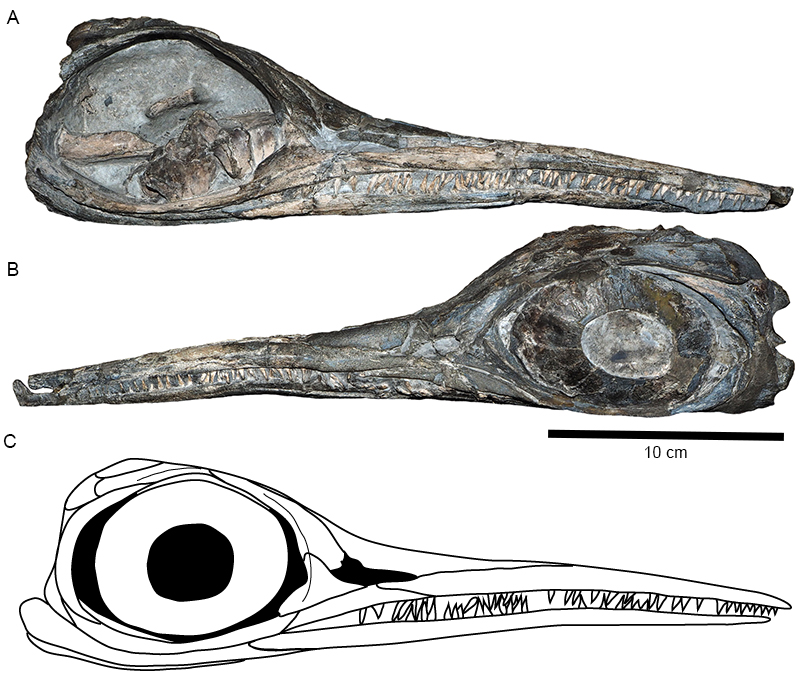
FIGURE 1. Hauffiopteryx typicus. A, lectotype, GPIT 1491/4; B, SMNS 51552; C, SMNS 80226. Part 1B © SMNS / M. Wahler.

FIGURE 2. Hauffiopteryx typicus, cranial morphology. A-G, overview of cranial morphology. A, lectotype, GPIT 1491/4; B, SMNS 51552; C, MHH 9; D, SMNS 80226. E, basioccipital in ventral view (SMNS 80226); F, maxillary and posterior dentary teeth (GPIT 1491/4); G, anterior mandible with displaced teeth (SMNS 80226). Scale bars in cm (parts B, D, E). Abbreviations: an, angular; bo, basioccipital; de, dentary; hc, hyoid corpus; hy, hyoid element; en, external narial opening; ex, exoccipital; f, frontal; j, jugal; la, lacrimal; lj, lower jaw; mx, maxilla; n, nasal; op, opisthotic; pa, parietal; pal, palatine; pf, prefrontal; pl, palate; pm, premaxilla; po, postorbital; pof, postfrontal; pt, pterygoid; Q, quadrate; qj, quadratojugal; sa, surangular; scr, sclerotic ring; sp, splenial; sq, squamosal; st, supratemporal; s, stapes; utf, supratemporal fenestra.
