FIGURE 1. The rostral neurovascular canals of Tyrannosaurus rex (FMNH PR 2081) in lateral view (top) and two cross-sections (CT slices, bottom). Scale bar equals 30cm.
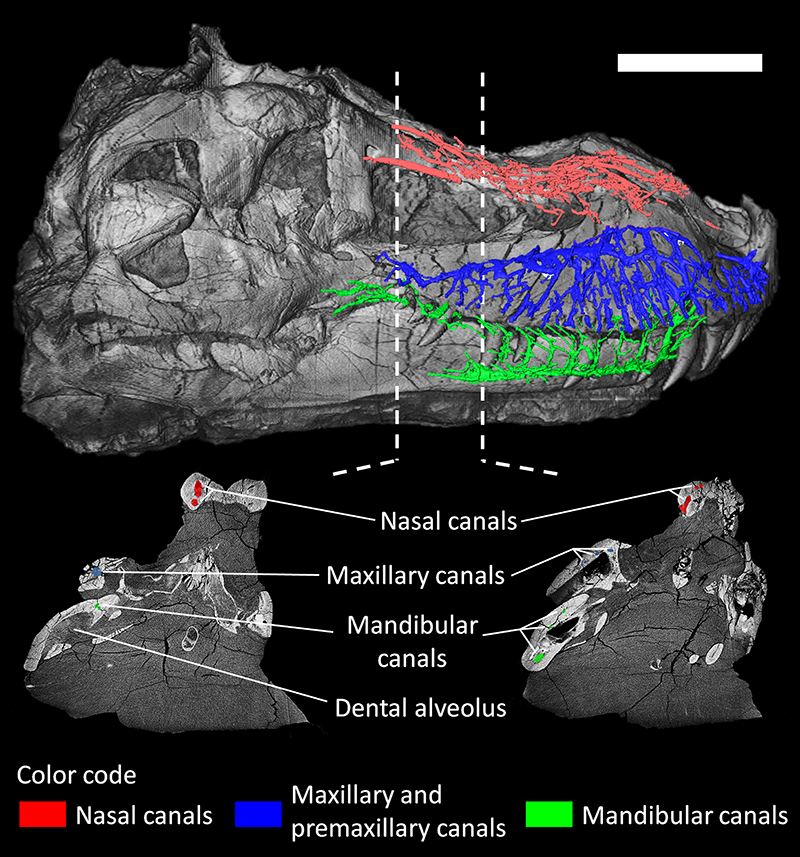
FIGURE 2. Nasal canals of Tyrannosaurus rex (FMNH PR 2081) in dorsal view (left) and lateral view (right). Scale bar equals 30 cm.
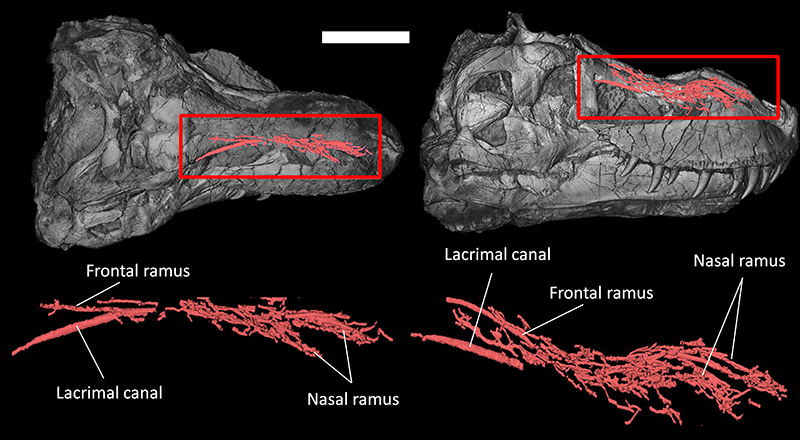
FIGURE 3. Premaxillary canal and canals for the dorsal alveolar (maxillary) vessels and maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve of Tyrannosaurus rex (FMNH PR 2081) in lateral view. Scale bar equals 30cm.
