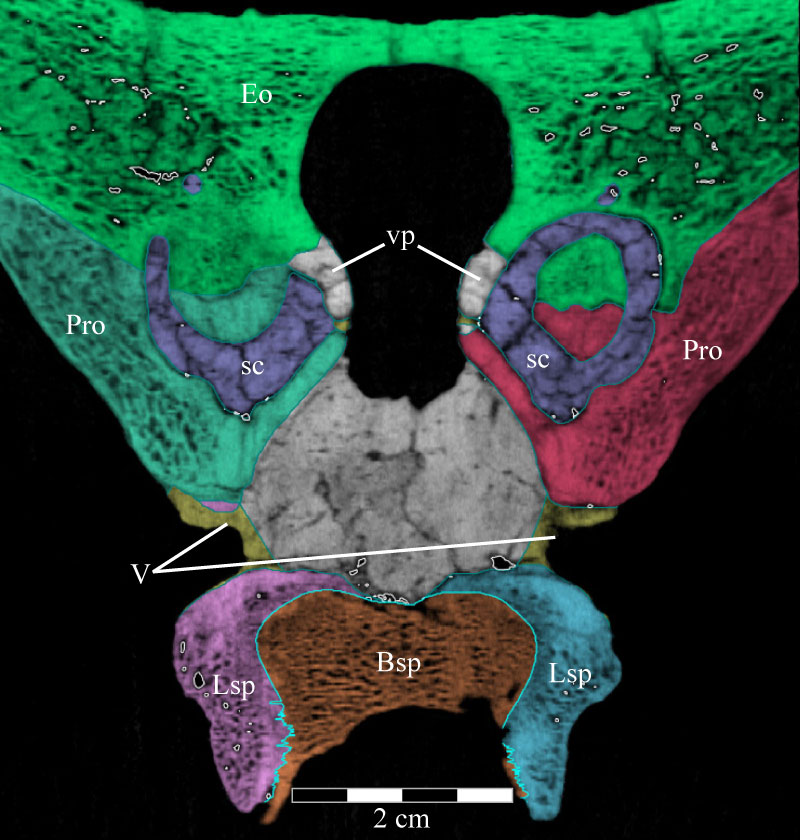
FIGURE 41. Anterior view of the virtual braincase of OMNH 58340 with the parietal, orbitosphenoid, left laterosphenoid, and basisphenoid/parasphenoid removed. The curvature along the left border is an artifact of the CT scanning and represents the limit of the data set. Black lines are used to denote particular features. Anterior is out of the page and ventral is down. Abbreviations: conical fossa; ds - dorsal sagittal sinus; fm - foramen magnum.
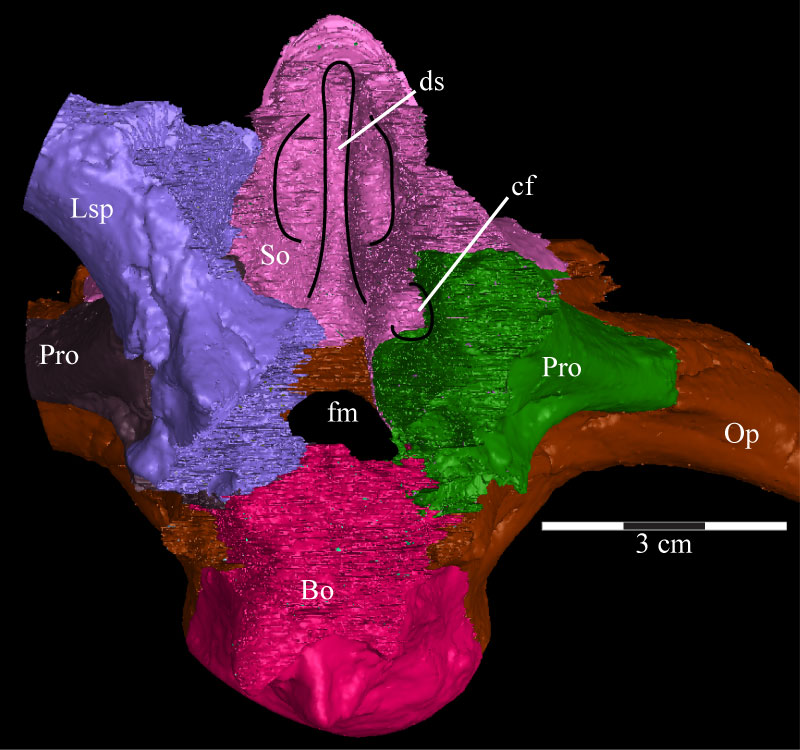
FIGURE 42. Posterodorsal view of the virtual braincase of OMNH 58340 with the parietal, supraoccipital, and exoccipital/opisthotic removed and the paths of the cranial nerves highlighted. Anterior is into the page. Abbreviations: i - infundibulum; mp - median process.
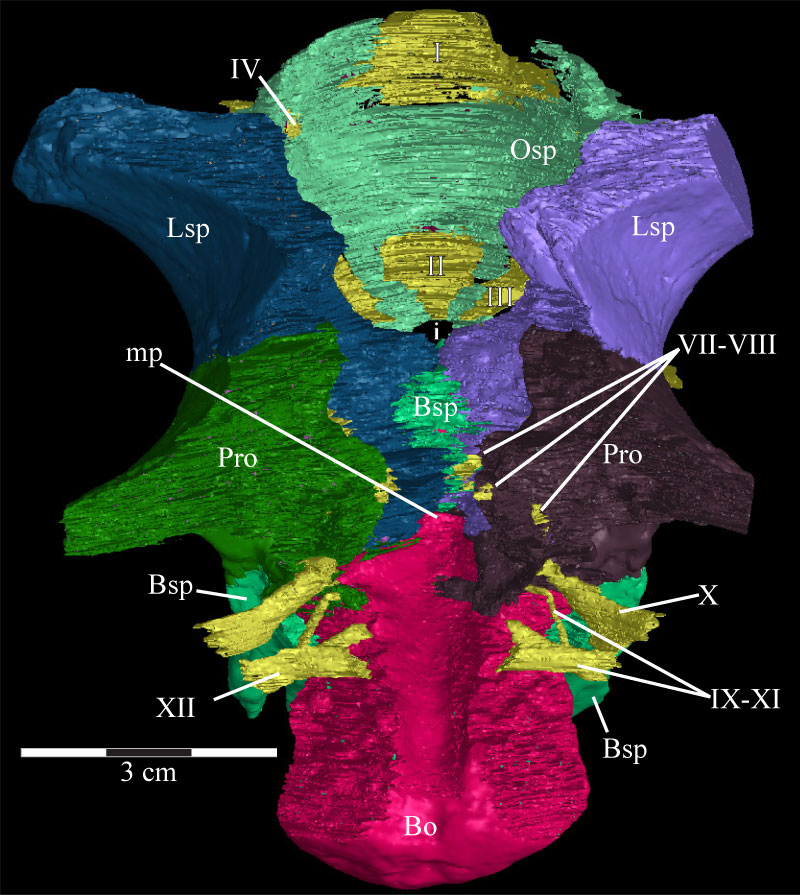
FIGURE 43. Photograph of the parasphenoid and basisphenoid complex and the anterior braincase of OMNH 58340. The parasphenoid extends forward (right) from the body of the basisphenoid and, at this angle, disappears behind the displaced right posterior process of the vomer. The trench running along the dorsal surface of the parasphenoid is visible (indicated by arrows). The ventral outline of the preotic pendant is indicated by the dashed line. Anterior is to the right and out of the page. Abbreviations: ct - possible crista trabecularis; pp - preotic pendant.
