FIGURE 1. Photographs (top) and interpretative line drawings (bottom) of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, left lateral view; B, right lateral view. Note that bones are labelled in bold, and other anatomical structures in regular font. Also note that tooth positions are numerically labelled but refer to preserved tooth position from anterior to posterior, not to anatomical tooth positions, which are unknown. Abbreviations: an, angular; aof, antorbital fenestra; ar, articular; boc, basioccipital; d, dentary; manf, mandibular fenestra; en, external naris; f, frontal; fb, foreign body; gf, glenoid fossa; iop, interorbital process of parabasisphenoid; itf, infratemporal fenestra; j, jugal; l, lacrimal; l.ar; left articular; l.d, left dentary; l.ep, left ectopterygoid; l.bpp, left basipterygoid process of the parabasisphenoid; l.sur, left surangular; l.sq, left squamosal; l.pa, left palatine; l.pra, left prearticular; l.pt, left pterygoid; l.q, left quadrate; m, maxilla; n, nasal; ma, maxillary antrum; mf, maxillary fragment; r.ar, right articular; r.epi, epipterygoid; r.pa, right palatine; r.sur, right surangular; lsp, laterosphenoid; m, maxilla; n, nasal; o, orbit; osp, orbitosphenoid; oto, otoccipital; pa, palatine; par, parietal; pbsp, parabasisphenoid; pm, premaxilla; po, postorbital; pro, prootic; prf, prefrontal; pt, pterygoid; ptw, pterygoid wing of left quadrate; qw, quadrate wing of right pterygoid; qj, quadratojugal; s, stapes; soc, supraoccipital; sq, squamosal; v, vomer; V, trigeminal nerve foramen (CN V); 1-10 mark preserved tooth positions of the maxillae (because of their size, position 11 and 12 on the maxillary fragment are not visible in this depiction).
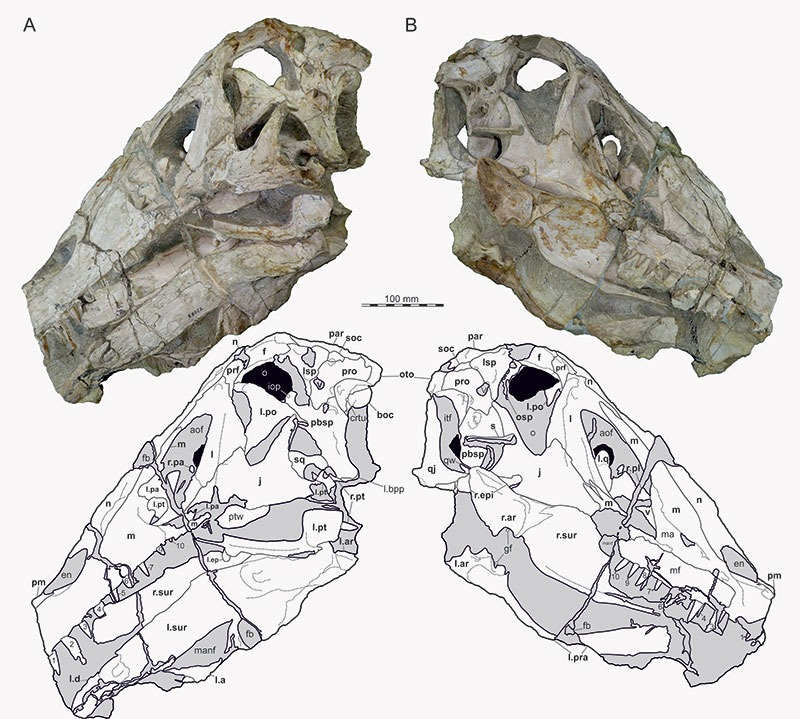
FIGURE 2. Interpretative line drawings of the re-arranged and articulated skull of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, right lateral view; B, sagittal cut with removed right skull half, revealing medial aspects of the left skull half. Speculatively, grey silhouettes add unknown parts to the skull known from other spinosaurids. Abbreviations: an, angular; ar, articular; boc, basioccipital; d, dentary; ep, ectopterygoid; epi, epipterygoid; f, frontal; j, jugal; l, lacrimal; ls; laterosphenoid; m, maxilla; n, nasal; osp, orbitosphenoid; oto, otoccipital; pa, palatine; par, parietal; pbsp, parabasisphenoid; pm, premaxilla; po, postorbital; pro, prootic; pra, prearticular; prf, prefrontal; pt, pterygoid; q, quadrate; qj, quadratojugal; s, stapes; sur, surangular; soc, supraoccipital; sq, squamosal; v, vomer.
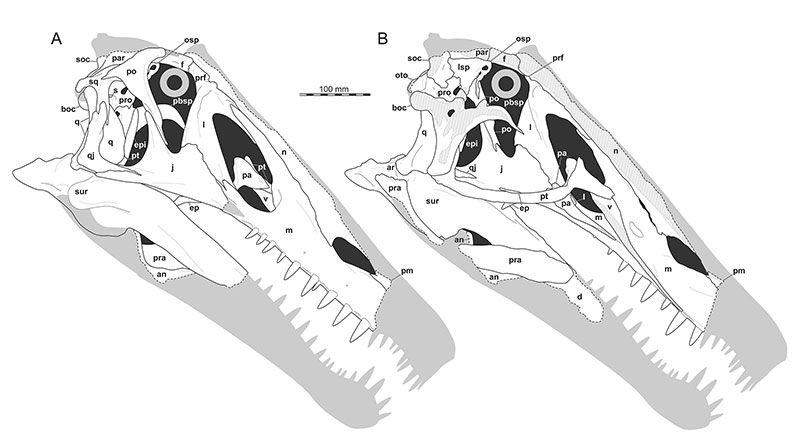
FIGURE 3. Interpretative line drawings of the re-arranged and articulated skull of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, anterior view; B, posterior view. Speculatively, grey silhouettes add unknown parts to the skull known from other spinosaurids. Abbreviations: an, angular; boc, basioccipital; ep, ectopterygoid; epi, epipterygoid; f, frontal; j, jugal; l, lacrimal; lsp, laterosphenoid; m, maxilla; n, nasal; oto, otoccipital; par, parietal; pbsp, parabasisphenoid; pm, premaxilla; po, postorbital; pra, prearticular; pt, pterygoid; q, quadrate; qj, quadratojugal; sur, surangular; soc, supraoccipital; sq, squamosal.
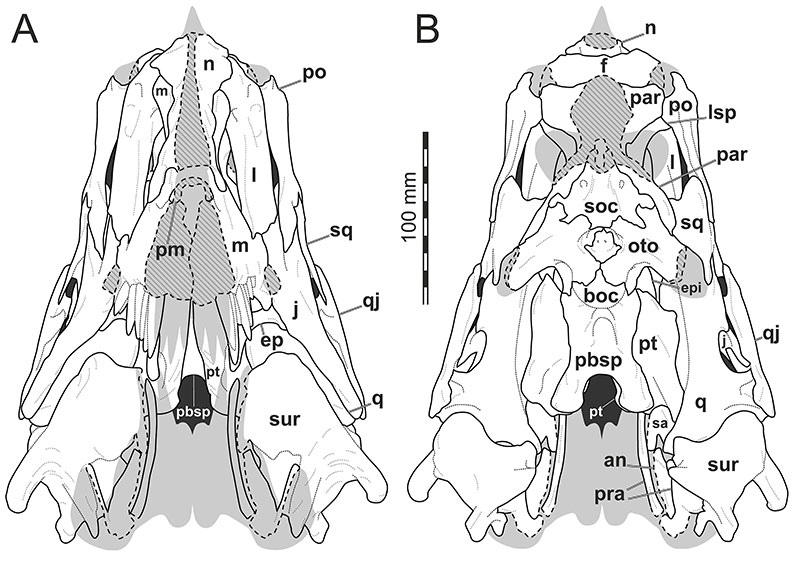
FIGURE 4. Interpretative line drawings of the re-arranged and articulated skull of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, dorsal view; B, ventral view without the lower jaw. Speculatively, grey silhouettes add unknown parts to the skull known from other spinosaurids. Abbreviations: boc, basioccipital; ep, ectopterygoid; f, frontal; j, jugal; l, lacrimal; lsp, laterosphenoid; m, maxilla; n, nasal; oto, otoccipital; par, parietal; pbsp, parabasisphenoid; pm, premaxilla; po, postorbital; pro, prootic; prf, prefrontal; pt, pterygoid; q, quadrate; qj, quadratojugal; sur, surangular; soc, supraoccipital; sq, squamosal.
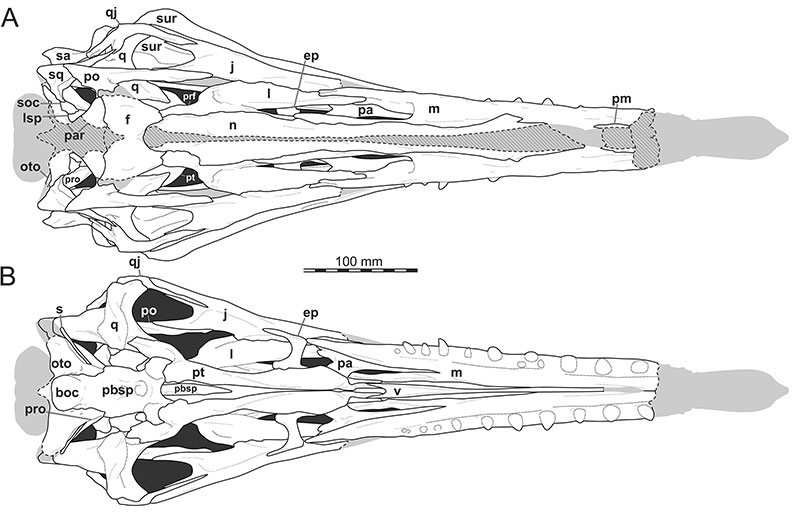
FIGURE 5. 3D renderings of the left maxilla of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, lateral view; B, lateral view with maxillary bone rendered transparent; C, medial view; D, medial view with maxilla bone rendered transparent; E, posterior view; F, ventral view (anterior to top); G, ventral view without teeth, showing alveoli. Note different scale for E. Also note that tooth positions are numerically labelled but refer to preserved tooth position from anterior to posterior, not to anatomical tooth positions, which are unknown. Replacement teeth are highlighted with dashed lines in D, and different generations are indicated with prime (’) or double prime (’’). Red arrow heads point to neurovascular foramina. Abbreviations: acp, ascending process; jr, jugal ramus; lac, lacrimal contact; llam, lateral lamina; nac, nasal contact; palgr, palatine groove; pdl, paradental lamina; pmxf, premaxillary facet; prmr, promaxillary recess; rt, replacement tooth; snf, subnarial fossa.