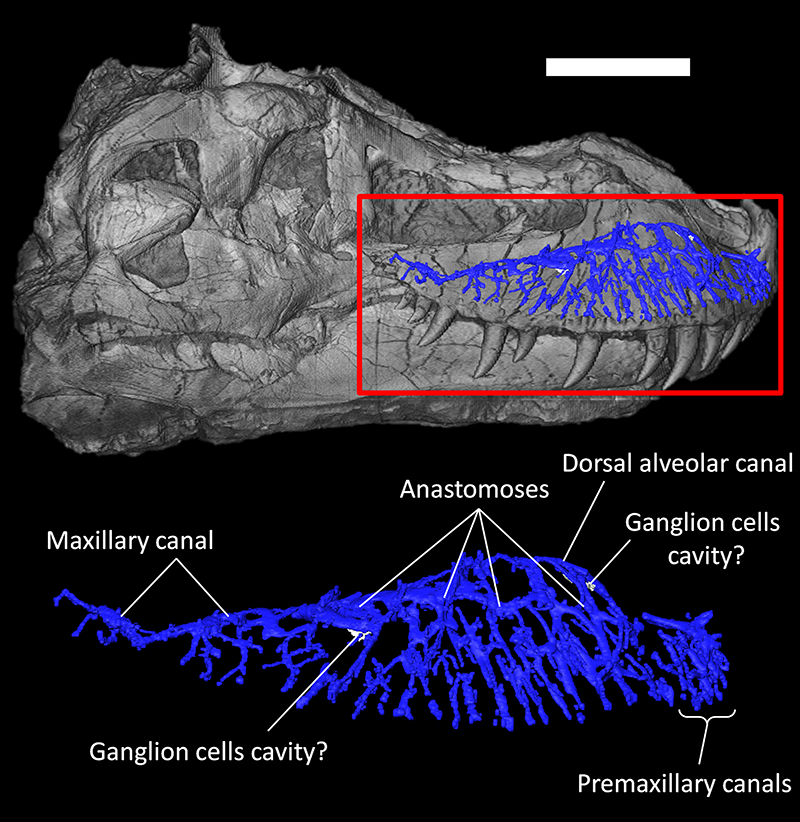
FIGURE 4. Premaxillary canals of Tyrannosaurus rex (FMNH PR 2081) in anterior view. Scale bar equals 30cm.
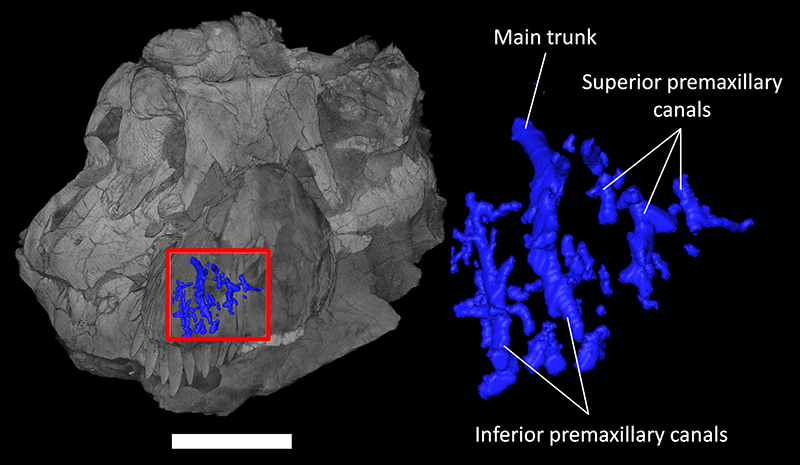
FIGURE 5. Canals for the mandibular vessels and mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve of Tyrannosaurus rex (FMNH PR 2081) in lateral view. Scale bar equals 30cm.
