FIGURE 1. Geographical and stratigraphical occurrence of Chelus sp. MUN-STRIdbid 38473. 1, map of the northernmost portion of South America, showing the location of Castilletes, on the Guajira Peninsula of Colombia. 2, stratigraphic column for the lower segment of the Castilletes Formation, Kaitamana section, including the horizon where Chelus sp. MUN-STRI-dbid 38473 was found, redrawn from Moreno et al. (2015). 3, landscape photograph of the locality where Chelus sp. MUN-STRI-dbid 38473 was found. 4, complete skeleton of Chelus fimbriata NMW 1859, orange shadowed area in the skull, represents the area preserved in the fossil Chelus sp. MUN-STRI-dbid 38473, down is the anterior view of the head of Ch. fimbriata (photo credit, Stuart Hamilton).
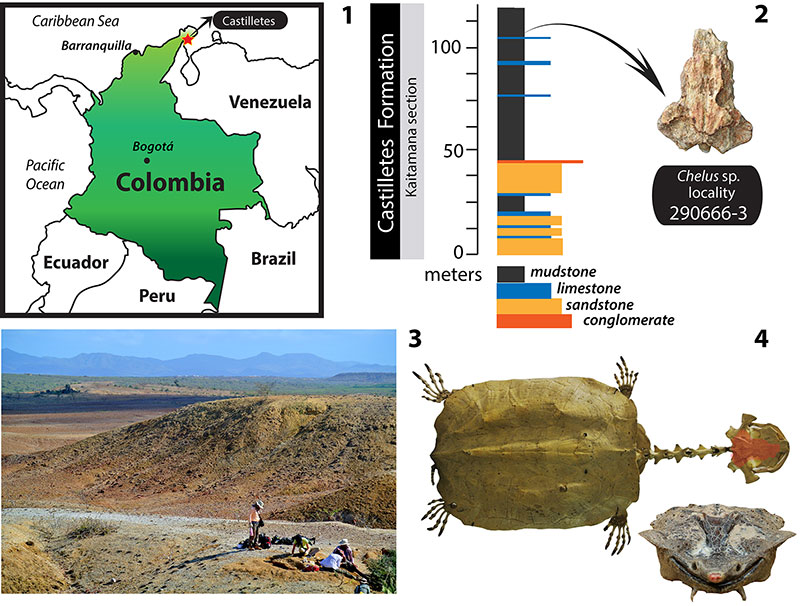
FIGURE 2. Skulls of Chelus fimbriata SM 37178 and Chelus sp. UNT-STRI-dbid 38473. Photographs and interpretative drawings. Chelus fimbriata SM 37178. 1-2, dorsal view; 3-4, ventral view; 5-6, posterior view. Chelus sp. MUN-STRI-dbid 38473 fossil from Castilletes Formation, Colombia. 7-8, dorsal view; 9-10, ventral view; 11-12, right lateral view; 13-14, posterior view. Abbreviations: bo, basioccipital; bs, basisphenoid; ex, exoccipital; fjp, foramen jugulare posterius; fm, foramen magnum; fn, foramen nervi hypoglossi, fp, fenestra postotica; fpcci, foramen posterior canalis caroticus cerebralis; fpp, foramen palatinum posterior; fr, frontal; fst, foramen stapedio temporalis; fts, fossa temporalis superior; ju, jugal; mx, maxilla; op, opisthotic; pa, parietal; pf, prefrontal; pl, palatine; pm, premaxilla; po, postorbital; pr, prootic; pt, pterygoid; qu, quadrate; so, supraoccipital; sq, squamosal; vo, vomer. Dotted line in 2 indicates sulci of skull scutes. Light grey areas in 8 indicate preservation of the dorsalmost surface of the bones. Scale bar applies for all figures.