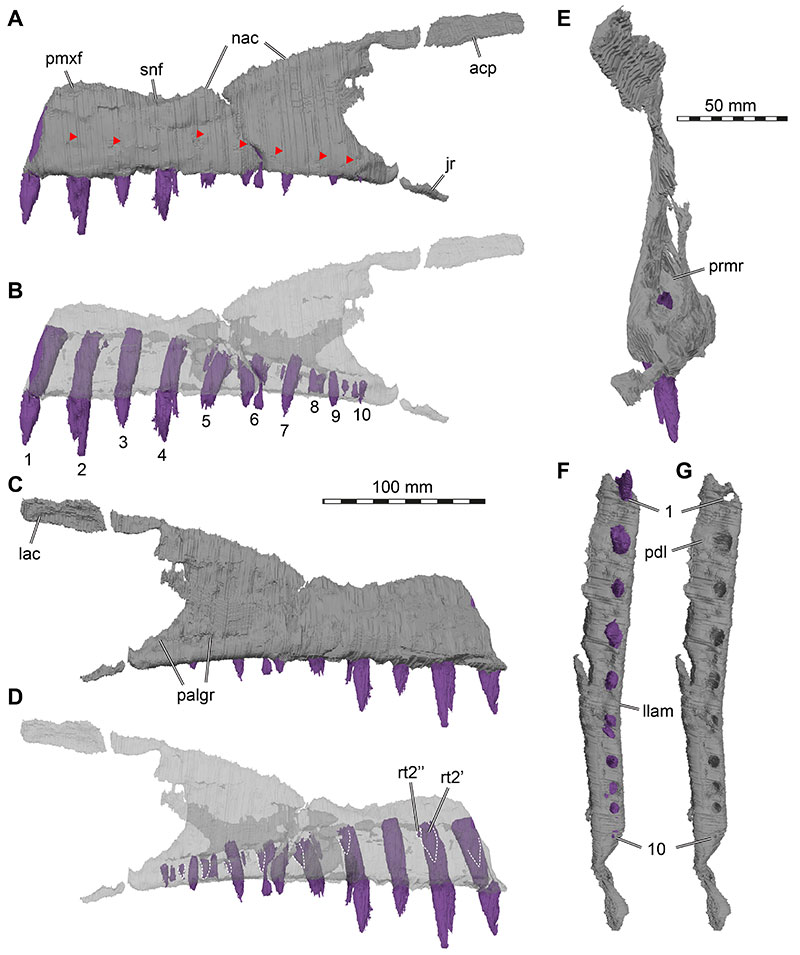
FIGURE 6. 3D renderings of the right maxilla of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, lateral view; B, lateral view with maxillary bone rendered transparent; C, medial view; D, medial view with maxillary bone rendered transparent; E, ventral view of tooth row fragment; F, ventral view with maxillary bone rendered transparent. Note different scale for E-F. Also note that tooth positions are numerically labelled but refer to preserved tooth position from anterior to posterior, not to anatomical tooth positions, which are unknown. Replacement teeth are highlighted with dashed lines in D, and different generations are indicated with prime (’) or double prime (’’). Arrows in A and C indicate approximate original position of tooth-bearing fragment. Abbreviations: acp, ascending process; jr, jugal ramus; lac, lacrimal contact; mw-prmr, medial wall of promaxillary recess; palgr, palatine groove; pdl, paradental lamina; prmr, promaxillary recess; rt, replacement tooth.
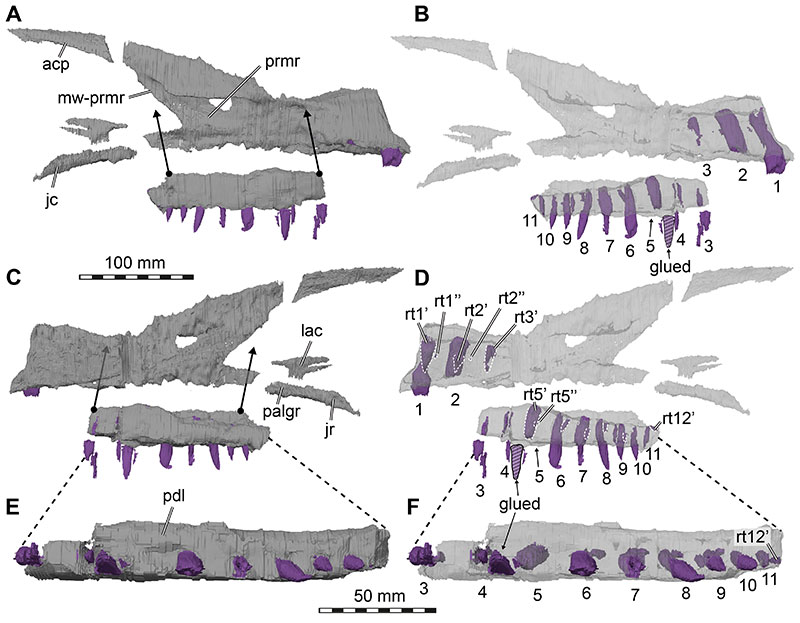
FIGURE 7. 3D renderings of the fused nasals of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, dorsal view; B, left lateral view; C, ventral view. Abbreviations: apmxp, anterior premaxillary process; frc, frontal contact; lac, lacrimal contact; mxc, maxillary contact; nc, nasal crest; prfc, prefrontal contact; vmxp, ventral maxillary process.
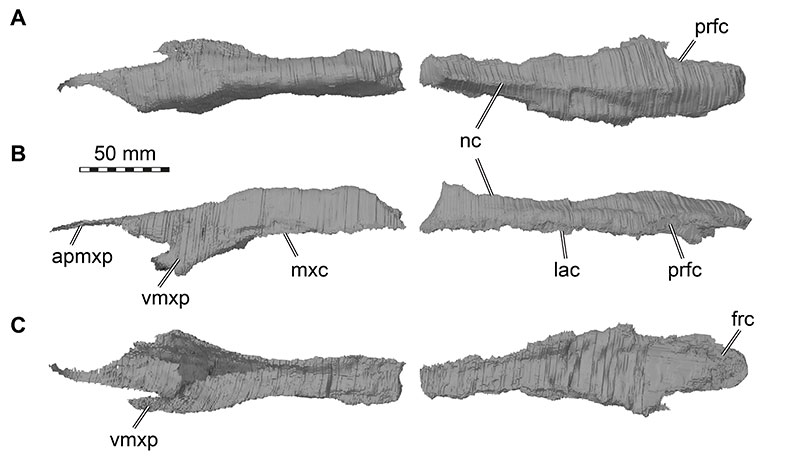
FIGURE 8. Photograph of posterior skull roof of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022) in dorsal view. Note that bones are labelled in bold, and other anatomical structures in regular font. Dashed lines mark sutures. Abbreviations: f, frontal; l, lacrimal; lsp, laterosphenoid; n, nasal; par, parietal; pop, paroccipital process; prf, prefrontal; soc, supraoccipital.
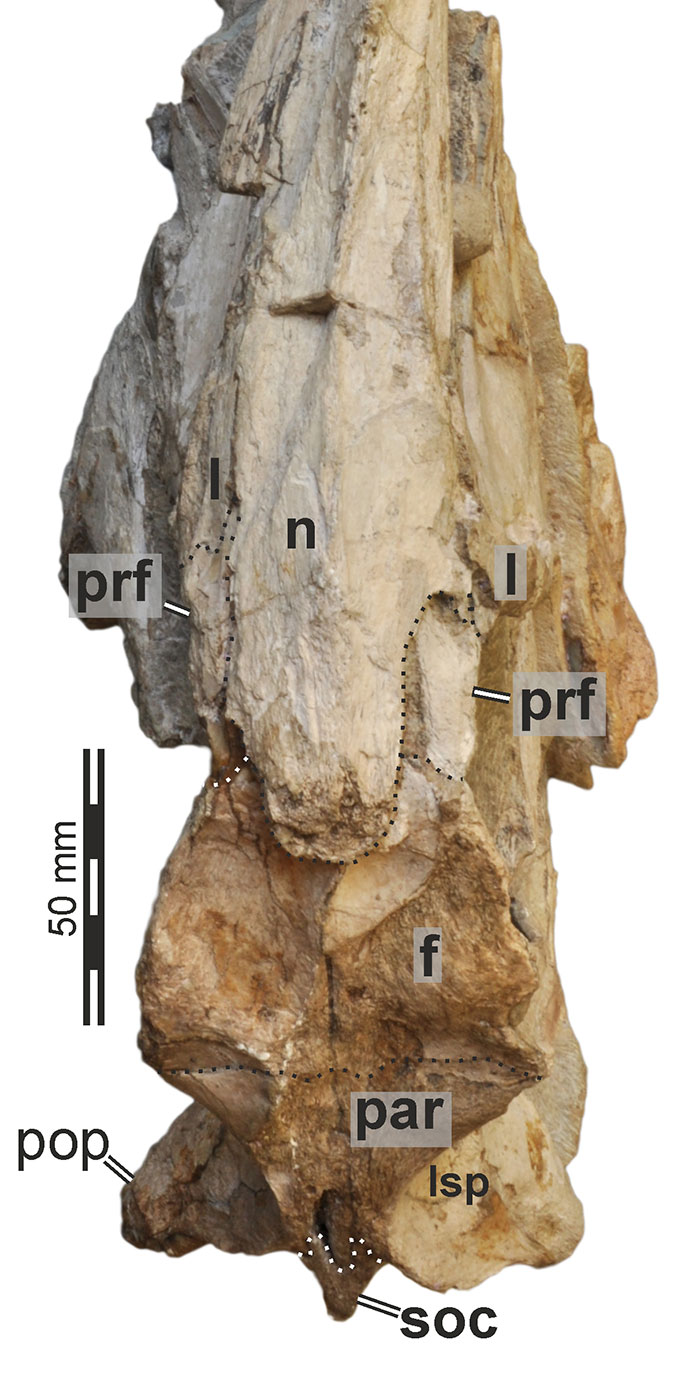
FIGURE 9. 3D renderings of the right lacrimal and prefrontal of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). Note that sutures between these two bones could not be identified in the CT data, but externally visible sutures on the specimen show that these bones are only partially fused (see Figure 10). A, lateral view; B, medial view. Abbreviations: frc, frontal contact; jc, jugal contact; la, lacrimal; laor, lacrimal antorbital recess; lap, lacrimal anterior process; lvp, lacrimal ventral process; mxc, maxillary contact, nc, nasal contact; onr, orbitonasal ridge; prf, prefrontal.
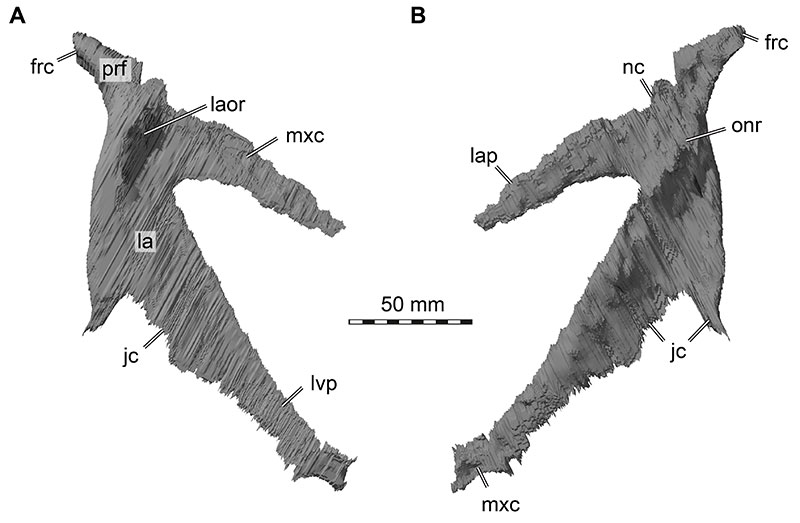
FIGURE 10. Close-up photographs of the lacrimal/prefrontal region of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, left posterolateral view; B, right posteroventral view. Note that bones are labelled in bold, and other anatomical structures in regular font. Dashed lines mark sutures. Abbreviations: aof, antorbital fenestra; f, frontal; l, lacrimal; l.po, left postorbital; o, orbit; prf, prefrontal.