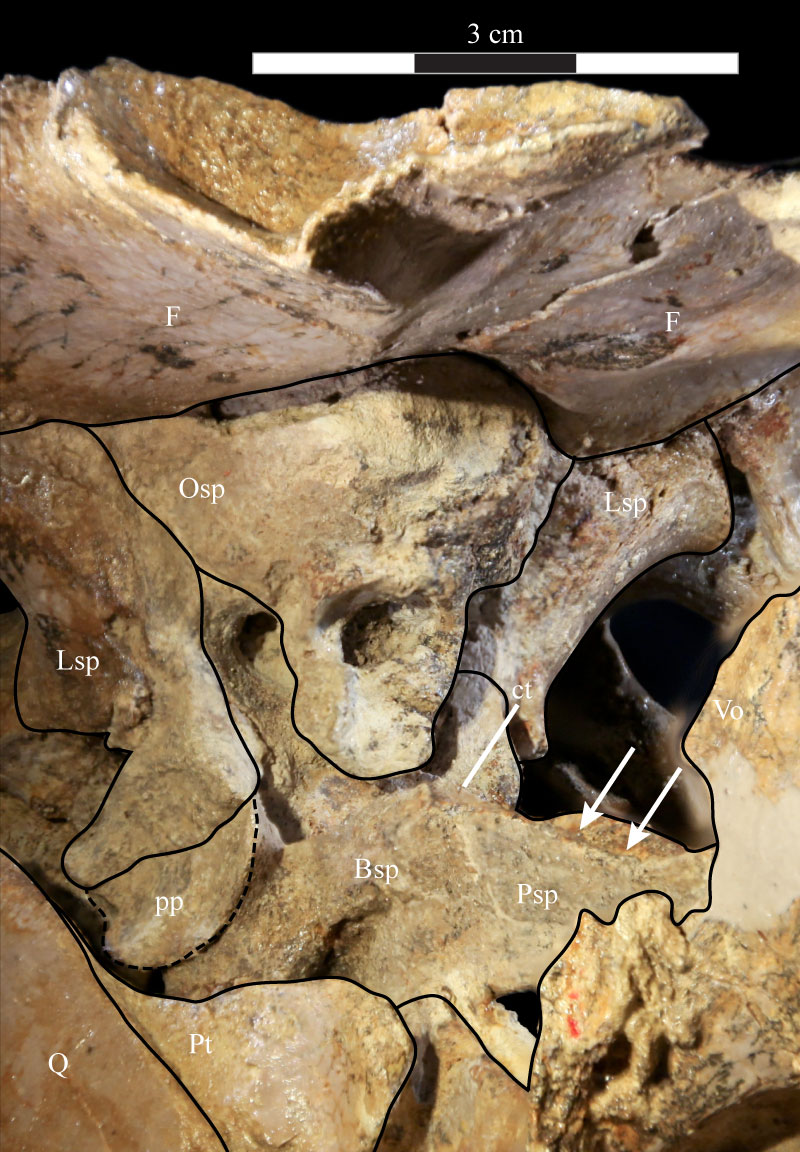
FIGURE 44. Right lateral (44.1), anteroventral (44.2), anterior (44.3), and posterior (44.4) views of the virtual endocast of OMNH 58340. 44.1 shows various landmarks for the passage of venous sinuses and cranial nerves. 44.2 highlights the waists between the cerebrum and cerebellum anterodorsally and the cerebellum and medulla posteroventrally. 44.3 shows the faint lobes present on the dorsal surface of the endocast, separated by a small trough (indicated by arrow). 44.4 shows the dorsal sagittal sinus in the middle and the flocculi of the endocast, as well as the dorsal bulbous expansions. Abbreviations: ad - anterodorsal ridge; av - anteroventral ridge; be - bulbous expansions; die - diencephalon; ds - dorsal sagittal sinus; dvs - dorsal venous sinus; f - flocculus; i - beginning of infundibular stalk; mes - mesencephalon; met - metencephalon; my - myelencephalon; pi - pineal process; pro - prosencephalon; rho - rhombencephalon; rV - ridge running to trigeminal nerve (CN V); rVI - ridge running to abducens nerves (CN VI) tel - telencephalon.