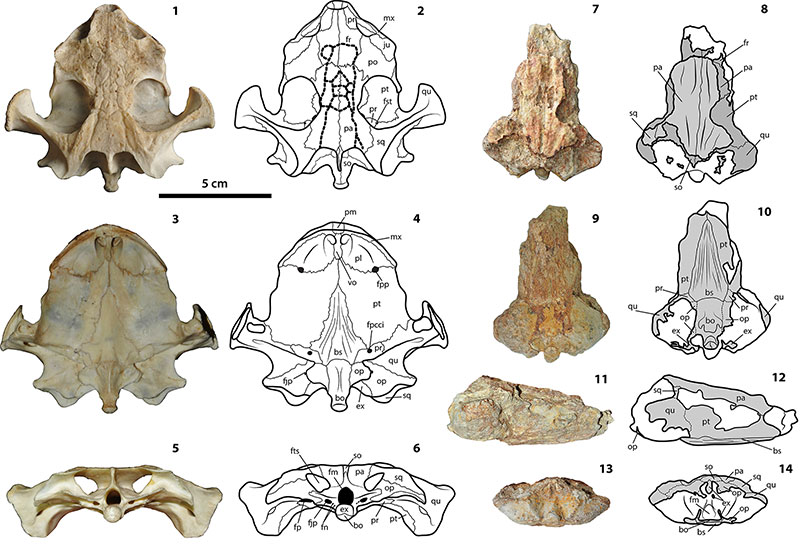
FIGURE 3. CT images of Chelus sp. MUN-STRI-dbid 38473. 1, skull in dorsal view, arrows indicate the position of the cuts shown in 4-7. 2, horizontal cut on the lower portion of the skull, anterior to the foramen magnum. 3, horizontal cut at the level of the widest portion of the skull. 4, sagittal cut on the left portion of the skull. 5, sagittal cut at the midline of the skull. 6, coronal cut very close to the level of the basisphenoid-basioccipital contact. 7, coronal cut on the anterior portion of the skull. Abbreviations are as in Figure 2, plus apb (anterior process of basisphenoid).
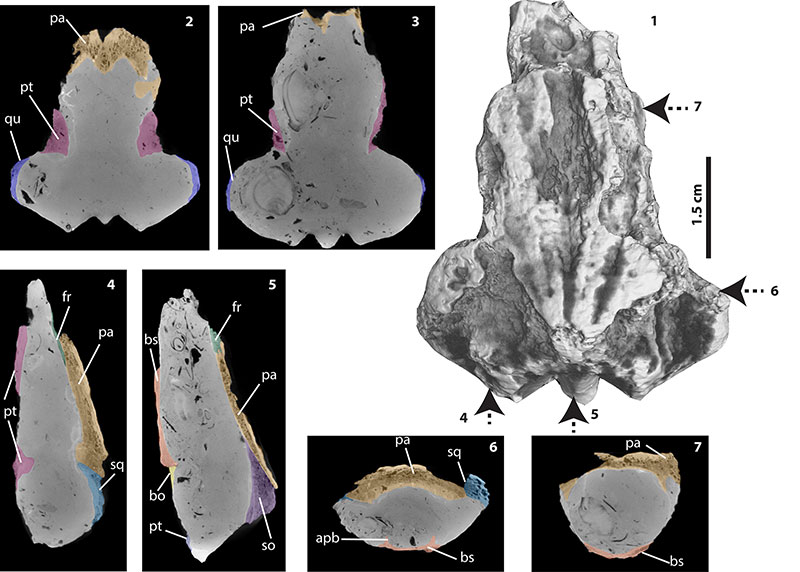
FIGURE 4. CT images of Chelus sp. and the extant C. fimbriata in sagittal view. These figures show the difference in the height of the endocranium between the fossil skull described here and juveniles and adults of the extant representative of Chelus ; all cuts are located at the midline of the skull. 1, Chelus sp. MUN-STRI-dbid 38473 (adult); 2, C. fimbriata SM 37178 (adult); 3, C. fimbriata UMA R-1376 (hatchling-juvenile?); 4, C. fimbriata SM 57977 (juvenile). The basisphenoid bone is delimited by light blue color.
