FIGURE 1. An example of damage caused by air-abrasion on a piece of dinosaur rib bone (unregistered float). The untreated bone surface is in the left-hand half of the image, while the right-hand half has been abraded for 5 seconds with 53µm aluminium oxide powder, delivered via a 1 mm diameter nozzle from 1 cm distance. The abraded half shows significant pitting and complete loss of the bone surface. (304 x magnification SEM image at 20Pa variable pressure and 12 mm working distance)
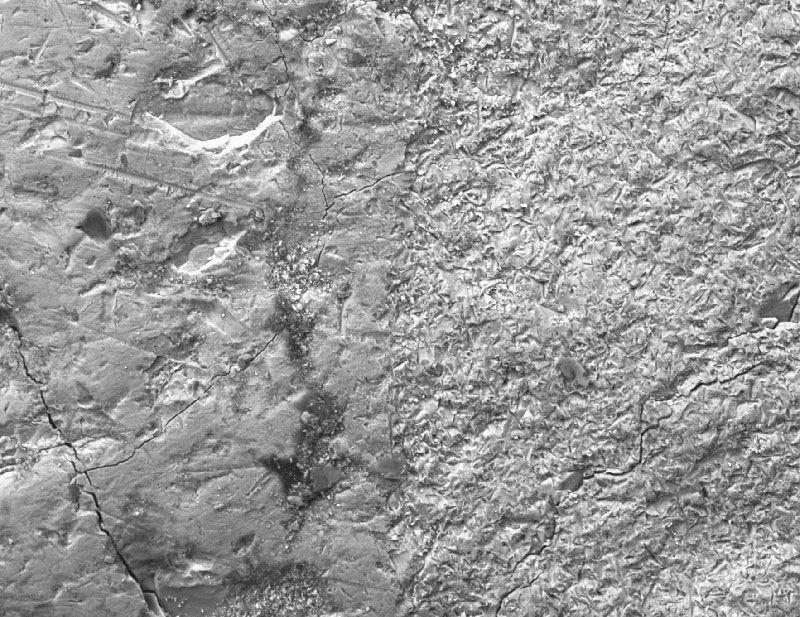

FIGURE 2. Powder type and size used by the respondents of the survey. Respondents also reported use of: Iron 150-200 μm, garnet, rice flour 100-200 μm, potato flour 20-200 μm, pumice 50 μm, Armex composite formula, Tantalum beads and calcium carbonate 150-200 μm.
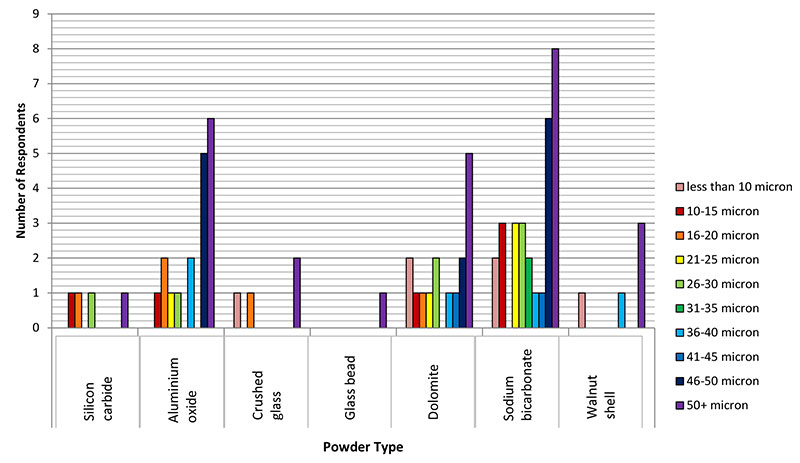
FIGURE 3. Health and safety precaution responses from the survey.
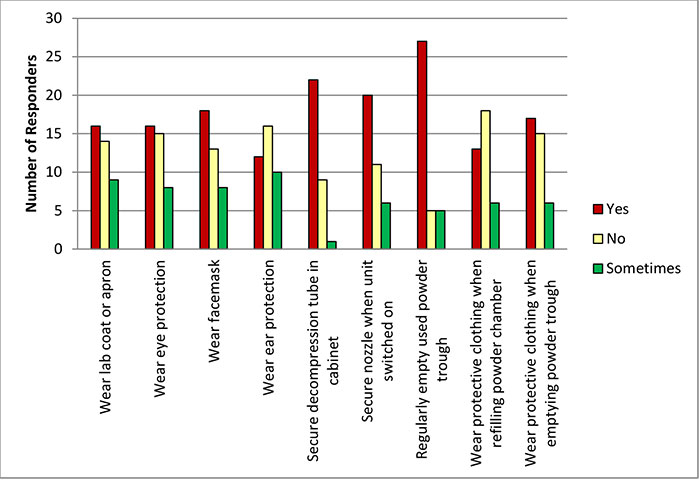
FIGURE 4. Twinned SEM images of glass bead powder. Left (4.1): before use. Right (4.2): after single use.