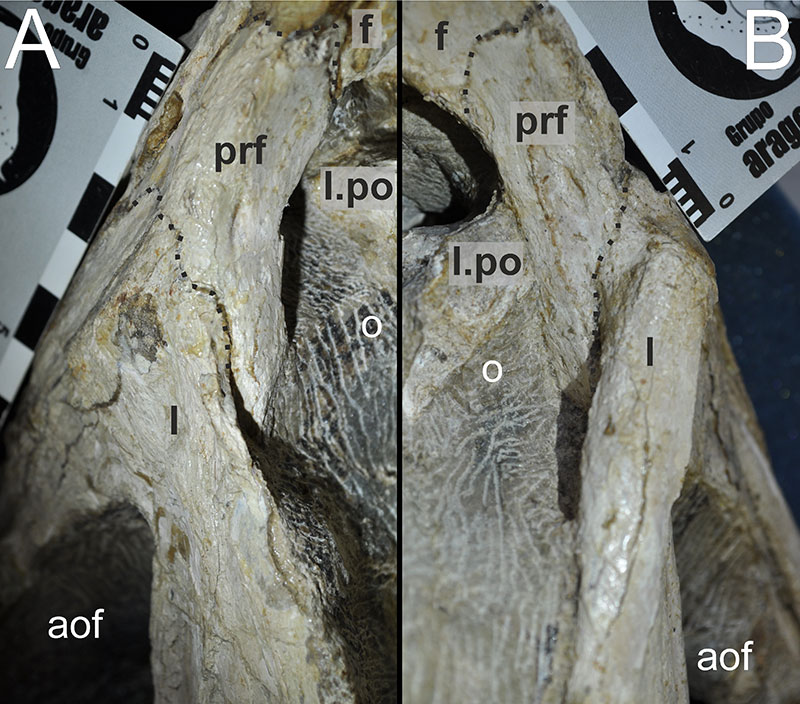
FIGURE 11. Close-up photograph of the lacrimal region of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022) in an earlier stage of preparation. Right lateral view. Arrows indicate the formerly more complete lamina on the dorsolateral aspect of the lacrimal. Abbreviations: aof, antorbital fenestra; j, jugal; l, lacrimal; o, orbit; V, trigeminal nerve foramen (CN V).
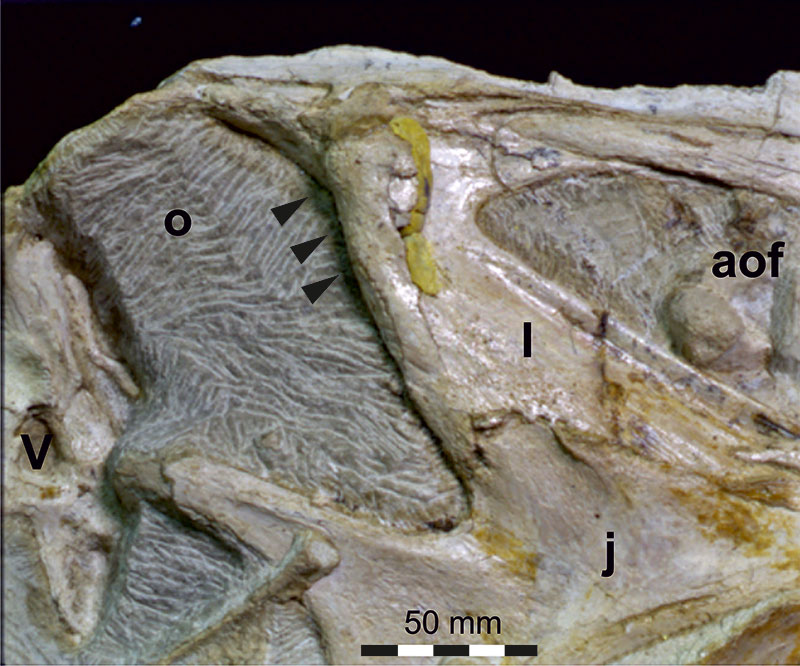
FIGURE 12. 3D renderings of the right and left frontals of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). Note that the interfrontal contact could not be identified in the CT data, but externally visible sutures on the specimen show that these bones are only partially fused (see Figure 8). A, dorsal view; B, ventral view; C, left lateral view; D, anterior view. Abbreviations: crcr, crista cranii; dmr, dorsal median ridge; lspc, laterosphenoid contact; nac, nasal contact; np, nasal process; olt, olfactory tract, poc, postorbital contact, stf, supratemporal fossa.
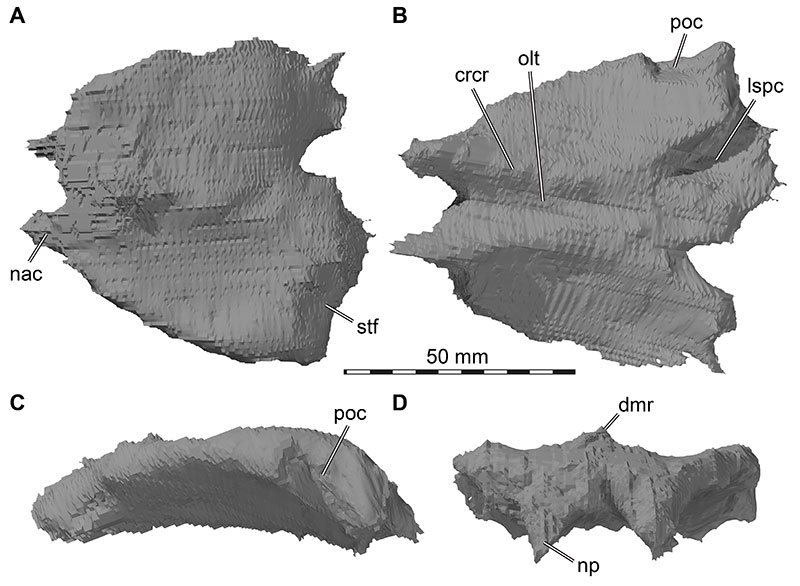
FIGURE 13. 3D renderings of the right and left parietals of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, dorsal view; B, ventral view. Abbreviations: fc, frontal contact; lspc, laterosphenoid contact; nuc, nuchal crest base; oto, otoccipital contact; poc, postorbital contact, socc, supraoccipital contact; stf, supratemporal fossa; sqc, squamosal contact.
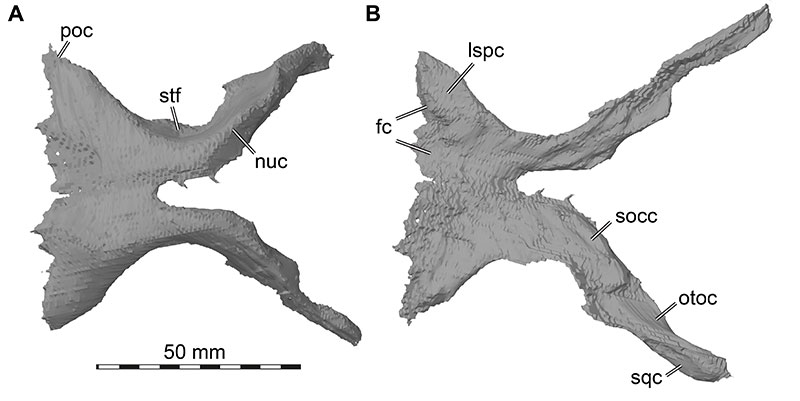
FIGURE 14. Photograph of the braincase of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022) in posterior view. Note that bones are labelled in bold, and other anatomical structures in regular font. Abbreviations: bpp, basipterygoid process of parabasisphenoid; bsr, basisphenoid recess; bt, basal tuber; crtu, crista tuberalis; fm, foramen magnum; occ, occipital condyle; pop, paroccipital process; pvf, posterior vagal foramen; r.qj, right quadratojugal; socc, supraoccipital crest; vcm, vena capitis media foramen.
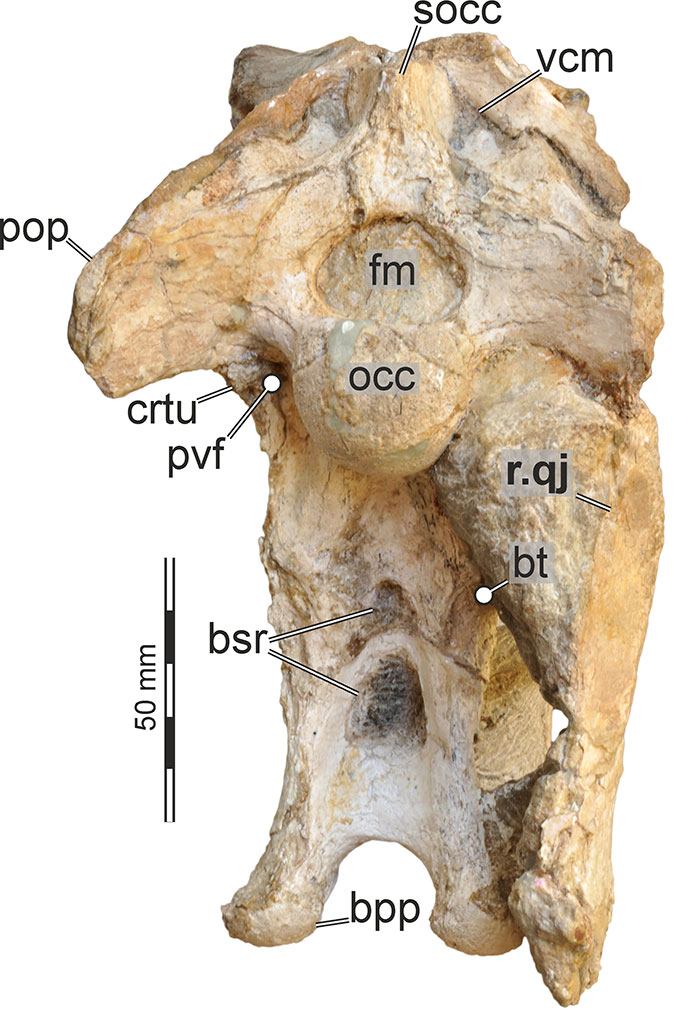
FIGURE 15. 3D renderings of the left postorbital of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, lateral view; B, anterior view; C, medial view. Abbreviations: ap, anterior process; fc, frontal contact; jf, jugal facet; jp, postorbital jugal process; lspc, laterosphenoid contact; orf, orbital fossa; pac, parietal contact; sqp, squamosal process.
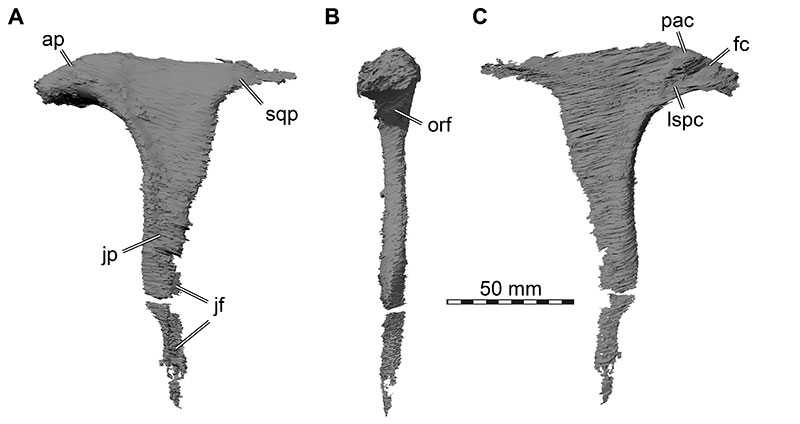
FIGURE 16. 3D renderings of the right jugal of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, lateral view; B, medial view. Abbreviations: drqjp, dorsal ramus of quadratojugal process; jmxp, maxillary process; jpop, postorbital process; lac, lacrimal contact; mxc, maxillary contact; mxcg, maxillary contact groove; poc, postorbital contact; qjc, quadratojugal contact; vrqjp, ventral ramus of quadratojugal process.