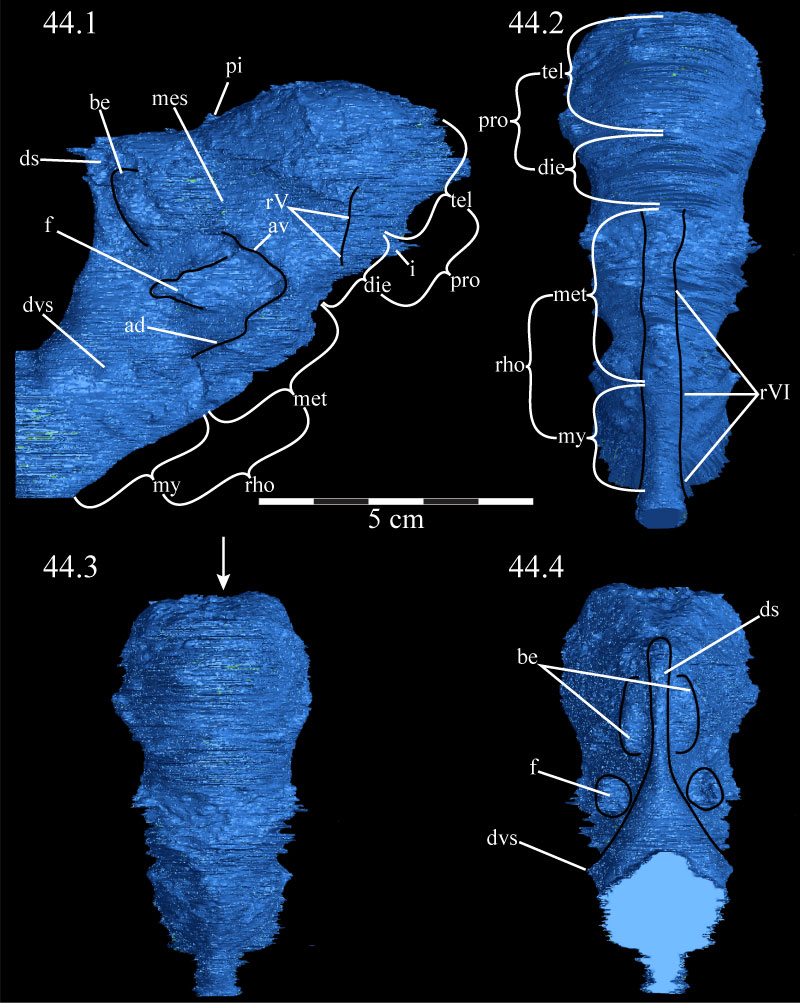
FIGURE 45. Dorsal (45.1), right lateral (45.2), anterior (45.3), and posterior (45.4) views of the virtual endosseous labyrinths of OMNH 58340. The canals are oriented in 45.1 such that anterior is above and posterior below. Ventral is down in all other images. Abbreviations: aa - anterior ampulla; asc - anterior semicircular canal; au - anterior utricle; ca - cavum capsularis; cc - common crus; fo - fenestra ovalis; lr - lagenar recess; lsc - lateral semicircular canal; pa - posterior ampulla; psc - posterior semicircular canal; pu - posterior utricle; v - vestibule.
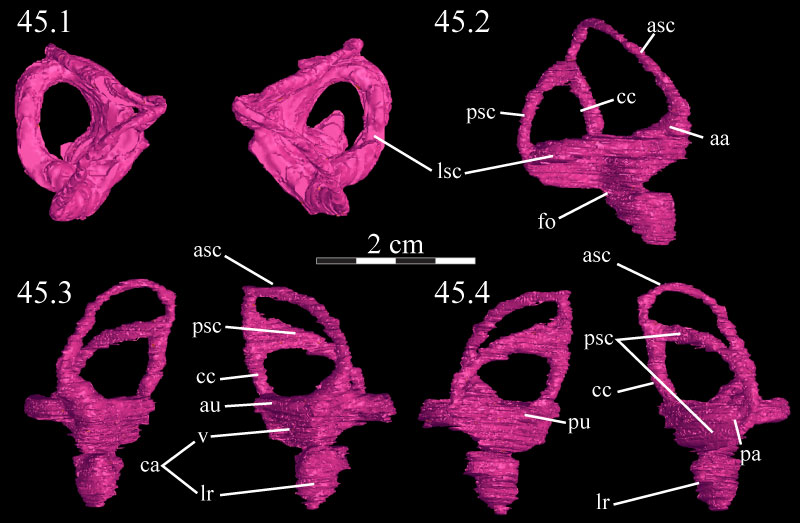
FIGURE 46. Lateral schematic of the left (above) and photographs of the left (middle) and right (below) mandibles of OMNH 58340. Note the amount of dorsoventral compression of the right mandible when compared with the left. Anterior is to the left in the first two images and to the right in the third. Abbreviation: sf - surangular foramen.
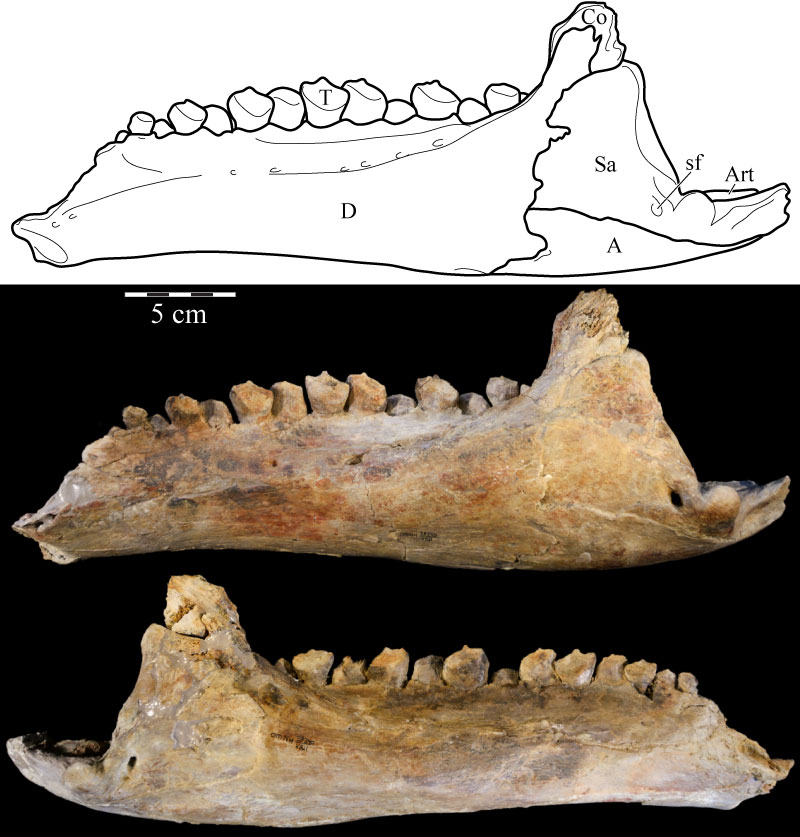
FIGURE 47. Medial schematic of the left (above) and photographs of the left (middle) and right (below) mandibles of OMNH 58340. Note the amount of dorsoventral compression of the right mandible when compared with the left. Anterior is to the right in the first two images and to the left in the third. Abbreviations: ap - alveolar parapet; imc - internal mandibular foramen; mc - Meckelian canal.