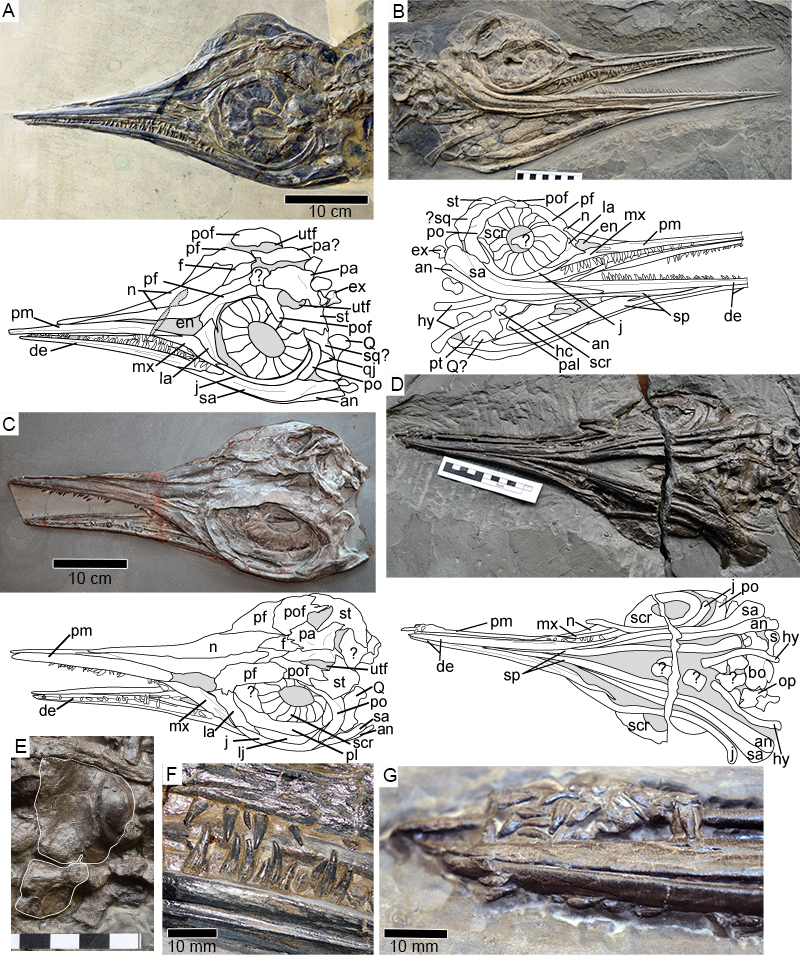
FIGURE 3. Hauffiopteryx typicus, cranial morphology of GPIT/RE/12905. A, lateral view; B; dorsal view of posterior skull roof. Abbreviations: an, angular; bo, basioccipital; de, dentary; en, external narial opening; ex, exoccipital; f, frontal; j, jugal; la, lacrimal; mx, maxilla; n, nasal; pa, parietal; pf, prefrontal; pm, premaxilla; po, postorbital; pof, postfrontal; sa, surangular; scr, sclerotic ring; sq, squamosal; st, supratemporal; utf, supratemporal fenestra.
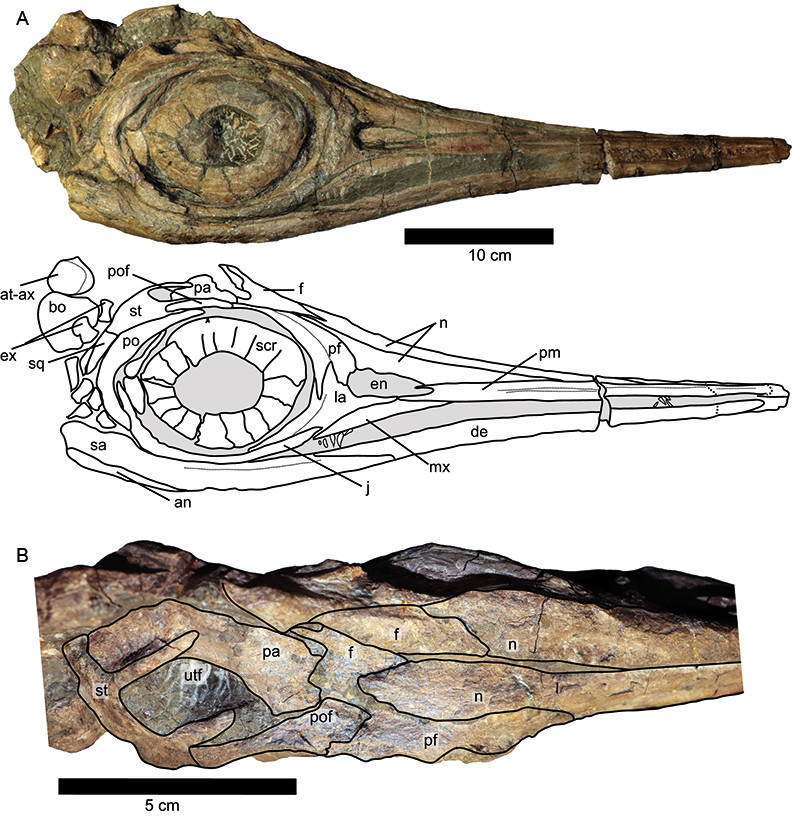
FIGURE 4. Postcranial morphology of Hauffiopteryx typicus. A, anterior neural spines of the lectotype GPIT 1491/4, note the broad axial neural spine of the same height as the neural spine of C3 but twice as wide. B, Fused atlas-axis complex (SMNS 80226); C, gastralia in the mid-dorsal region of SMNS 80226, the arrow indicates the boomerang-shaped medial element (see also inset); D, reconstruction of Hauffiopteryx typicus; the shape and position of the dorsal and caudal fins are based on the lectotype. Anterior is to the left in all parts. Scale bars in cm (parts B, C). Abbreviations: at-ax, atlas-axis complex; ns2, neural spine (axis).