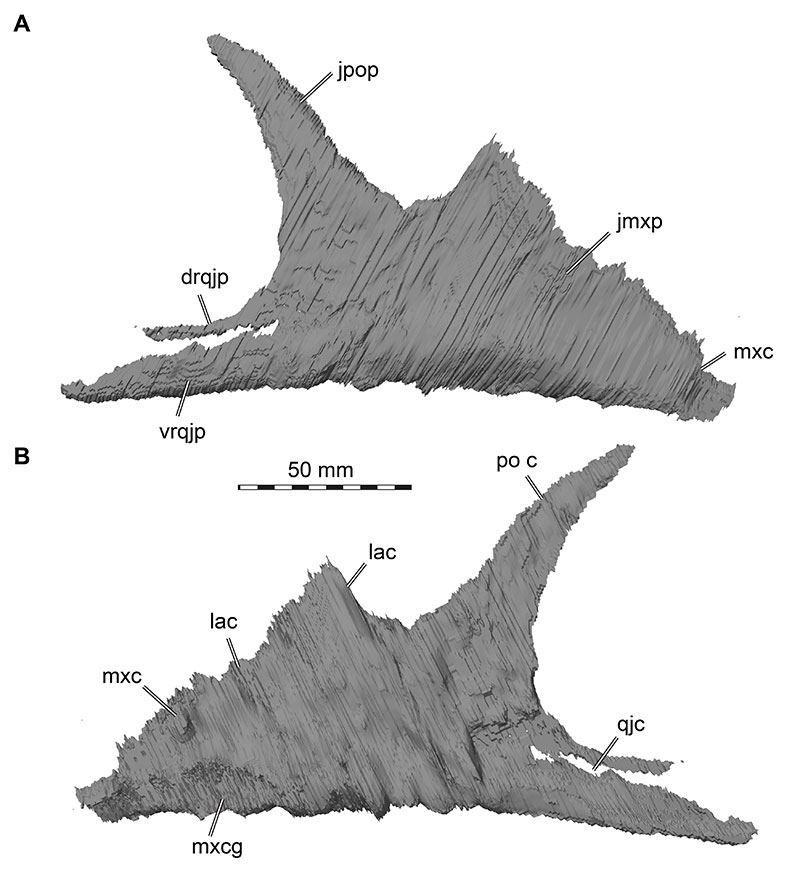
FIGURE 17. 3D renderings of the right quadratojugal of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, lateral view; B, medial view. Abbreviations: jc, jugal contact; jp, jugal process; pp, posterior process; qc, quadrate contact; sqp, squamosal process; sqr, squamosal ridge.
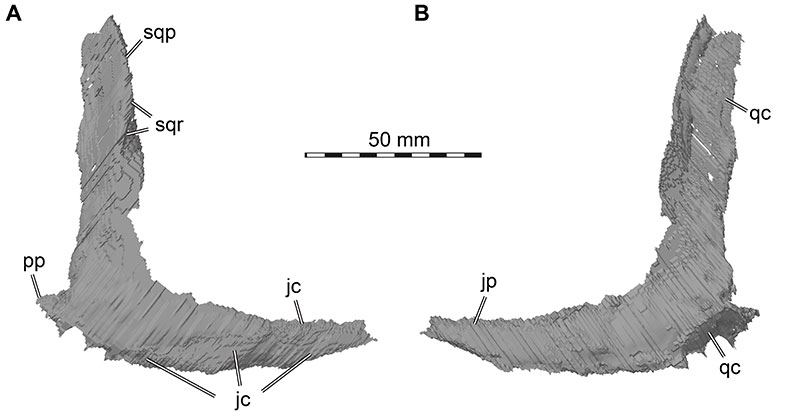
FIGURE 18. 3D renderings of the left squamosal of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, lateral view; B, medial view; C, dorsal view. Abbreviations: amp, anteromedial process; drap, dorsal ramus of anterior process; emdl, emarginated dorsal lamina; lar, lateral ridge; mr, medial ridge; pogr, postorbital groove; qhf, quadrate head facet; qjp, quadratojugal process; qp, quadrate process; vrap, ventral ramus of anterior process.
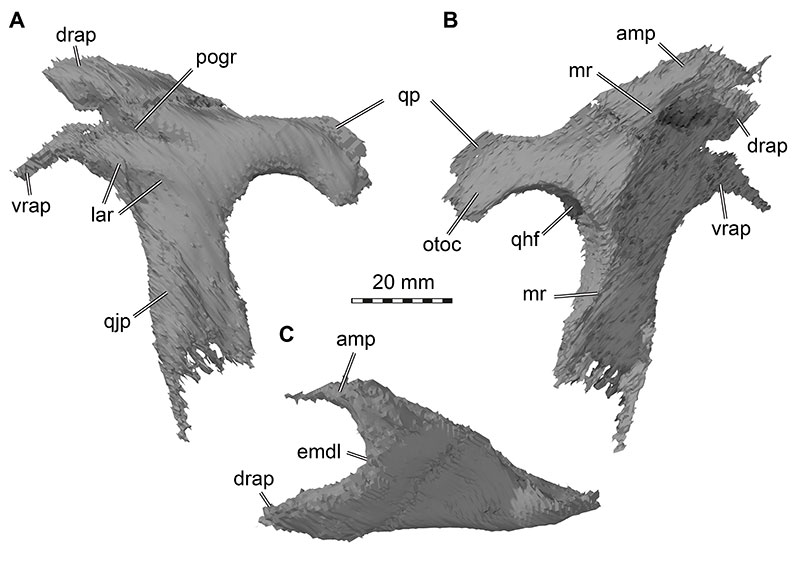
FIGURE 19. 3D renderings of the left quadrate of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, anterior view; B, lateral view; C, posterior view; D, medial view; E, ventral view (anterior at top). Note that A-D are to same scale, E with separate scale bar. Dashed lines in E are approximate shapes of quadrate articulation condyles. Abbreviations: ecc, ectocondyle; enc, entocondyle; ics, intercondylar sulcus; ptw, pterygoid wing; qh, quadrate head; qjf, quadratojugal flange; qf, quadrate foramen; qfs, quadrate foramen spur; qsh, quadrate shaft; vqjc, ventral quadratojugal contact.
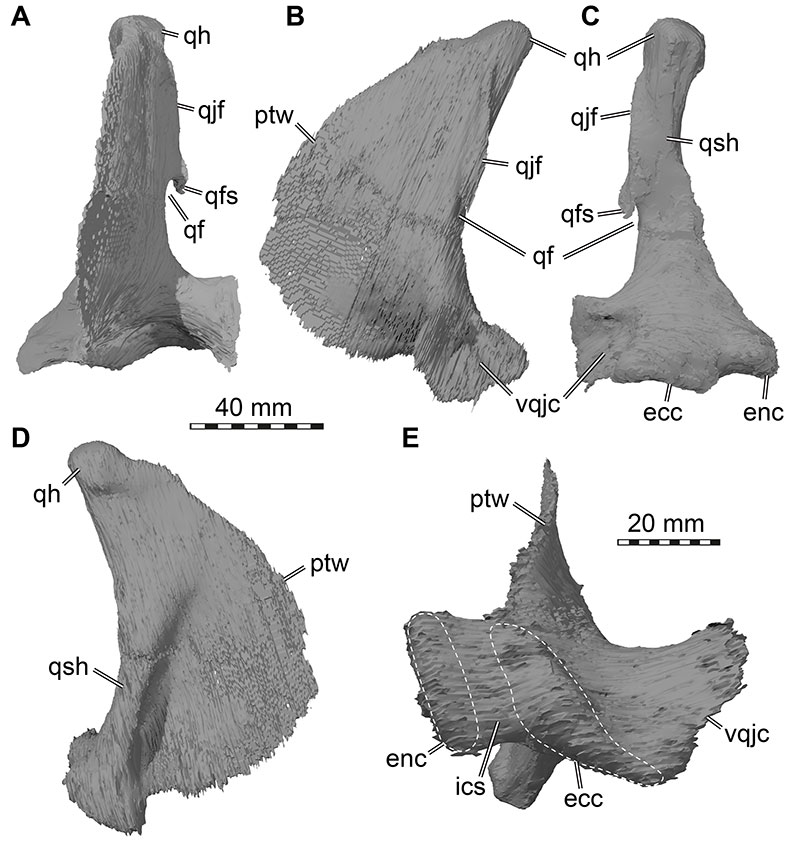
FIGURE 20. 3D renderings of the articulated braincase elements of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, anterior view; B, anterior view with interpretative line drawings; C, posterior view; D, posterior view with interpretative line drawings. Note that bones are labelled in bold, and other anatomical structures in regular font. Abbreviations: aoc, antotic crest; boc, basioccipital; bpp, basipterygoid process; bsr, basisphenoid recess; bt, basal tuber; cap, capitate process; crtu, crista tuberalis; crvl, crista ventrolateralis; cup, cultriform process; ds, dorsum sellae; fm, foramen magnum; lsp, laterosphenoid; mlsp, medial laterosphenoid process; occ, occipital condyle; osp, orbitosphenoid; oto, otoccipital; orsc, orbitosphenoidal crest; pbsp, parabasisphenoid; pcor, paracondylar recess; pop, paroccipital process; pro, prootic; ptf, posttemporal fenestra; pvf and XII, posterior vagal foramen and hypoglossal nerves (CN XII), see Figure 23 for details of this region; soc, supraoccipital; socc, supraoccipital crest; ssr, subsellar recess; vcm, vena capitis media foramen; I, olfactory nerve (CN I) foramen; II, optic nerve (CN II) foramen; III, oculomotor nerve (CN III) foramen; IV, trochlear nerve (CN IV) foramen; V, trigeminal nerve (CN V) foramen; V1gr, ophthalmic groove for V1 branch.