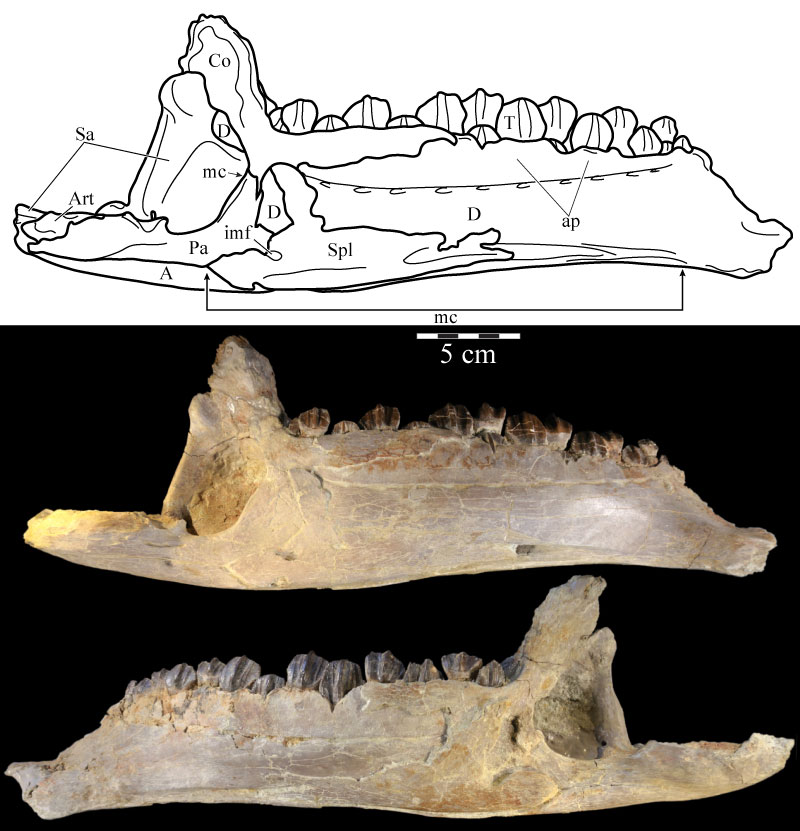
FIGURE 48. Photographs of the predentary of OMNH 58340 in dorsal (48.1), anterior (48.2), lateral (48.3), posterior (48.4), and ventral (48.5) views. Abbreviations: dp - dentary process; mt - median tab; pd - primary denticle; vp - ventral process; vs - ventral sulcus.
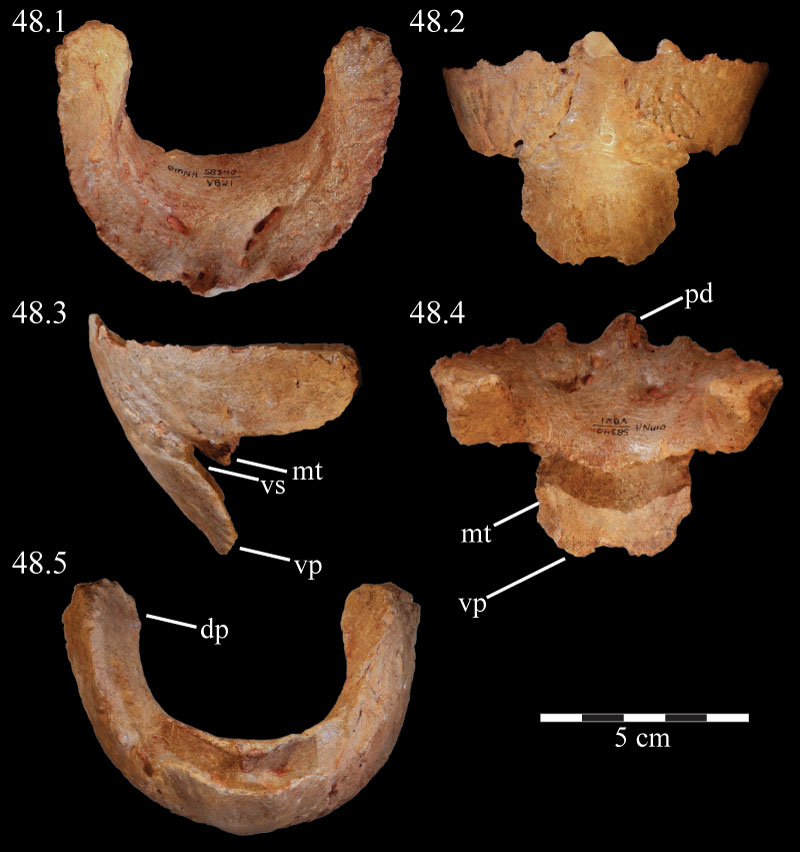
FIGURE 49. Dorsal (49.1), lateral (49.2), and medial (49.3) views of the virtual left dentary of OMNH 58340, disarticulated. Anterior is to the left in the first two images and to the right in the third. Abbreviations: at - alveolar trench; au - alveolar undulations; ca - area for articulation with coronoid; Mc - Meckelian canal; pf - predentary foramina; sa - area for articulation with surangular.
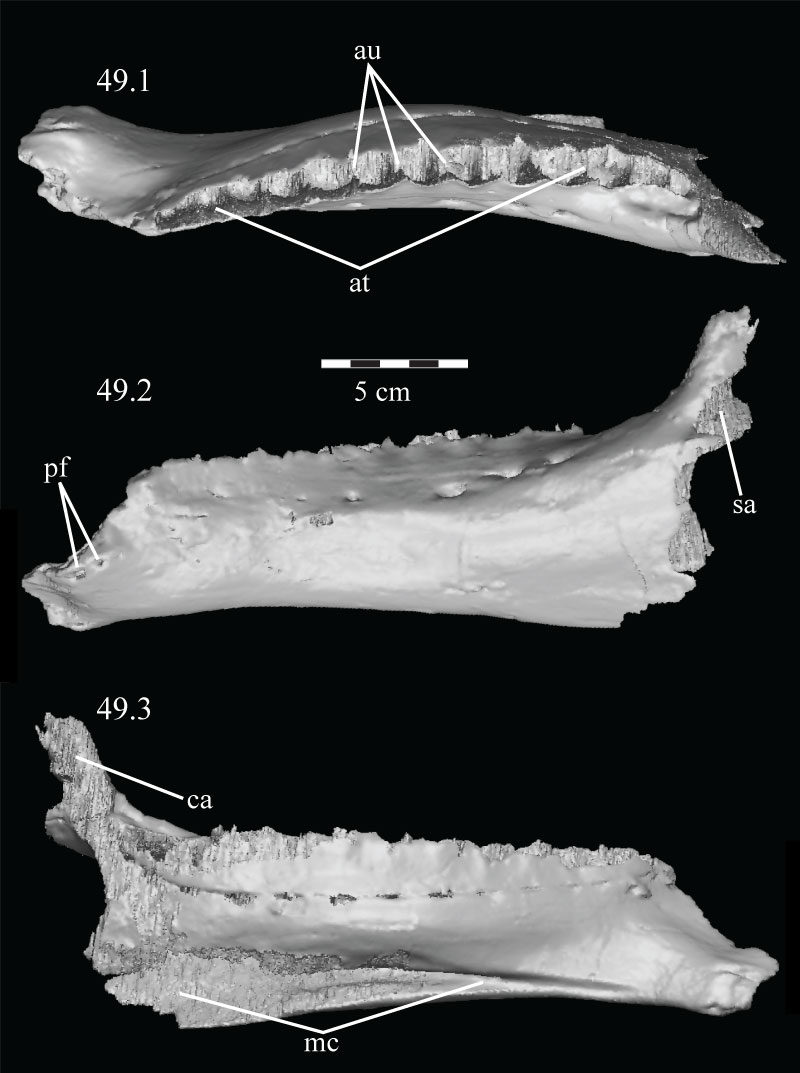
FIGURE 50. Lateral (50.1) and medial (50.2) views of the disarticulated virtual left coronoid of OMNH 58340. The parallel texturing covering most of 50.1 is an artifact of the sectioning process used to isolate the element and represents the articular surface for the surangular and dentary. Anterior is left in 50.1 and right in 50.2. Abbreviations: ap - anterior process; cp - coronoid process; da - articular surface for dentary; sa - articular surface for surangular; vt - ventral tab.