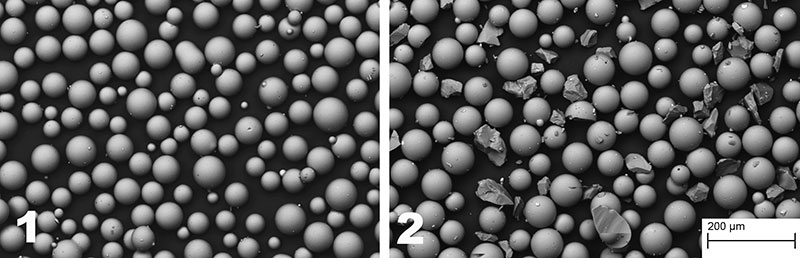
FIGURE 5. Twinned SEM images of sodium bicarbonate powder. Left (5.1): before use. Right (5.2): after single use.
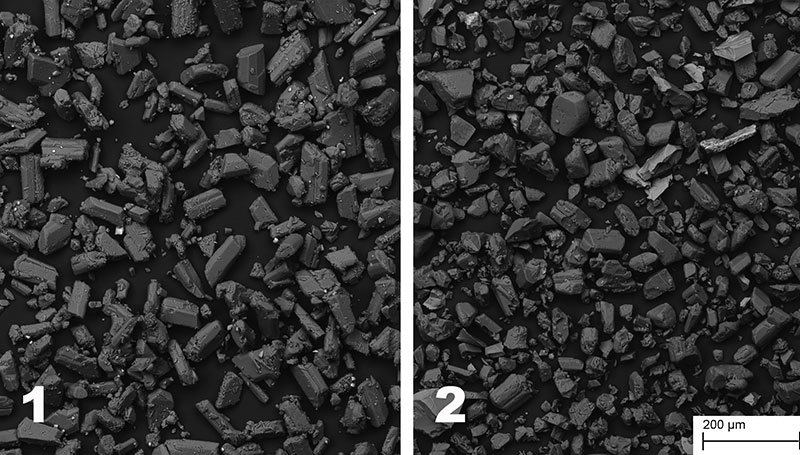

FIGURE 6. Four polished limestone samples, painted with Paraloid B72 and copper powder, each showing an abraded central area with a polished copper halo surrounding it, which would not normally be visible with the naked eye.
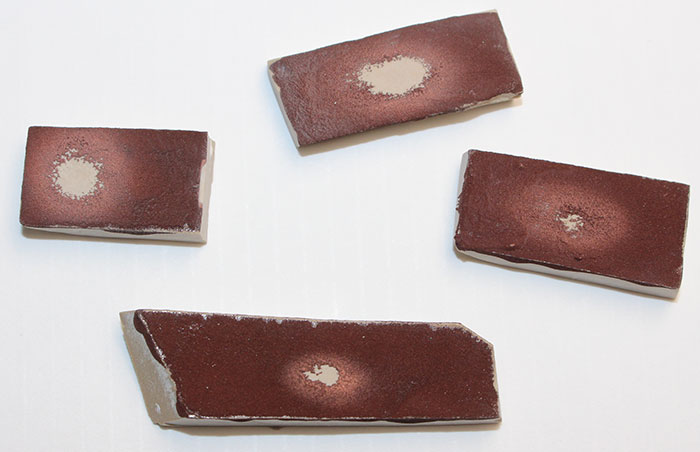

FIGURE 7. Comparison between powder types at 50 μm particle size, 30o angle and 30 mm working distance between nozzle and substrate.
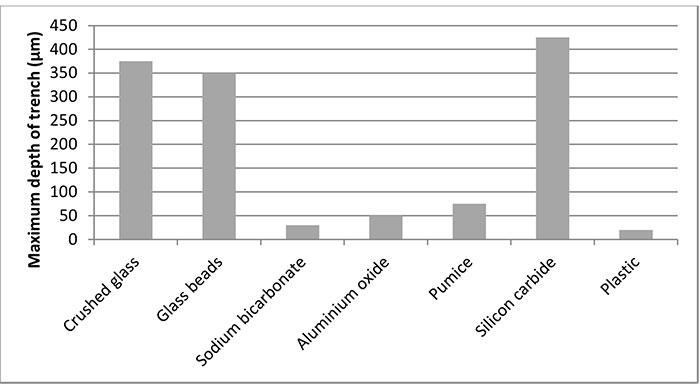
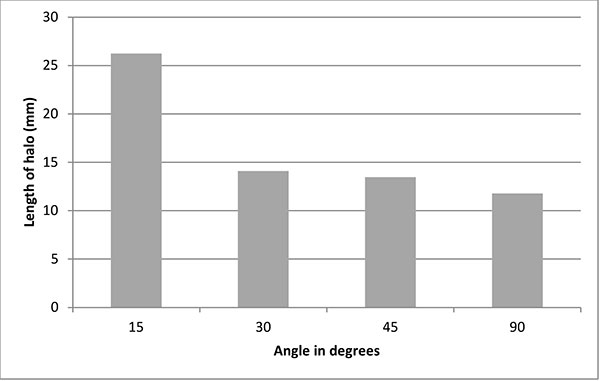
FIGURE 8. Comparison between nozzle angles in relation to the substrate using 50 μm Aluminium oxide powder.