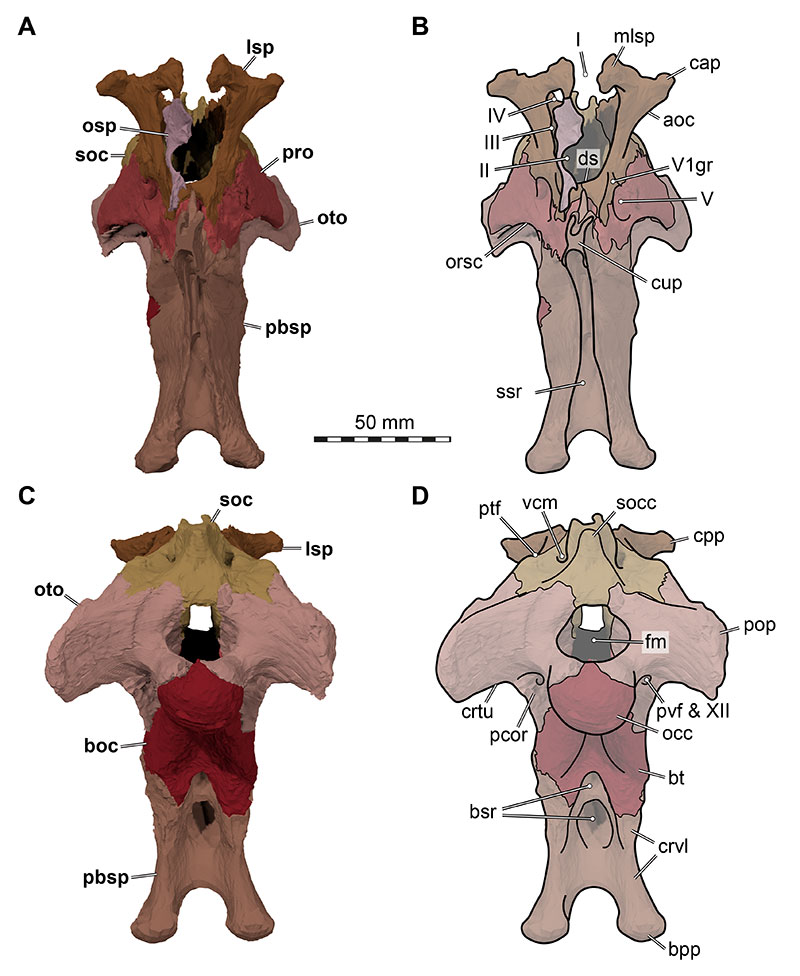
FIGURE 21. 3D renderings of the articulated braincase elements of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, dorsal view; B, dorsal view with interpretative line drawings; C, ventral view; D, ventral view with interpretative line drawings. Note that bones are labelled in bold, and other anatomical structures in regular font. Abbreviations: aoc, antotic crest; boc, basioccipital; bpp, basipterygoid process; bsr, basisphenoid recess; cap, capitate process; crtu, crista tuberalis; cup, cultriform process; ds, dorsum sellae; lsp, laterosphenoid; mlsp, medial laterosphenoid process; occ, occipital condyle; osp, orbitosphenoid; oto, otoccipital; pbsp, parabasisphenoid; pit, pituitary fossa (sella turcica); pop, paroccipital process; pro, prootic; soc, supraocciptal; socc, supraoccipital crest; ssr, subsellar recess; vcm, vena capitis media foramen; V, trigeminal nerve (CN V) foramen; VI, (posterior) foramen for abducens nerve (CN VI); VII-VIII, medial fossa for entry of facial nerve (CN VII) and optic nerve (CN VIII) into prootic; XII, hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) foramen.
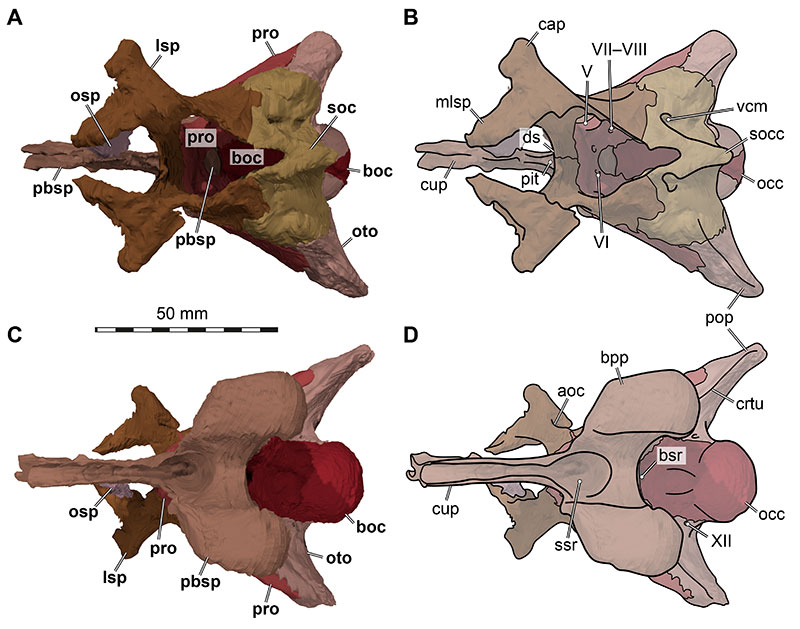
FIGURE 22. 3D renderings of the articulated braincase elements of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, right lateral view; B, right lateral view with interpretative line drawings; C, left lateral view; D, left lateral view with interpretative line drawings. Note that bones are labelled in bold, and other anatomical structures in regular font. Abbreviations: aoc, antotic crest; atyr, anterior tympanic recess; avf, (anterior) vagal foramen (connecting recessus scalae tympani region with paracondylar recess via a vagal canal); boc, basioccipital; bt, basal tuber; cap, capitate process; car, external foramen for the internal carotid artery (=vidian) canal; cor, columella recess; cif, crista interfenestralis; crtu, crista tuberalis; cup, cultriform process; fov, fenestra ovalis; iop, interorbital process of the parabasisphenoid; lsp, laterosphenoid; mvf, medial vagal foramen (connecting brain cavity with recessus scalae tympani); occ, occipital condyle; opr, ophthalmic ridge defining groove for ophthalmic branch (CN V1); oto, otoccipital; orsc, orbitosphenoidal crest; pbsp, parabasisphenoid; pop, paroccipital process; pro, prootic; rst, recessus scalae tympani/tympanic region of middle ear; soc, supraoccipital; II, medially open foramen for optic nerve (CN II); III, oculomotor nerve (CN III) foramen; IV, trochlear nerve (CN IV) foramen; V, trigeminal nerve (CN V) foramen; VII, facial nerve (CN VII) foramen.
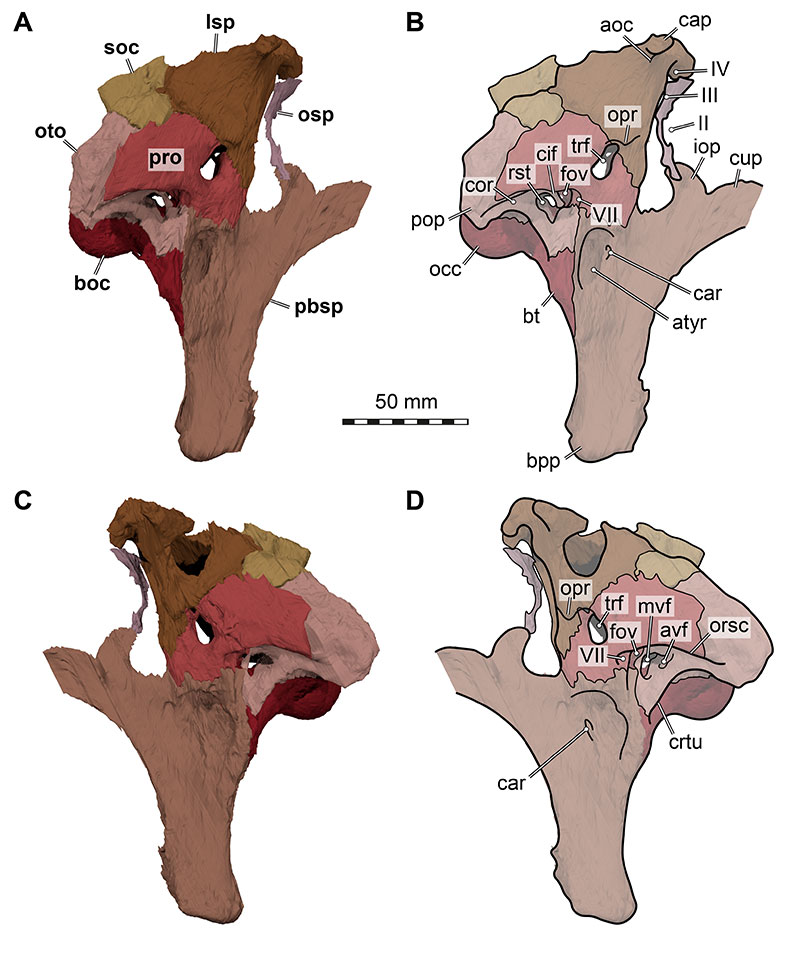
FIGURE 23. 3D renderings of the articulated braincase elements of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, slightly posteriorly rotated view of left side; B, detailed view of tympanic region; C, as B, with interpretative line drawings; D, strongly posteriorly rotated view of left side; E, detailed view on paracondylar region; F, as E, with interpretative line drawings. Note that bones are labelled in bold, and other anatomical structures in regular font. Abbreviations: atyr, anterior tympanic recess; boc, basioccipital; bsr, basisphenoid recess; bt, basal tuber; car, external foramen for the internal carotid artery (=vidian) canal; cif, crista interfenestralis; crtu, crista tuberalis; crvl, crista ventrolateralis; fm, foramen magnum; fov, fenestra ovalis; fpr, fenestra pseudorotunda (anteroposterior opening between labyrinth cavity and recessus scalae tympani); mcv, mid cerebral vein foramen; mvf, medial vagal foramen (connecting brain cavity with recessus scalae tympani); occ, occipital condyle; oto, otoccipital; orsc, orbitosphenoidal crest; pbsp, parabasisphenoid; pcor, paracondylar recess; pop, paroccipital process; pro, prootic; pvf, posterior vagal foramen; rst, recessus scalae tympani/tympanic region of middle ear; V, trigeminal nerve (CN V) foramen; VII, facial nerve (CN VII) foramen; XII, hypoglossal nerves (CN XII) foramina.
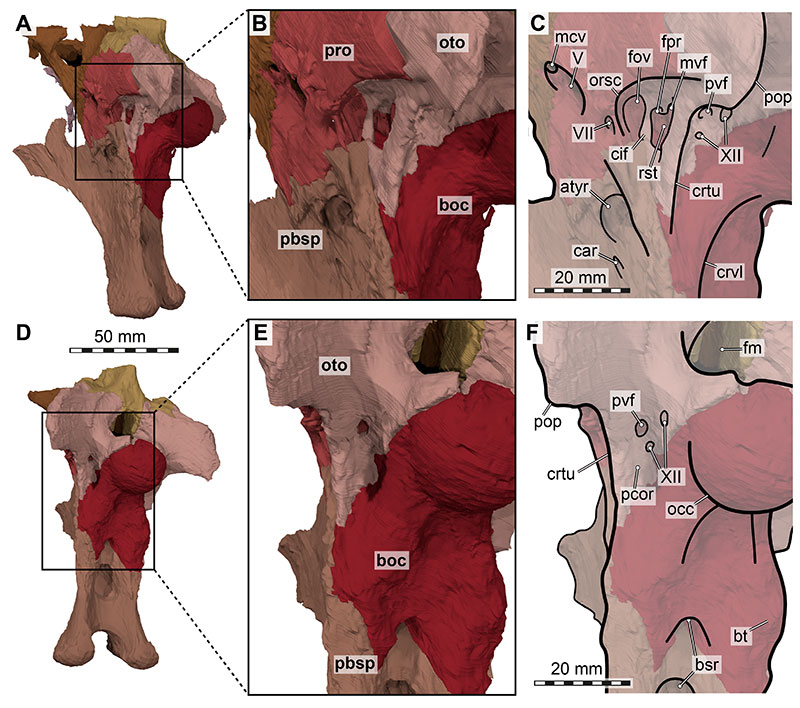
FIGURE 24. 3D renderings of the sagitally sectioned articulated braincase elements of the right side of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022) in medial view. A, complete rendering of right side; B, detailed view endocranial cavity; C, as A, with interpretative line drawings; D, as B, with interpretative line drawings. Note that bones are labelled in bold, and other anatomical structures in regular font. White arrows indicate internal connections of basisphenoid recess not covered in section. Abbreviations: atyr, anterior tympanic recess; boc, basioccipital; bsr, basisphenoid recess; cif, crista interfenestralis; ds, dorsum sellae; flr, floccular recess opening; fm, foramen magnum; icc, internal carotid artery (=vidian) canal; lsp, laterosphenoid; mvf, medial vagal foramen (connecting brain cavity with recessus scalae tympani); osp, orbitosphenoid; oto, otoccipital; pbsp, parabasisphenoid; pit, pituitary fossa; pop, paroccipital process; pro, prootic; soc, supraoccipital; ssr, subsellar recess; vcm, vena capitis media foramen; II, medially open foramen for optic nerve (CN II); III, oculomotor nerve (CN III) foramen; IV, trochlear nerve (CN IV) foramen; V, trigeminal nerve (CN V) foramen; VII, facial nerve (CN VII) foramen; XII, hypoglossal nerves (CN XII) foramina.