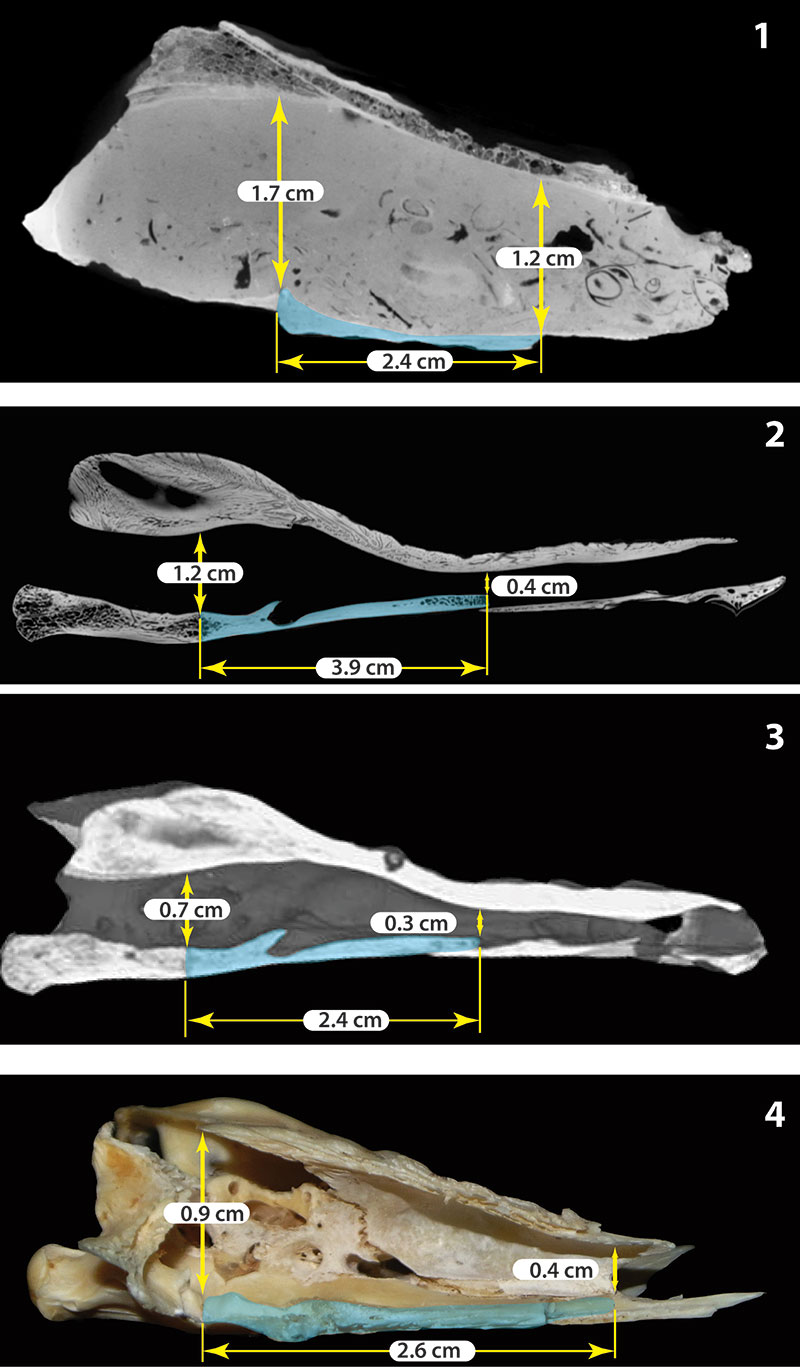
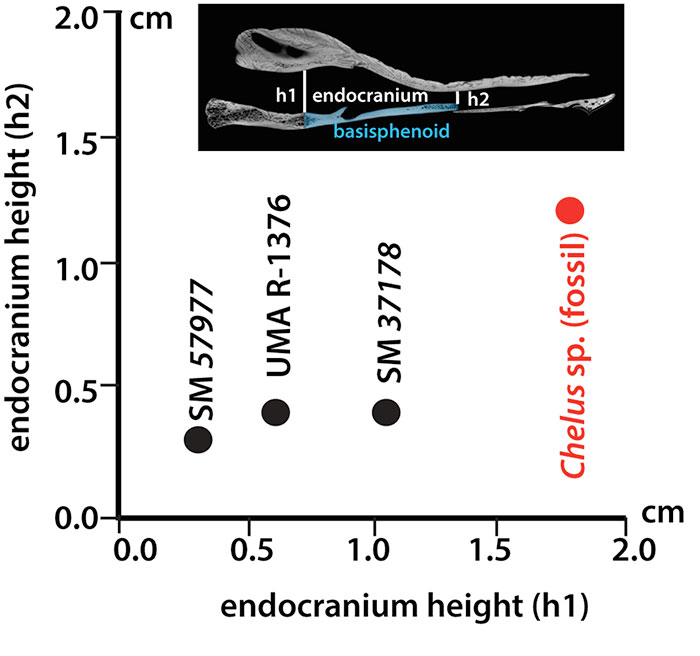
FIGURE 5. Comparison between height of the endocranium at the anterior (h1) and posterior (h2) end of the basisphenoid for three extant Chelus fimbriata specimens (black dots) vs the fossil Chelus sp. described here (red dot).