|
|
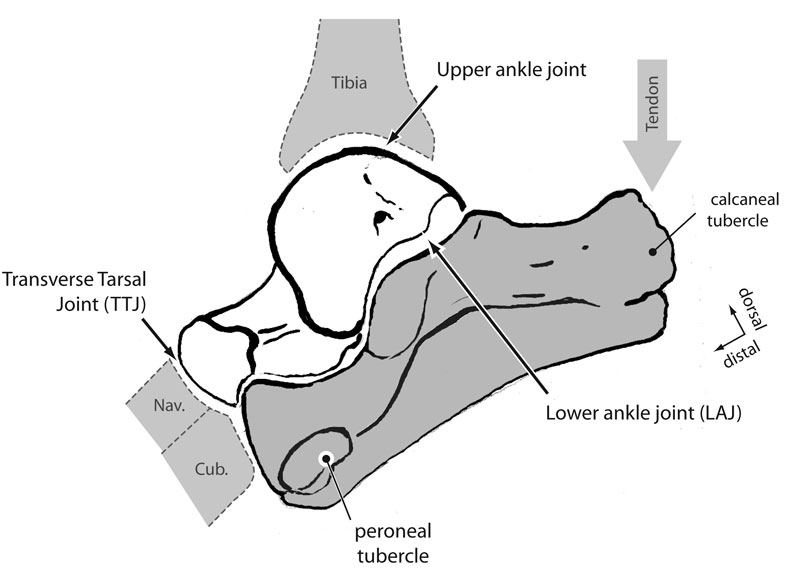
Figure 1. Anatomy and function of the mammalian calcaneum. The calcaneum is shown in life position in lateral view (grey) along with the astragalus (white). The relation of these two bones to the distal tibia, navicular (nav.), and cuboid (cub.) bones are also indicated. The main upper ankle joint is between the tibia and astragalus, but there is also a joint between the astragalus and calcaneum (lower ankle joint) and between those two bones and the navicular and cuboid, respectively (transverse tarsal joint). Extension of the foot is powered by contraction of the Achilles tendon (arrow) pulling dorsally on the calcaneal tubercle.
|