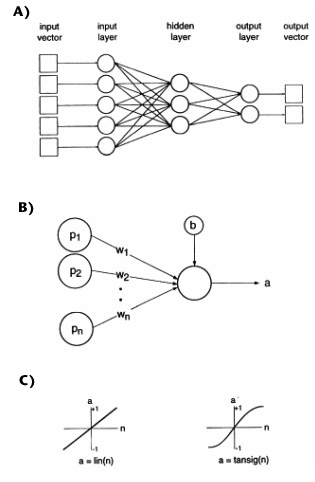
Figure 1. (A) Diagram showing the general architecture of a backpropagation (BP) network. Each neuron in the hidden and output layers receives weighted signals from the neurons in the previous layer. (B) Diagram showing the elements of a single neuron in a BP network. In forward propagation, the incoming signals from the neurons of the previous layer (p) are multiplied by the weights of the connections (w) and summed. The bias (b) is then added, and the resulting sum is filtered through the transfer function (C), linear or sigmoidal, to produce the activity of the neuron.