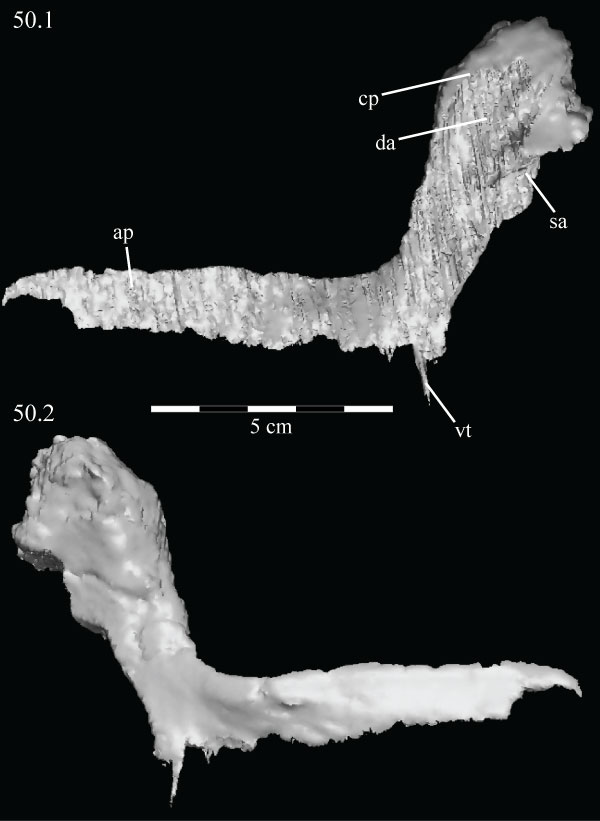
FIGURE 51. Medial view of the virtual left mandible of OMNH 58340 with the splenial and prearticular removed to show the extent of the Meckelian canal as it traverses the mandible. Anterior is right. Abbreviation: mc - Meckelian canal.
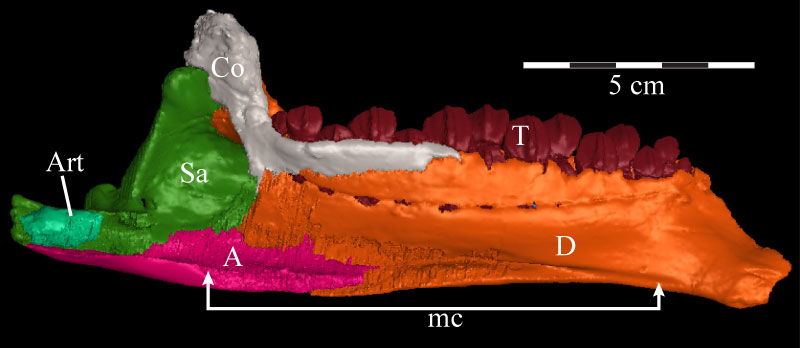
FIGURE 52. Lingual (above) and labial (below) views of the complete virtual tooth set of the left dentary of OMNH 58340, demonstrating the method of replacement, with groups of teeth beginning to be replaced in alternating succession from posterior to anterior. Individual Zahnreihen are indicated by dots of the same color placed at the occlusal tips of the teeth. Anterior is to the left in the upper image and to the right in the lower image.
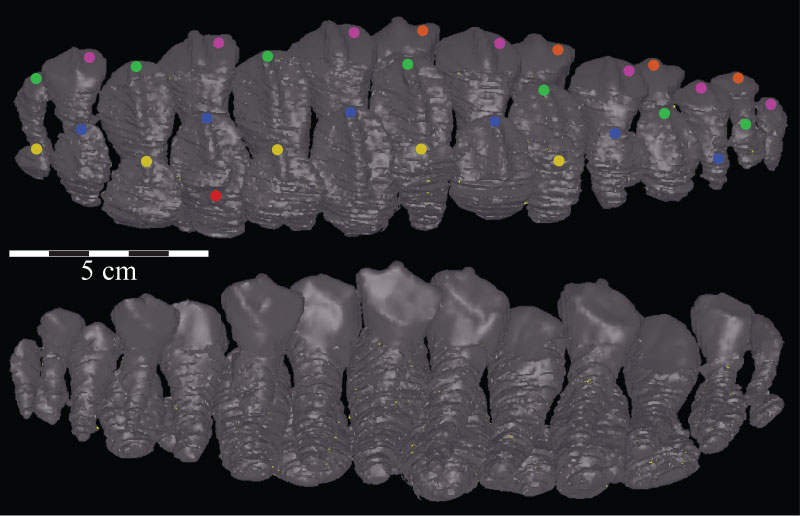
FIGURE 53. Lateral view of the virtual left splenial of OMNH 58340, disarticulated. Anterior is left. Abbreviations: ar - axial ridge; dp - dorsal process; imf - internal mandibular foramen; pr - posterior ridge.
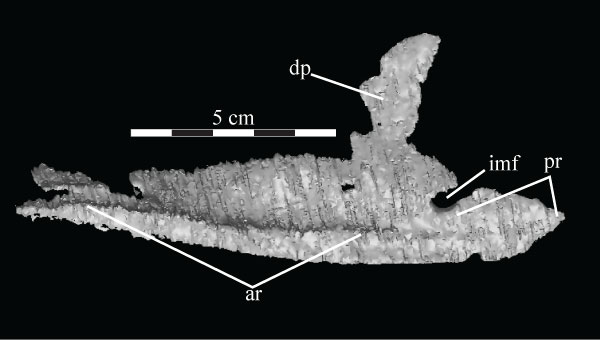
FIGURE 54. Lateral (54.1) and medial (54.2) views of the virtual left angular of OMNH 58340. Anterior is left in the upper image and right in the lower image. Abbreviations: da - articular surface for the dentary; mr - medial ridge; vr - ventral ridge.