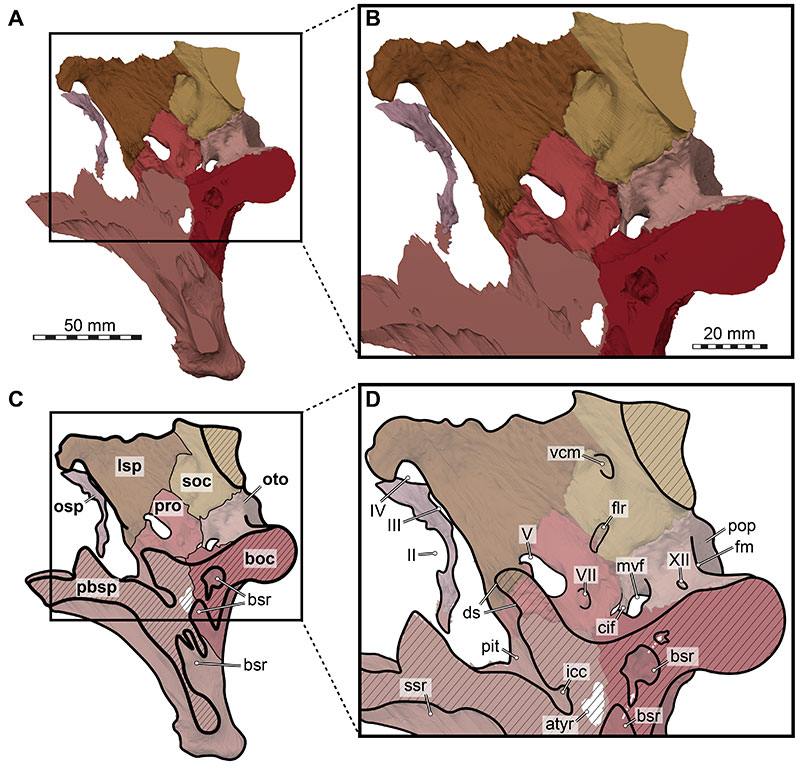
FIGURE 25. Close-up photographs of right lateral braincase of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, right lateral view; B, magnified anterior tympanic recess. Note that bones are labelled in bold, and other anatomical structures in regular font. Abbreviations: atyr, anterior tympanic recess; car, external foramen for the internal carotid artery (=vidian) canal; cif, crista interfenestralis; crtu, crista tuberalis; d, damage; fov, fenestra ovalis; mcv, mid cerebral vein foramen; opr, ophthalmic ridge defining groove for ophthalmic branch (CN V1); pd, (blind) pneumatic depression; sg, stapedial groove; vf, (lateral) vagal foramen; ?sha, potential sphenoidal artery opening; II, medially open foramen for optic nerve (CN II); III, oculomotor nerve (CN III) foramen; V, trigeminal nerve (CN V) foramen; V1gr, ophthalmic groove for V1 branch; VII, facial nerve (CN VII) foramen.
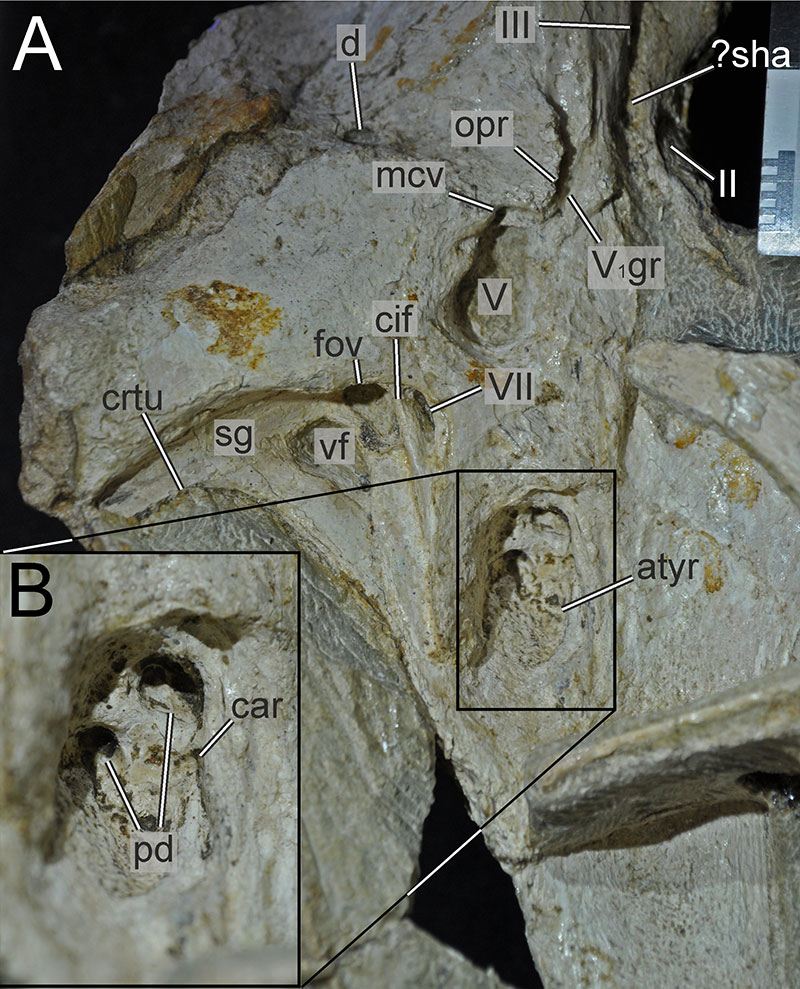
FIGURE 26. 3D renderings of the intracranial cavities within the articulated braincase of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, posterior view; B, ventral view; C, right anterolateral view. Colours reflect cavity identity, where green cavities are within the otic bones, purple cavities are within the basioccipital (boc), blue cavities are within the parabasisphenoid (pbsp), and yellow recesses are within the orbitosphenoid. Abbreviations: bsr, basisphenoid recess; osr, orbitosphenoid recess; otor, otoccipitical recess; pror, prootic recess; sor, supraoccipital recess.
FIGURE 27. Close-up photograph of the stapes of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). Abbreviation: s, stapes.

FIGURE 28. 3D renderings of the vomer of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, ventral view (anterior to left); B, left lateral view; C, dorsal view (anterior to left); D, right lateral view; E, posterior view. Note different scale in E. Abbreviations: dmt, dorsomedian trough of vomer; mxc, maxillary contact, palc, palatine contact; papr, posterior articular process of vomer; ptc, pterygoid contact.
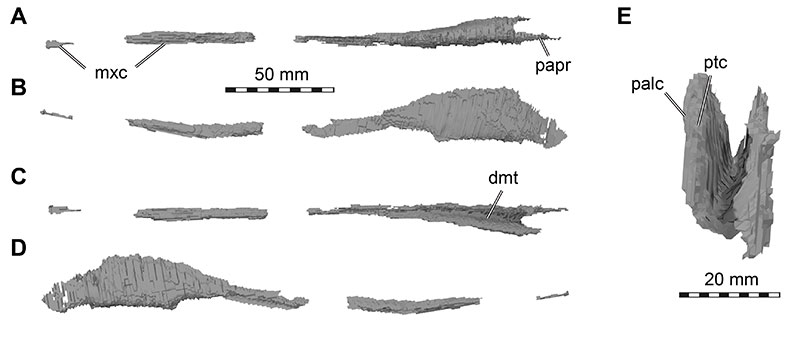
FIGURE 29. 3D renderings of the palatines of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A-D, right palatine in A, lateral view; B, posterior view; C, medial view; D, ventral view (anterior direction to the right). E-F, left palatine in E, medial view; F, lateral view. Abbreviations: jp, jugal process; lap, lacrimal process; mxp, maxillary process; palf, posterior palatine fossa; ptp, pterygoid process; vc, surface for contact with vomer; vptp, vomeropterygoid process.
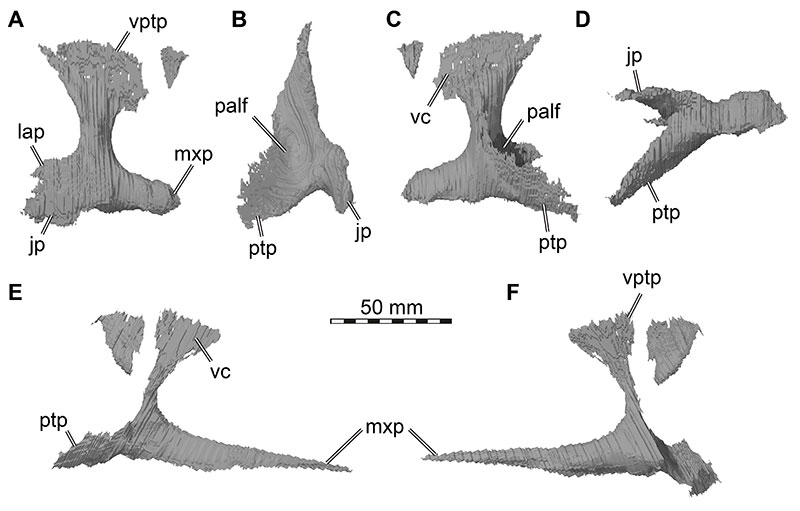
FIGURE 30. Close-up photograph of the left cheek region of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). Note that bones are labelled in bold, and other anatomical structures in regular font. Abbreviations: j, jugal; l, lacrimal; l.ep, left ectopterygoid; ecpl, ectopterygoid lamina of the left pterygoid; l.bpp, left basipterygoid process of the parabasisphenoid; l.pa, left palatine; l.pt, left pterygoid; l.sur, left surangular; l.sq, left squamosal; m, maxilla; ptw, pterygoid wing of left quadrate; qw, quadrate wing of left pterygoid; r.pa, right palatine; r.sur, right surangular; 10, tenth preserved tooth position of the left maxilla.
