FIGURE 1. Surface models of the outer enamel surface and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) of adapine upper molars in the study sample. Note the consistent presence of a dentine horn at the distolingual margin of the tooth crown in (1.4) and (1.6). The crest running from the protocone does not connect with the hypocone. Note also the metameric variation within individual specimens. An asterisk (*) marks the hypocone at either the enamel or EDJ surface.
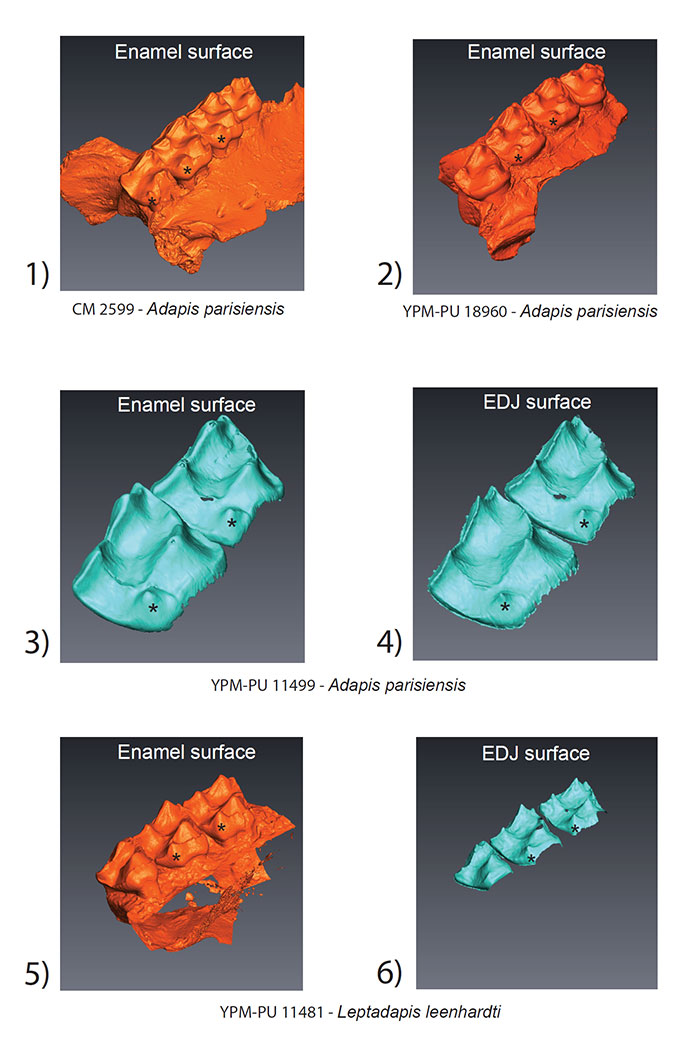
FIGURE 2. Surface models of the outer enamel surface and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) of Notharctus upper molars in the study sample. The hypocone in Notharctus forms on the crest running distally from the protocone (*). This is particularly evident at the EDJ (2.4) where there is also clear presence of a dentine horn. The morphology of the exposed dentine on CM 40735 is suggestive of a dentine horn (2.2). The black circle in (2.3) shows the buccal and distal crests which tend to form on the protocone in Notharctus specimens.
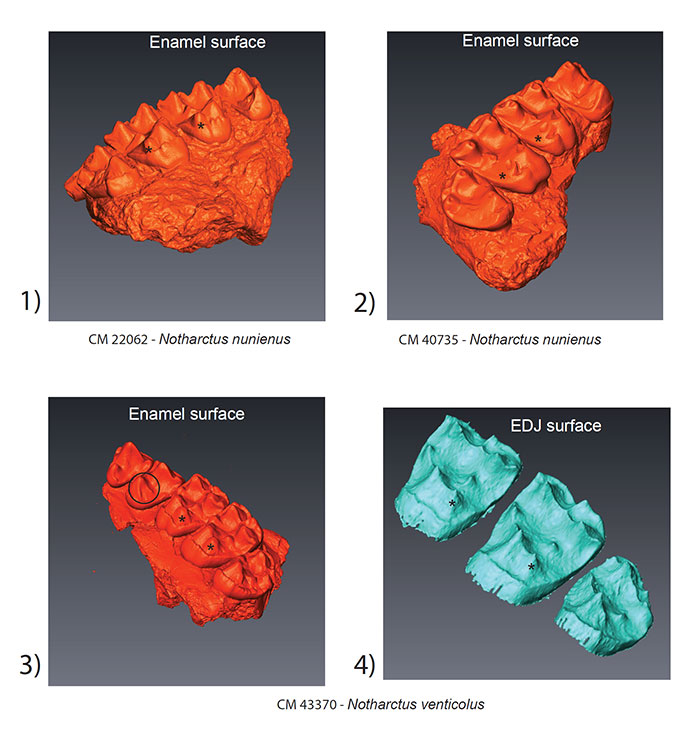
FIGURE 3. Surface models of the outer enamel surface and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) of Cantius upper molars in the study sample. The similarity between Cantius and Notharctus specimens can be seen in (3.1) and (3.2) with the hypocone highlighted with an asterisk (*). WMU 4834 shows only a distal crest from the protocone at the EDJ (3.4). WMU 2588 exhibits a unique configuration of accessory cusps (3.6) on the distal margin of the tooth crown (white asterisk; see text for details).