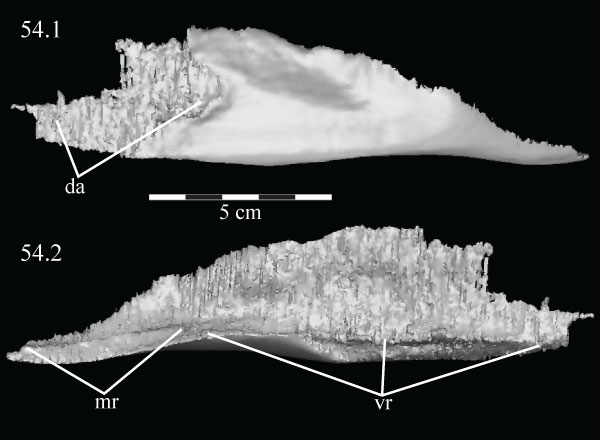
FIGURE 55. Medial view with the dorsal tip rotated lingually (55.1) of the virtual left angular (blue) and surangular (pink) and medial view (55.2) of the disarticulated virtual left surangular of OMNH 58340. Anterior is to the right. Abbreviations: aa - anterior angle; aw - anterior wing; da - dorsal angle; sf - surangular foramen; rp - retroarticular process; va - ventral angle.
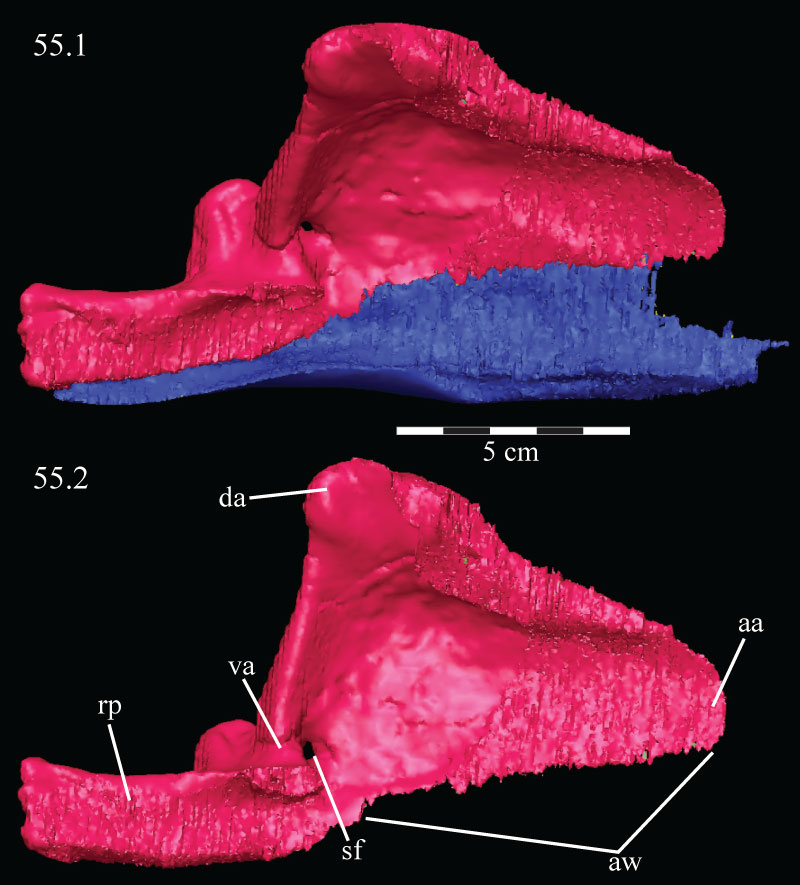
FIGURE 56. Photograph of the articular surface of the left mandible of OMNH 58340, detailing the facets present on the dorsal surfaces of the surangular and prearticular. The dashed lines circumscribe the articular fossae of the prearticular. Anterior is up. Abbreviations: lf - lateral articular fossa; m - matrix; mf - medial articular fossa.
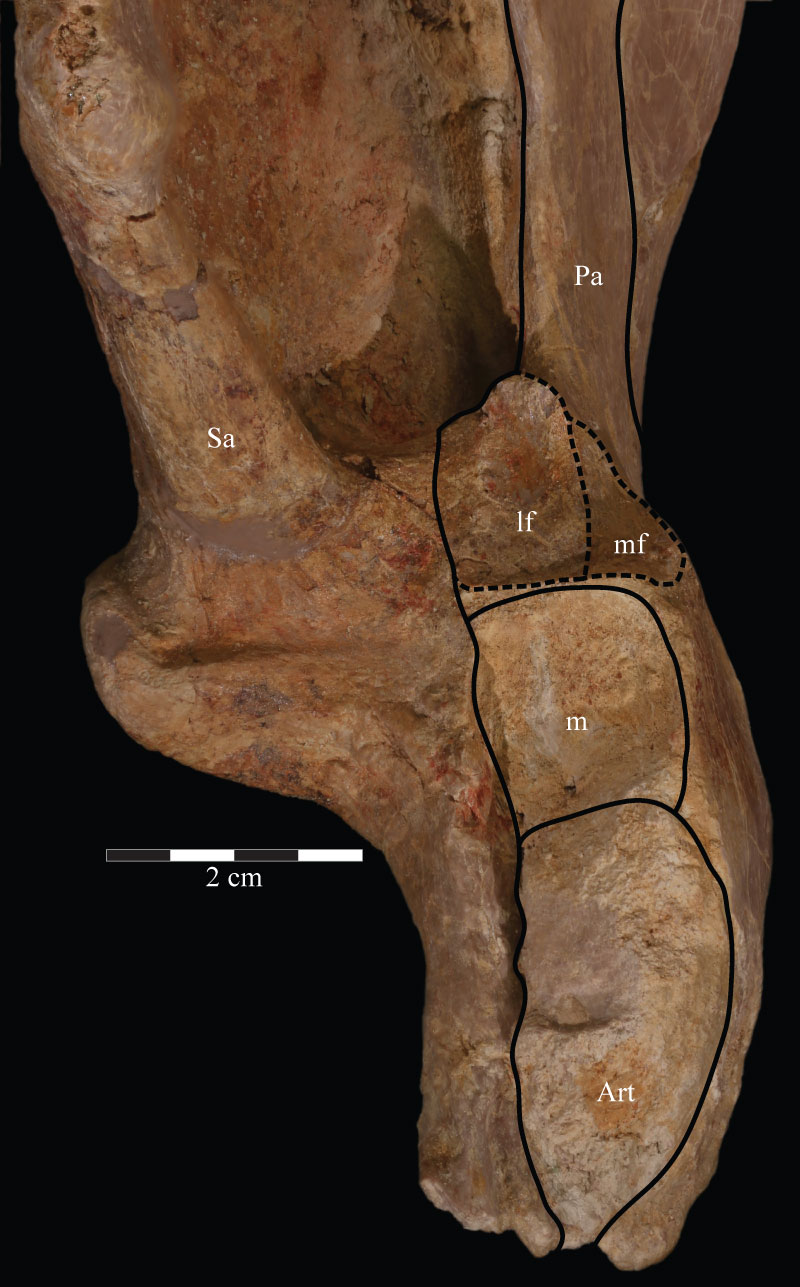
FIGURE 57. Dorsal schematic of the left (above) and photographs of the left (middle) and right (below) mandibles of OMNH 58340. Anterior is to the right. Abbreviation: df - dental foramina.