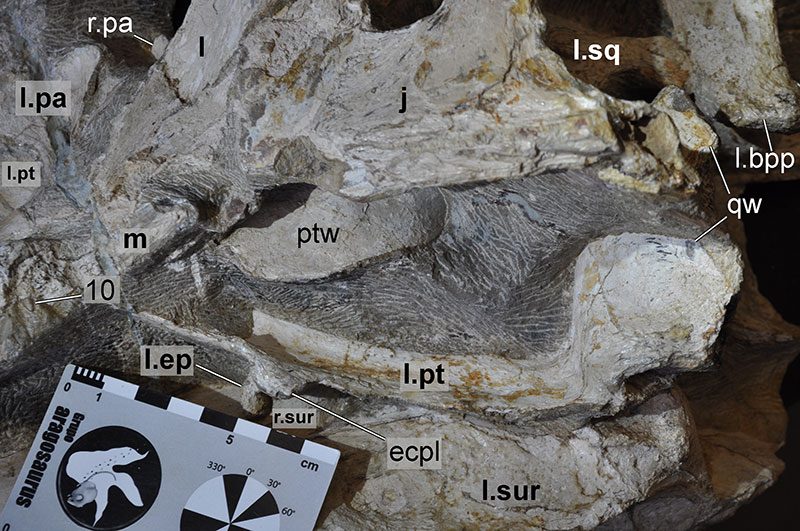

FIGURE 31. 3D renderings of the left pterygoid of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, lateral view; B, posterior view; C, dorsal view; D, medial view. Abbreviations: bptp, basipterygoid process; ecpl, ectopterygoid lamina; epic, epipterygoid contact; palc, palatine contact; qw, quadrate wing; vc, vomer contact; vpap, vomeropalatine process.
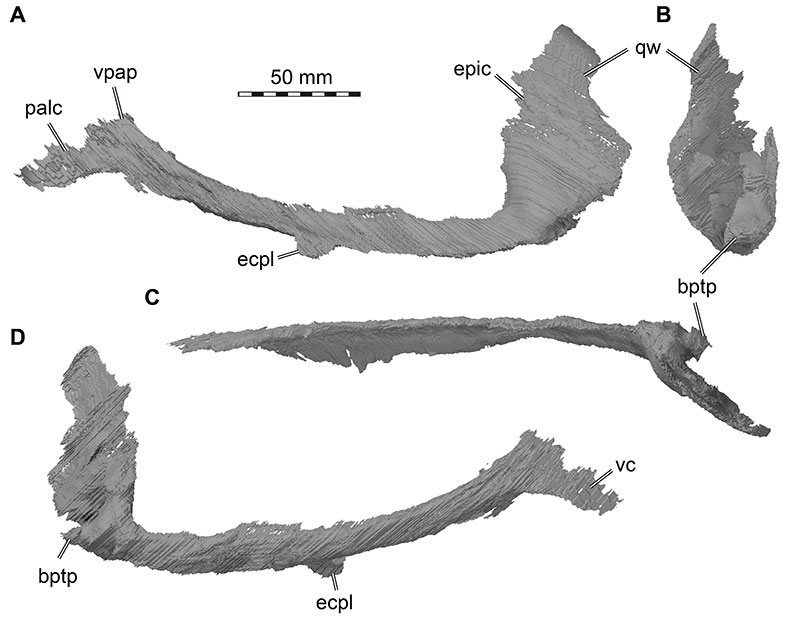
FIGURE 32. 3D renderings of the left ectopterygoid of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, dorsal view; B, ventral view; C, lateral view; D, medial view. Arrow in A valid for A-C. Note that dashed line indicates approximate former extent of bone. Abbreviations: jc, jugal contact; jp, jugal process; ptc, pterygoid contact; ptf, pterygoid flange; pvp, posteroventral process; vr, ventral recess.
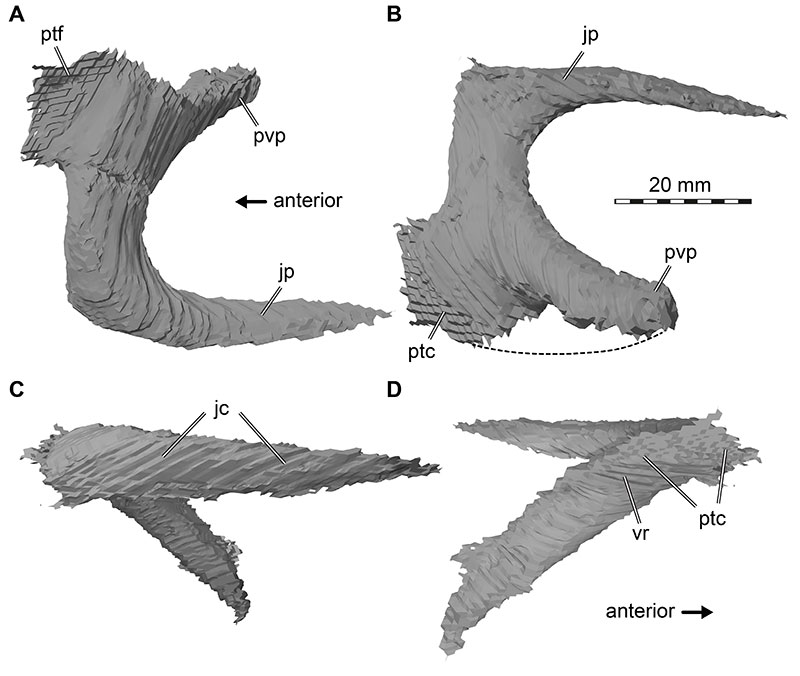
FIGURE 33. 3D renderings of the left epipterygoid of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, medial view; B, lateral view. Abbreviations: ptc, pterygoid contact; tanm, thickenend anterior margin.
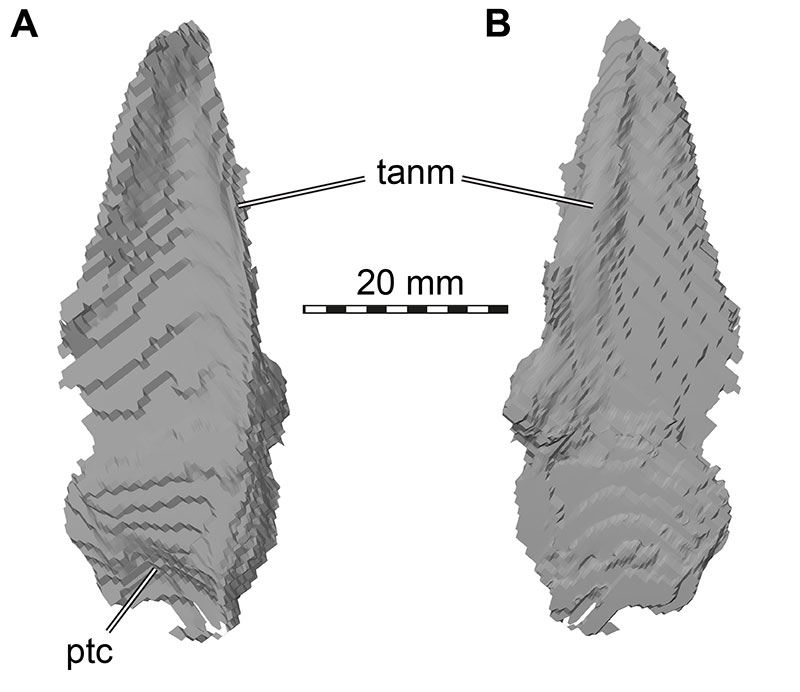
FIGURE 34. 3D renderings of left mandibular elements of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, lateral view; B, dorsal view; C, medial view. Abbreviations: addf, adductor fossa; an, angular; d, dentary; glf, glenoid fossa; lss, lateral surangular shelf; manf, mandibular fenestra; mhp, medial hook process; mics, medially inclined coronoid shelf; pra, prearticular; rap, retroarticular process; sur, surangular. Note that different bones are rendered in different colours, and that bone labels are in bold. Also note that the articular is fused with the surangular and thus segmented in a joint model with that bone.
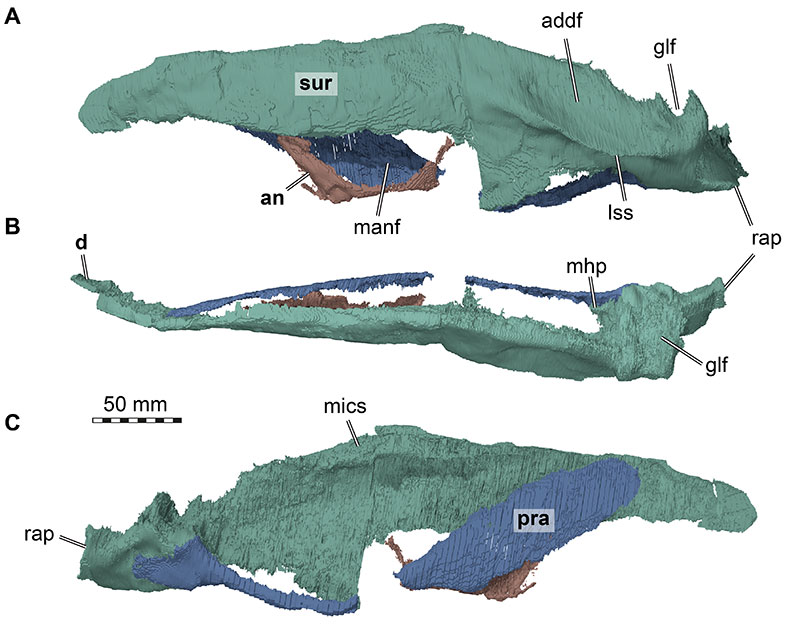
FIGURE 35. 3D renderings of right surangular of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, lateral view; B, dorsal view; C, medial view. Abbreviations: addf, adductor fossa; glf, glenoid fossa; lss, lateral surangular shelf; mics, medially inclined coronoid shelf; rap, retroarticular process. Note that the articular is fused with the surangular and thus segmented in a joint model with that bone.
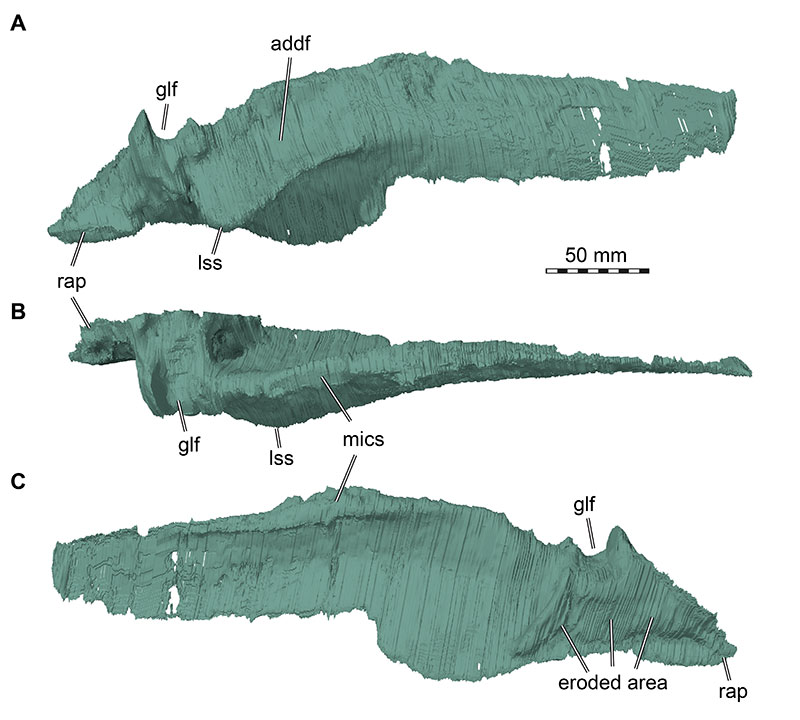
FIGURE 36. Phylogenetic results from parsimony analysis using the full dataset. A, strict consensus tree of 8184 MPTs retained from an equal weighting analysis (see methods for details); B, partial reduced consensus tree, showing the clade Spinosauridae after removal of the taxon Vallibonavenatrix; C, strict consensus tree of 406 MPTs retained from an implied weighting analysis using a concavity constant of k=10 (see Methods for details). Important clades are labelled. Irritator as the main focus of our study is highlighted in bold face within the clade Spinosauridae.

