|
|
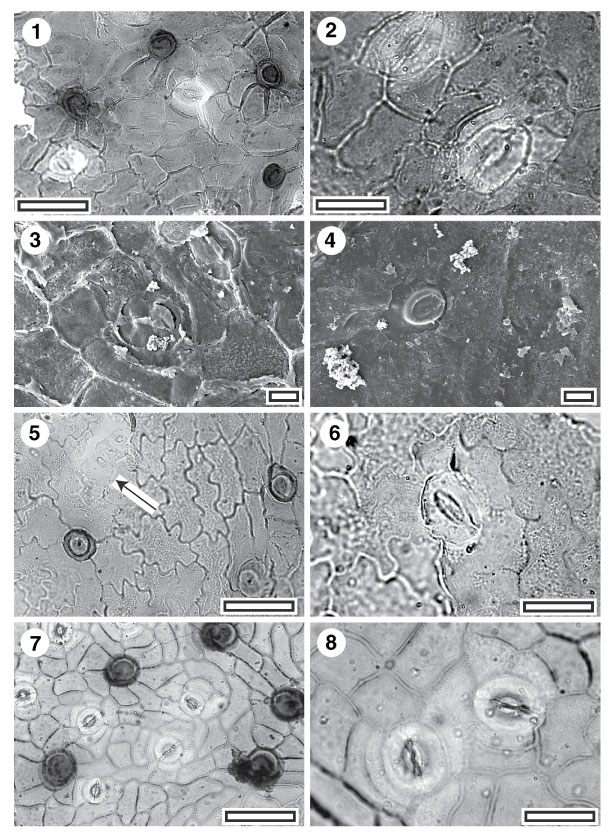
Figure 15. 1-8. Fossil and extant Menispermaceae. 1. CUT-Z-FCA, TLM view showing stomatal complexes (with cuticle over guard cell and subsidiary cells thinner than over normal epidermal cells) and very densely staining trichome attachment scars (SL2877, scale-bar = 50 Ám); 2. CUT-Z-FCA, TLM view showing two stomatal complexes. Note the ovate outline and each has a distinct lateral subsidiary cell on the left hand side (SL2877, scale-bar = 20 Ám); 3. CUT-Z-FCA, SEM view of inner cuticular surface showing two stomatal complexes (S-1384, scale-bar = 10 Ám); 4. CUT-Z-FCA, SEM view of outer cuticular surface showing a single stomatal complex (S-1384, scale-bar = 10 Ám); 5. CUT-Z-FEC, TLM view showing stomatal complexes (the lower of a pair is arrowed) and densely staining trichome attachment scars. Note the cuticle over guard cell and subsidiary cells is thinner than over normal epidermal cells (SB1321, scale-bar = 50 Ám); 6. CUT-Z-FEC, TLM detail of single stomatal complex, note ovate outline (SB1321, scale-bar = 20 Ám); 7. Extant Pleiogyne australis, TLM view showing stomatal complexes (with cuticle over guard cell and subsidiary cells thinner than over normal epidermal cells) and densely staining trichome attachment scars (AQ568296, scale-bar = 50 Ám); 8. Extant P. australis, TLM view showing two stomatal complexes. Note the distinct lateral subsidiary cell on the left of the left hand complex, and lower side of the right hand complex (AQ568296, scale-bar = 20 Ám).
|