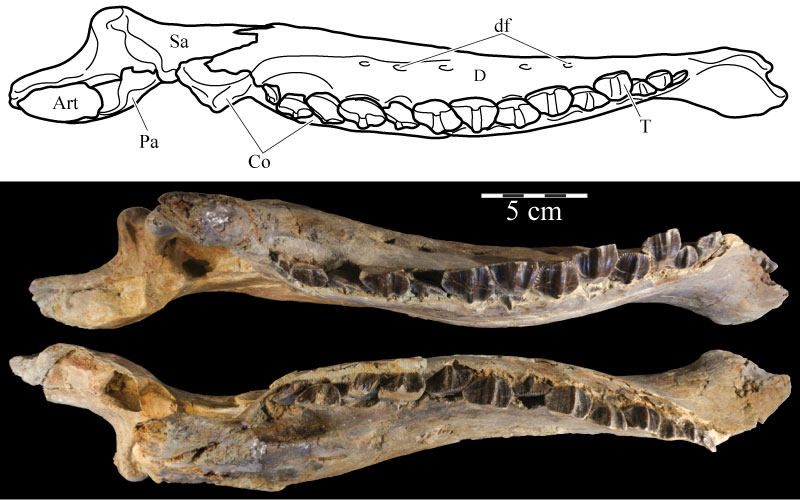
FIGURE 58. Posterodorsal view (58.1) of the virtual left surangular (pink) and prearticular (green) and medial view (58.2) of the virtual left prearticular of OMNH 58340. The left image shows the nature of the articulation of the two elements at the point of articulation of the mandible with the quadrate (indicated by arrow). Anterior is into the page in 58.1 and to the right in 58.2. Abbreviations: ap - anterior process; rp - retroarticular process; sa - area of articulation with the splenial.
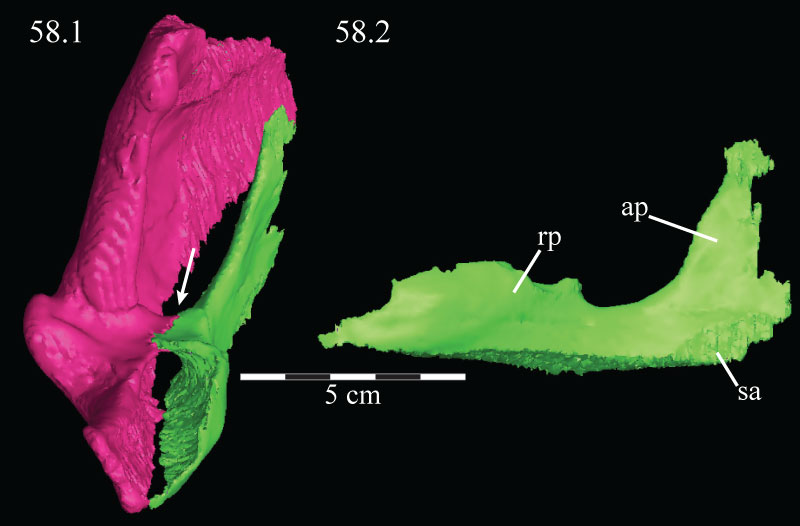
FIGURE 59. Ventral schematic (above) and photographs of the right (middle) and left (below) mandibles of OMNH 58340. Anterior is to the left.
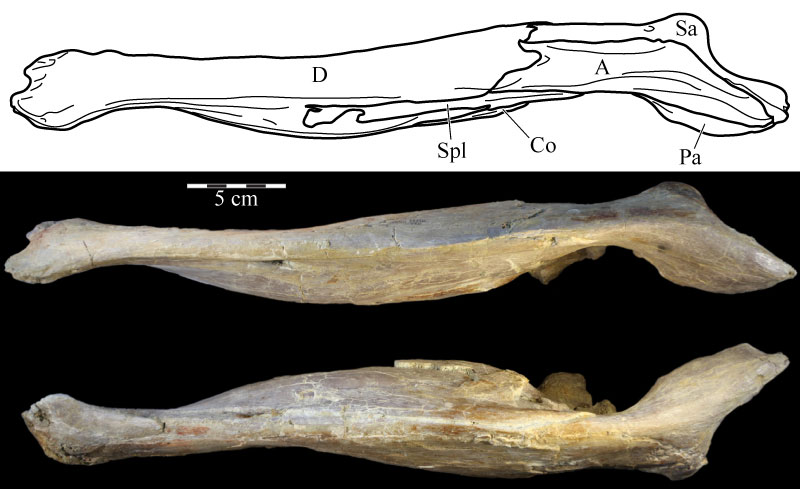
FIGURE 60. Coronal CT images of the maxillary (above) and dentary (below) teeth, taken midway along the length of the respective elements, of OMNH 58340 showing the method of lingual replacement and the concurrent resorption of the tooth being replaced. Dorsal is up and anterior is into the page. Abbreviations: ca - carina; ci - cingulum; e - enamel.