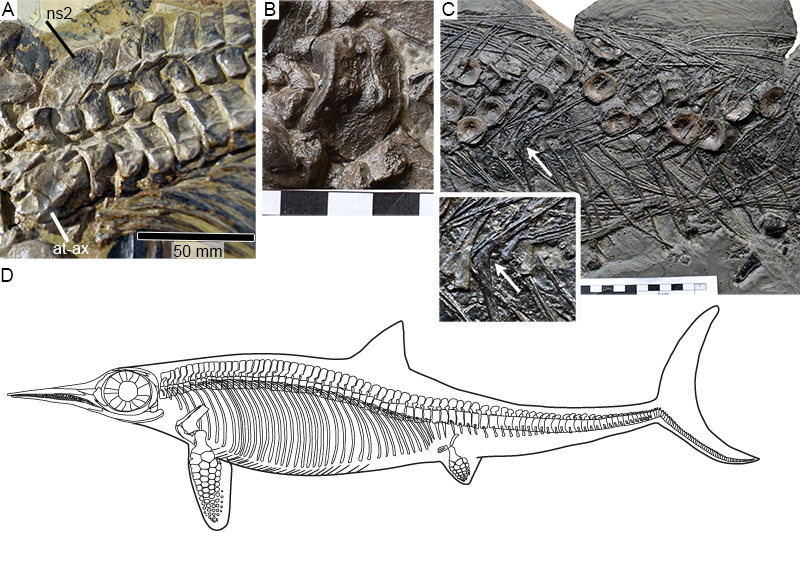
FIGURE 5. Hauffiopteryx typicus, pectoral girdle, and forelimb. A, pectoral girdle and humerus in ventral view (SMNS 80226); B, left forelimb in dorsal view (lectotype GPIT 1491/4); C, coracoids and left forelimb in ventral view (SMNS 51552). Scale bars in cm (parts A, C). Abbreviations: 2-4, distal carpals; cl, clavicle; co (r/l), right and left coracoids; H, humerus; i, intermedium; ic, interclavicle; pi, pisiform; R, radius; re, radiale; sc, scapula; U, ulna; ue, ulnare; v, metacarpal V.
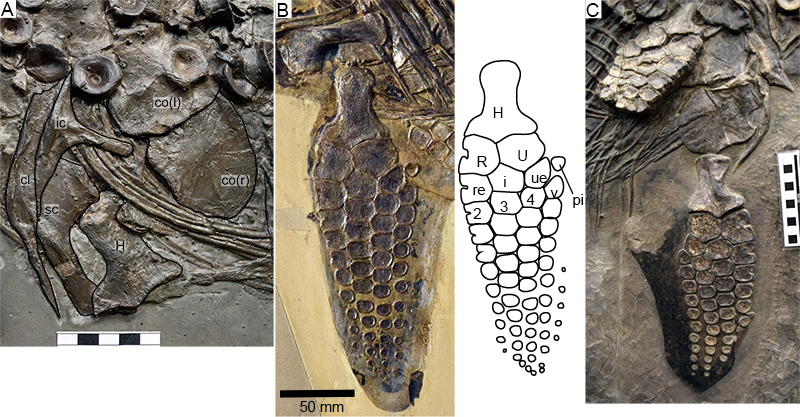
FIGURE 6. Hauffiopteryx typicus, pelvic girdle and hind limb. A, proximal left femur and pelvic girdle (SMNS 80226). B, pelvic girdle and hind limbs in dorsal view (lectotype GPIT 1491/4); C-D, interpretive drawings of hind limbs of same. E, hind limb of SMNS 51552. Abbreviations: 2-4, distal tarsals; a, astragalus; c, calcaneum; F, femur; Fi, fibula; il, ilium; is, ischium; pi, pisiform; pb, pubis; Ti, tibia; v?, putative metatarsal V; note the homology issues regarding both digit V and distal tarsal 2 in Hauffiopteryx and many other parvipelvians.