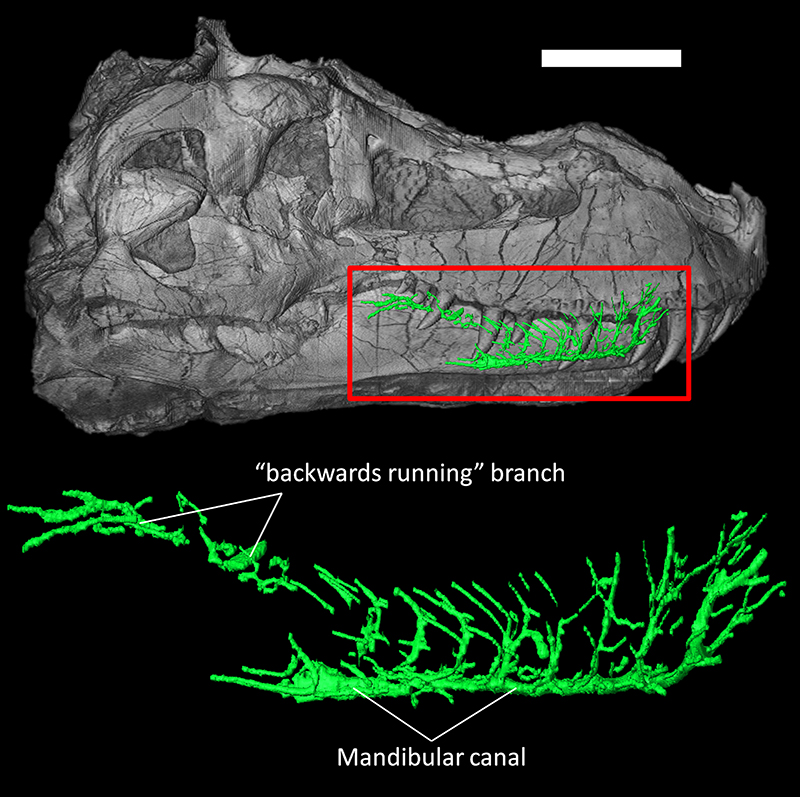
FIGURE 6. Simplified evolution of the rostral neurovascular systems in Sauropsida in lateral view. A, F, and I figure the course of some branches of the trigeminal nerve, whereas B, C, D, E, G, and H figure the canals of the rostral neurovascular system (see text for descriptions and references). Abbreviation: Cc, conical cavity. Color code: Black, teeth; Blue, maxillary canal (or nerve when applicable); Green, mandibular canal (or nerve when applicable); Red, ophthalmic nerve; Yellow, premaxillary canal. Dotted lines represent non-nervous structures (e.g., orbits, nostrils, cranial fenestrae, and conical cavity). Drawings not to scale.
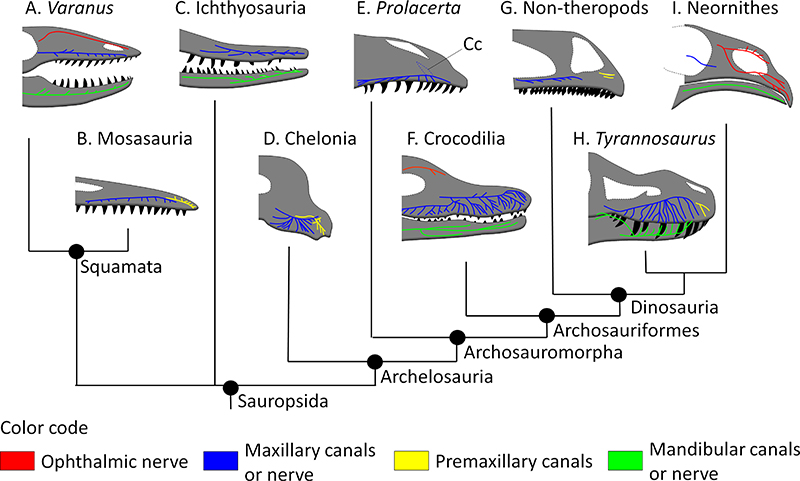
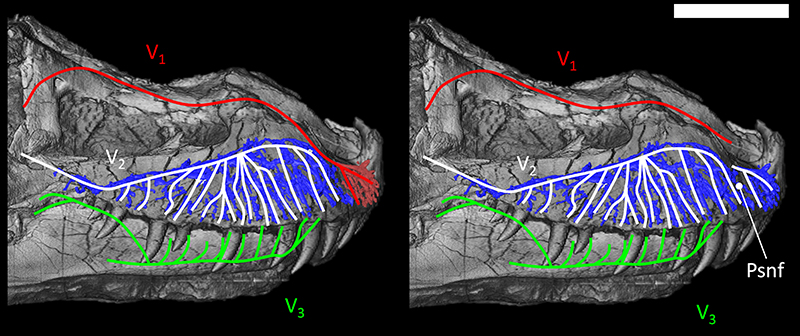
FIGURE 7. Reconstruction of the trigeminal branches pathway in the snout of Tyrannosaurus rex (FMNH PR 2081) in lateral view. Left, dominant ophthalmic branch hypothesis (“bird-like” condition). Right, dominant maxillary branch hypothesis (“reptile-like” condition). Abbreviations: V1, Ophthalmic branch; V2, Maxillary branch; V3, Mandibular branch; Psnf, position of the palatal sub-narial foramen. Scale bar equals 30 cm. Color code same as Figure 6.