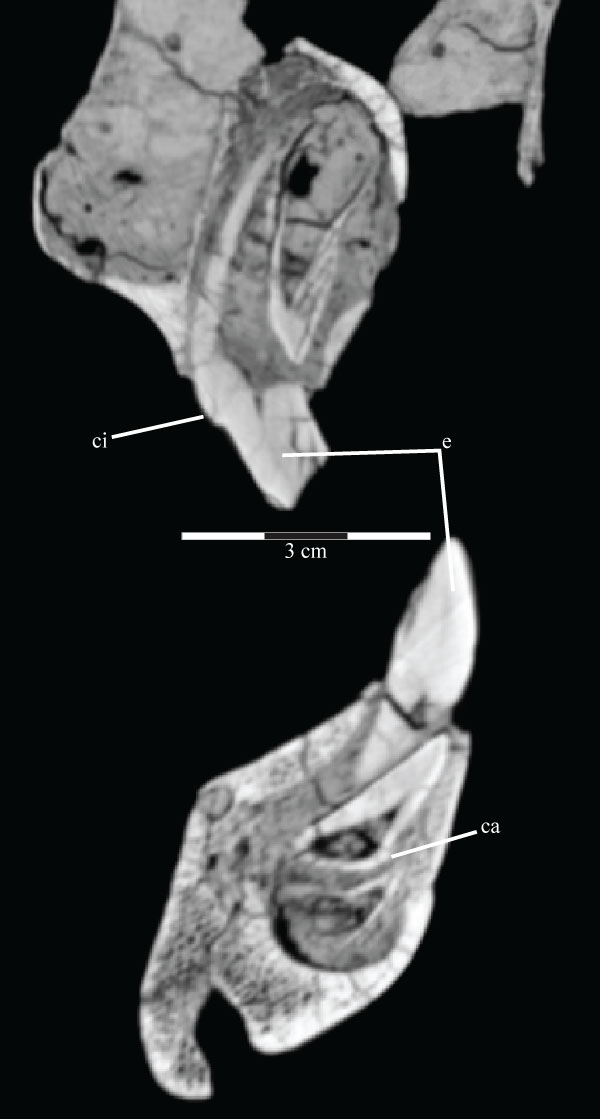
FIGURE 61. Photograph of the left (above, in lingual view) and right (below, in buccal view) hyoids of OMNH 58340. Anterior is to the left in the upper image and to the right in the lower image.
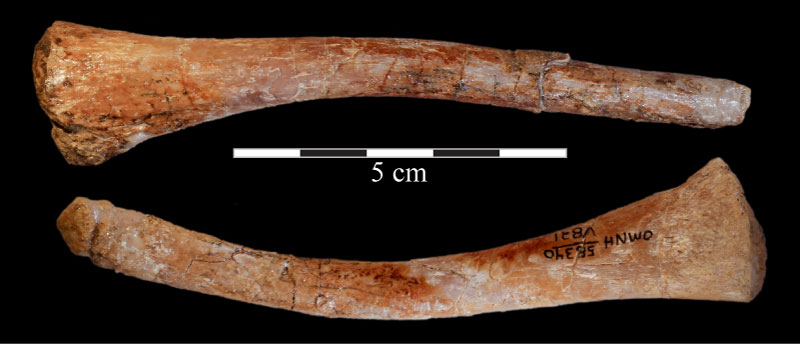
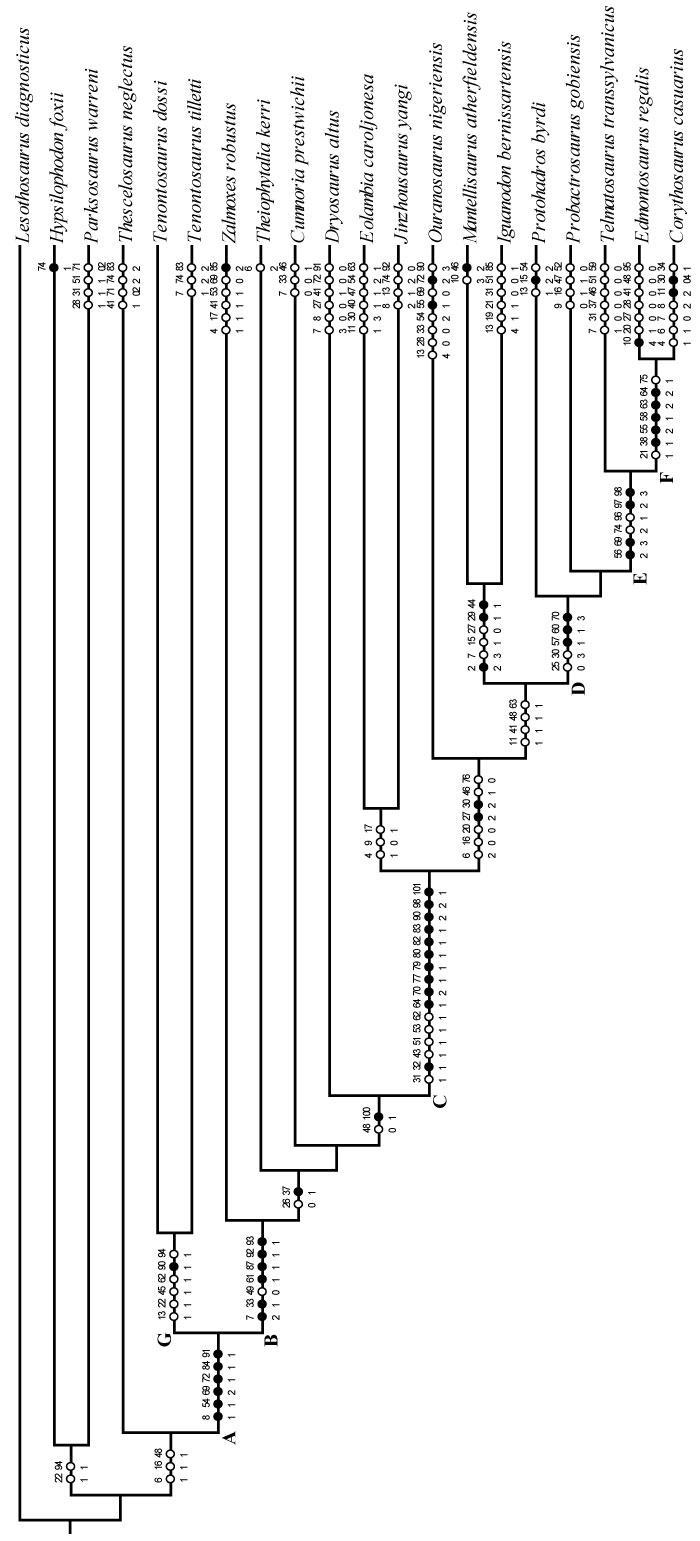
FIGURE 62. Optimized character distribution showing unambiguous character state changes on one of 12 most parsimonious trees (MPTs) recovered in this analysis. Character number and state present are indicated by the number above and below each line, respectively. Synapomorphic character states are indicated by black circles, while white circles denote homoplastic character states. Certain nodes are noted with letters referenced in the text. Optimization was performed in PAUP* version 4.0b10 (Swofford, 2002) and checked in TNT (Goloboff et al., 2008).