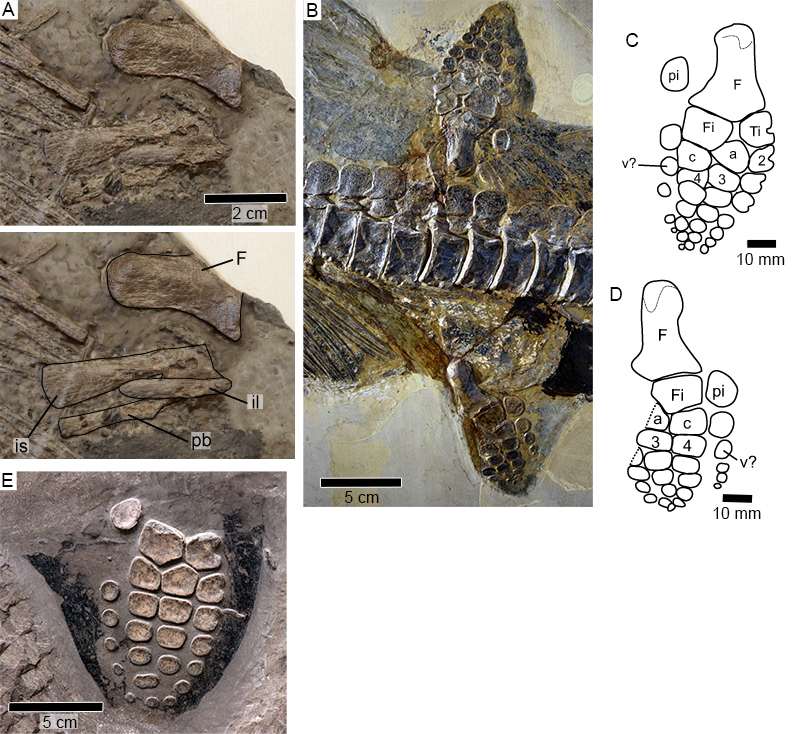
FIGURE 7. Hauffiopteryx altera, sp. nov., holotype FWD-129. A, B, right and left lateral views; C, D, interpretation of the cranial sutures in lateral view; E, F, ventral view of skull with interpretation; G, H, dorsal view of skull with interpretation. Abbreviations: an, angular; de, dentary; en, external narial opening; f, frontal; j, jugal; lac, lacrimal; mx, maxilla; n, nasal; ns2, neural spine (axis); pa, parietal; par, parietal ridge; pf, prefrontal; pm, premaxilla; po, postorbital; pof, postfrontal; qj, quadratojugal; sa, surangular; scr, sclerotic ring; sp, splenial; st, supratemporal.
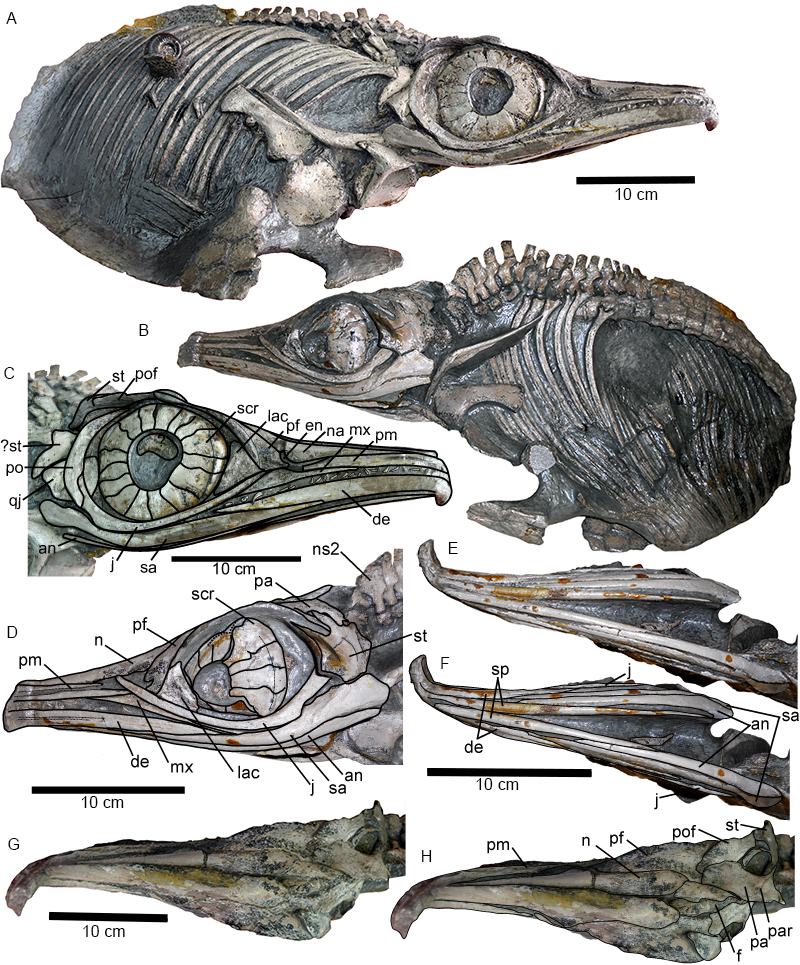
FIGURE 8. Hauffiopteryx altera, sp. nov., holotype FWD-129. A, left dorsal temporal region, illustrating the palmate morphology of the supratemporal; B, premaxillary and dentary teeth illustrating the thin, smooth enamel; scale bar is in mm; C, anterior neural arches, note the size and shape differentiation between the neural spines