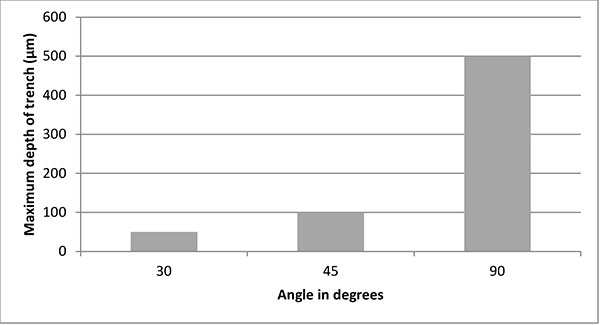
FIGURE 9. Comparison between nozzle angles in relation to the substrate using 50 μm crushed glass.
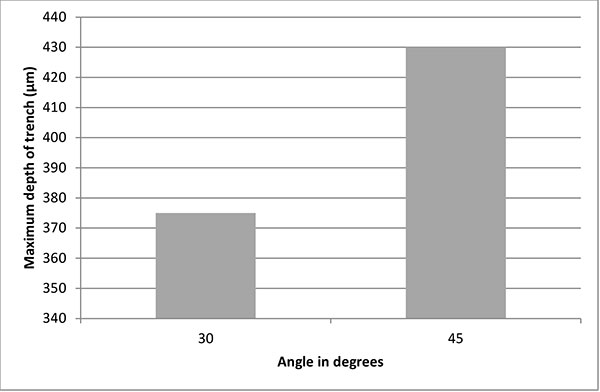
FIGURE 10. Comparison between working distances between the nozzle and the substrate using 50 μm aluminium oxide powder.
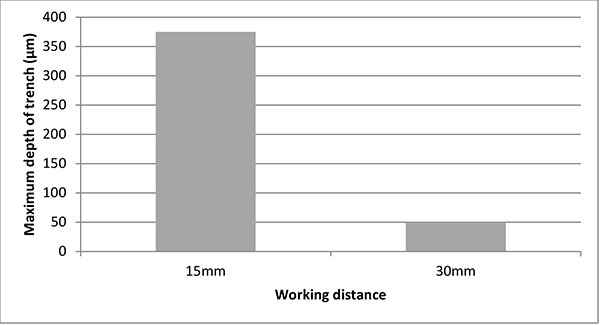
FIGURE 11. Comparison between powder size using aluminium oxide 30o angle and 30 mm working distance between nozzle and substrate.
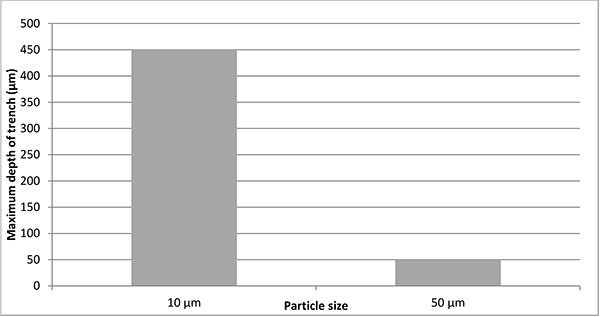
FIGURE 12. Comparison between trench scatter halo lengths of the various powders trialled with 30o angle and 30 mm working distance between nozzle and substrate.
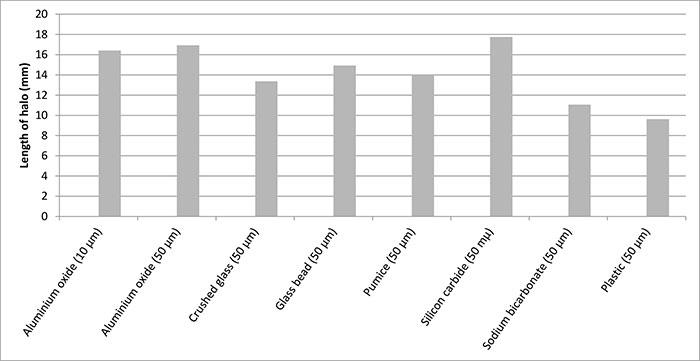
FIGURE 13. Comparison between trench scatter halos with varying angles using 50 μm aluminium oxide powder.