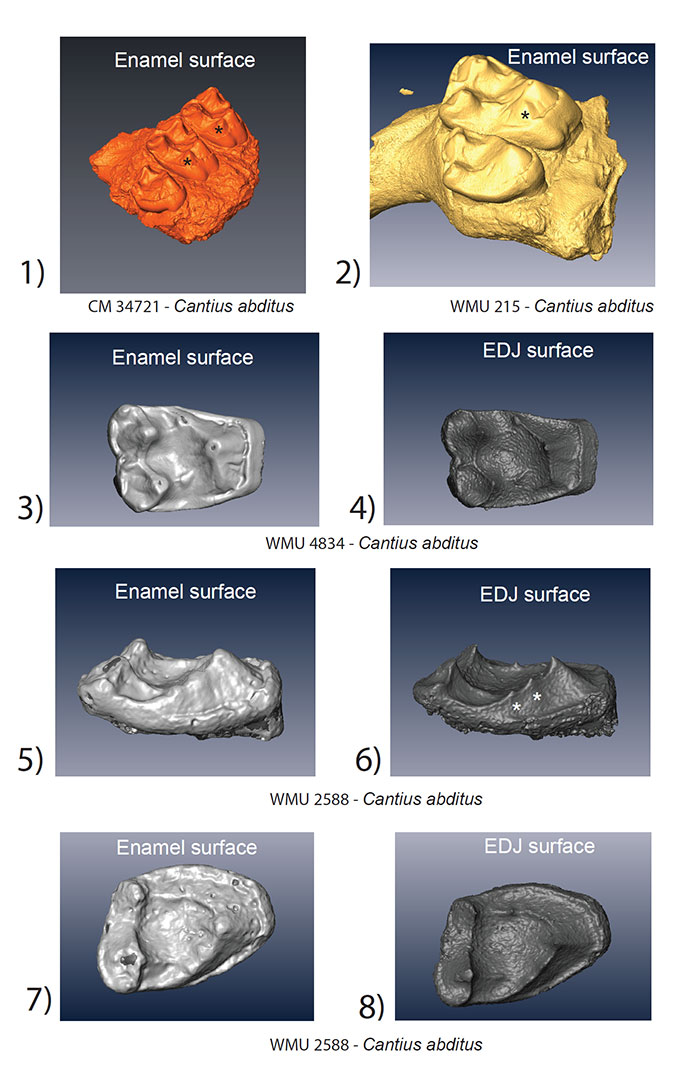
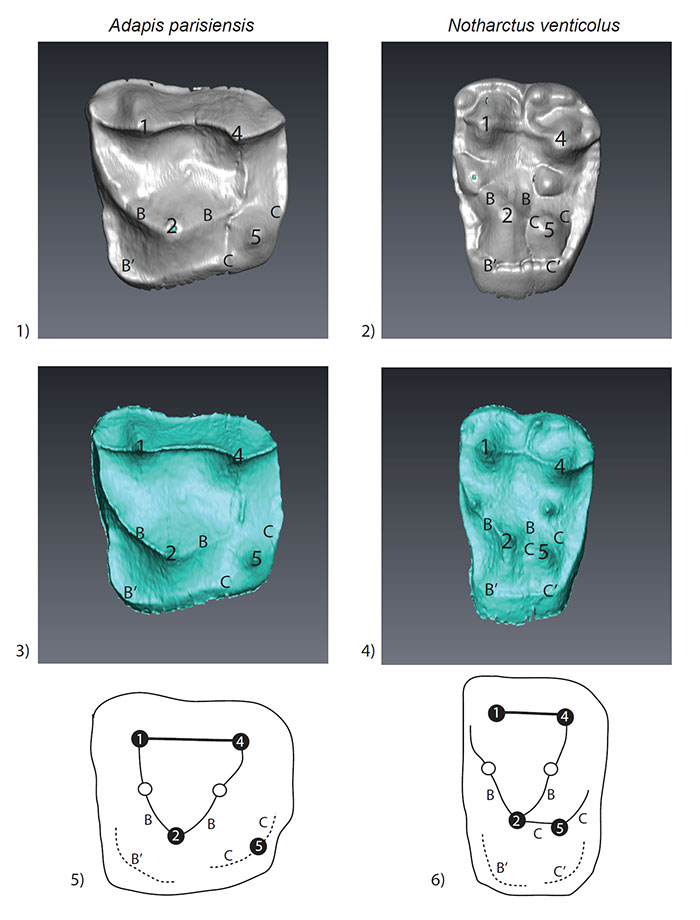
FIGURE 4. Left upper second molars of A. parisiensis (YPM-PU 11499) and N. venticolus (CM 43370) labeled following Hershkovitz (1977; specifically fig. V.14, p. 288). The distinction between the two types is that 1) no secondary posterolingual cingulum (C’) has formed in Adapis and 2) there is no link between the primary anterolingual cingulum (B) and the primary posterolingual cingulum (C) in Adapis. Letters and symbols as follows: 1 - paracone; 2 - protocone; 4 - metacone; 5 - hypocone; B - primary anterolingual cingulum; C - primary posterolingual cingulum; B’ - secondary anterolingual cingulum; C’ - secondary posterolingual cingulum. Note that YPM-PU 11499 is a right tooth that has been reversed in this image for ease of comparison with CM 43370.