of the atlas, axis, and more posterior vertebrae; D, proximal right forelimb in dorsal view; E, pectoral girdle in external view. Abbreviations: cl, clavicle; co (r)/co (l), right and left coracoids; H, humerus; i, intermedium; ic, interclavicle; ns1, neural spine (atlas); ns2, neural spine (axis); ns3, neural spine (C3); pa, parietal; pof, postfrontal; R, radius; re, radiale; sc, scapula; st, supratemporal; st.a, medial process of the anterior ramus of the supratemporal; st.m, medial ramus of the supratemporal; U, ulna; ue, ulnare; utf, supratemporal fenestra.
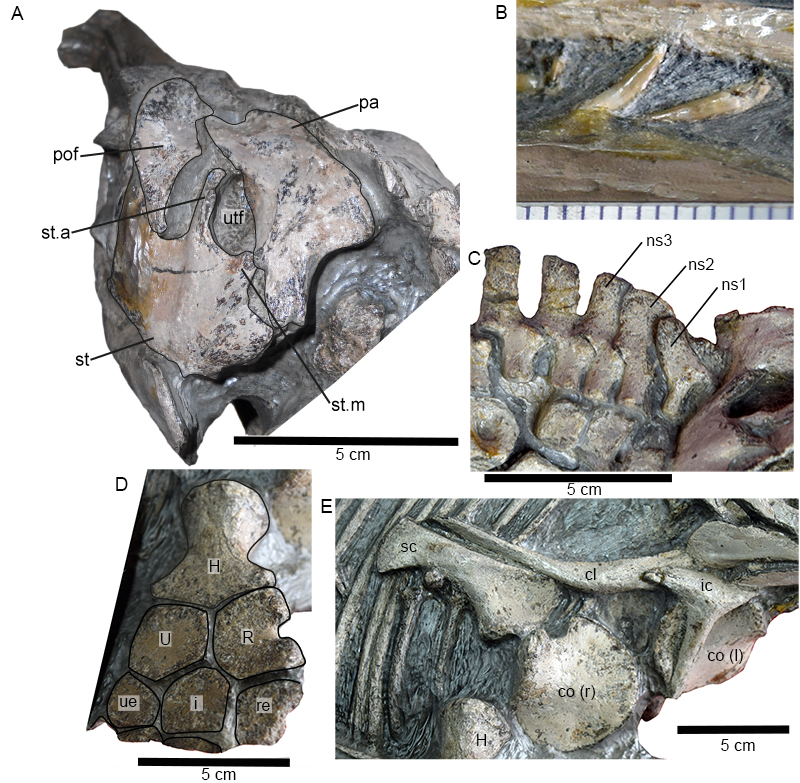
FIGURE 9. Hauffiopteryx sp. A, SMNS 81367; B, SMNS 80225; C, SMNS 81962; D, SMNS 81965. Photos © SMNS / M. Wahler.

FIGURE 10. Strict consensus of 158 most parsimonious trees of length 1663; taxa flagged by IterPCR as being unstable have been pruned from the figure. The arrow indicates OTUs included in the genus Hauffiopteryx. Bremer support values greater than 1 are indicated to the left of the nodes.

FIGURE 11. 50% majority rule tree derived from Bayesian analysis. Clade credibility values indicated to the left of the nodes. The arrow indicates OTUs included in the genus Hauffiopteryx.
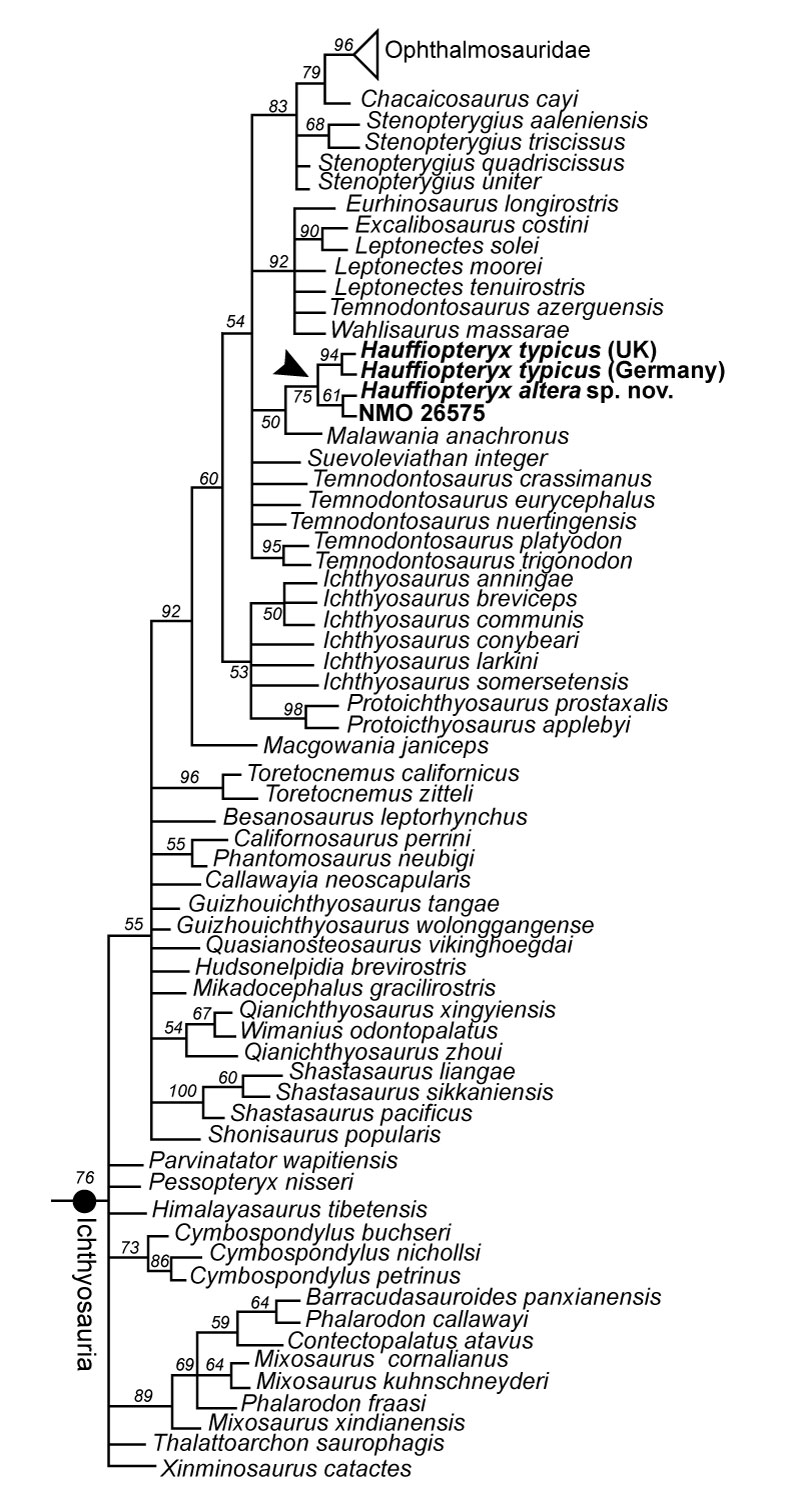
FIGURE 12. Hauffiopteryx typicus, NMO 26575. Skull in (A) right and (B) left lateral view; 3, reconstruction, redrawn from Maisch and Reisdorf (2006).