FIGURE 37. Phylogenetic results from parsimony analysis using the cranial dataset. A, strict consensus tree of 153 MPTs retained from an equal weighting analysis (see Methods for details); B, reduced consensus tree, pruning wild card taxa from the strict consensus. Wild card taxa are highlighted with coloured boxes in A, and their possible topological positions are shown with same coloured squares in B. Important clades are labelled.
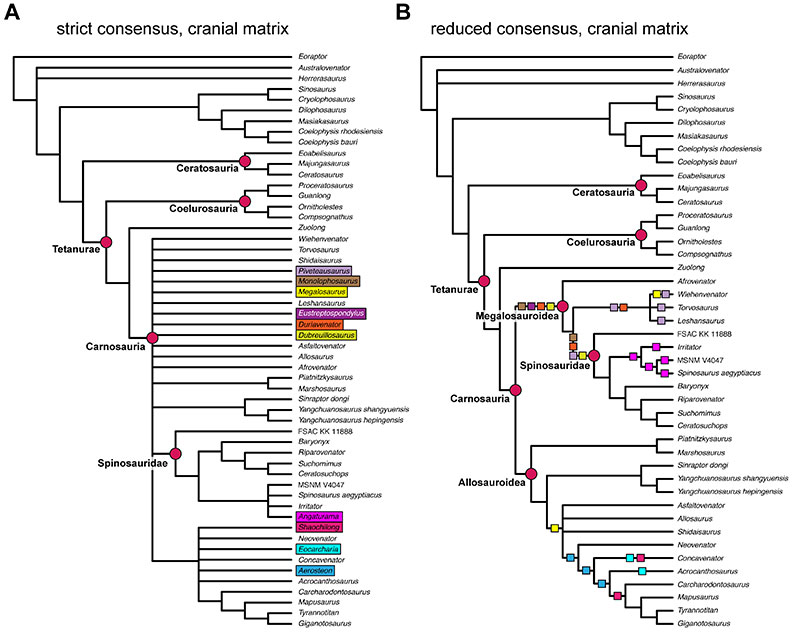
FIGURE 38. Tip-dated allcompat tree from posterior sample of Bayesian analysis (with full dataset), showing posterior probability values for internal nodes. Red values represent nodes below 50% posterior probability.
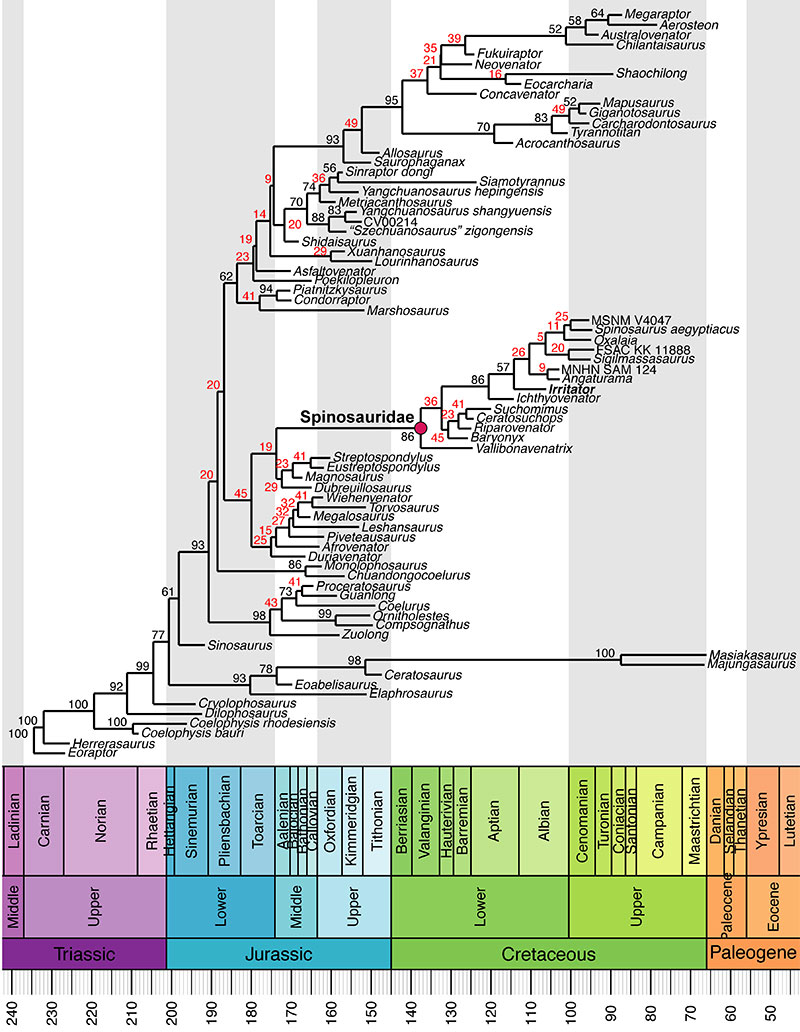
FIGURE 39. Tip-dated allcompat tree from posterior sample of Bayesian analysis (with full dataset). Branch colours show evolutionary character state transition rates (in character transitions per million year). Nodes below 50% posterior probability are collapsed into polytomies for which evolutionary rates cannot be calculated.
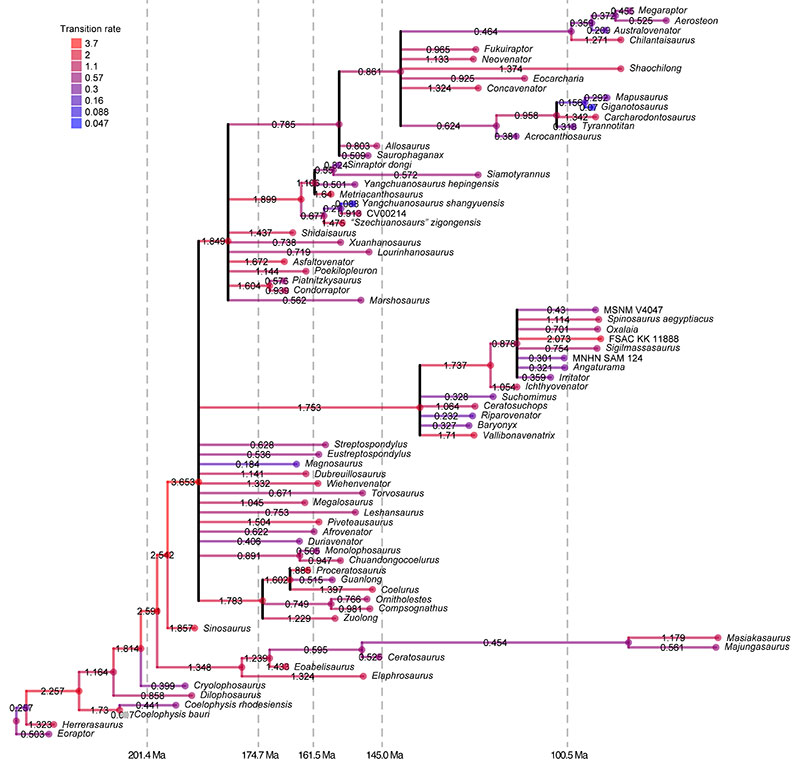
FIGURE 40. Medical CT data-based 3D print of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022) with reconstructed jaw muscle anatomy in left lateral view. A, with superficial muscles; B, with removed cheek bones, revealing deeper muscles. mAMEP, m. adductor mandibulae externus profundus; mAMES, m. adductor mandibulae externus superficialis; mAMP, m. adductor mandibulae posterior; mDM, m. depressor mandibulae; mPSTs, m. pseudotemporalis superficialis; mPTd, m. pterygoideus dorsalis; mPTv, m. pterygoideus ventralis.
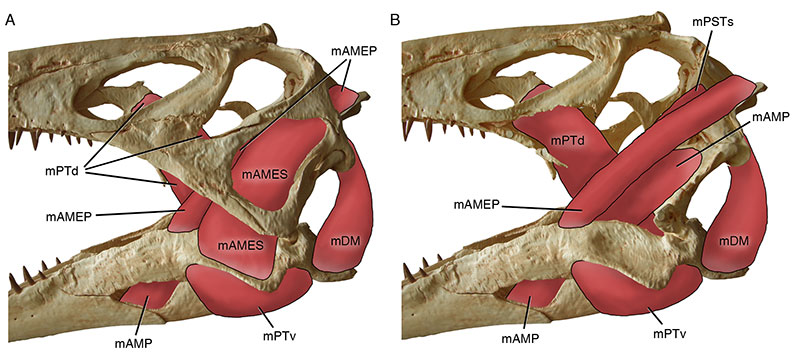
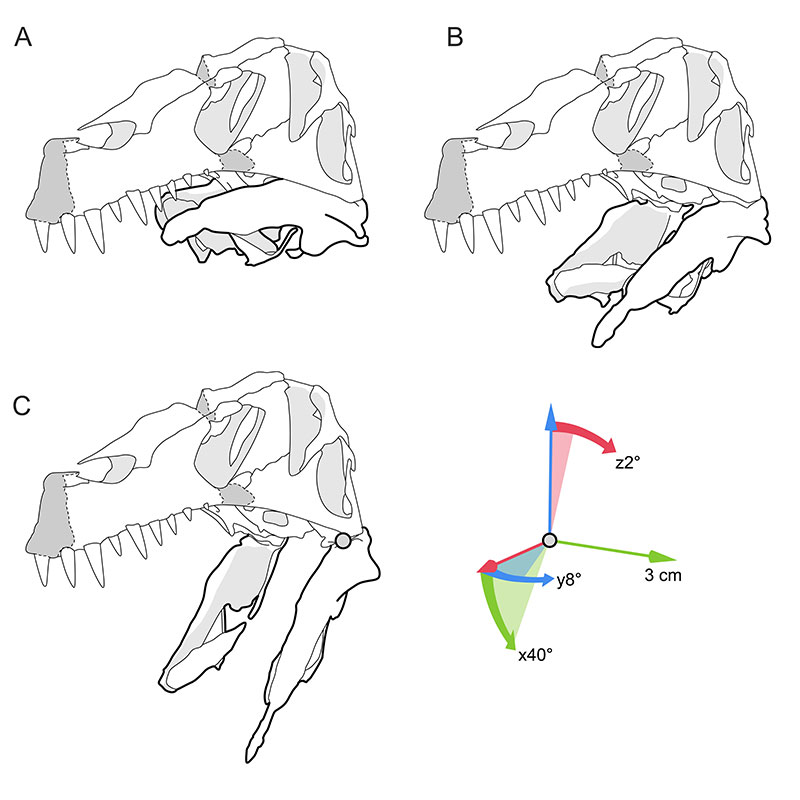
FIGURE 41. Line drawings of the re-arranged and articulated skull of Irritator challengeri (SMNS 58022). A, completely closed lower jaw; B, laterally spreading and rotating lower jaw rami during depression; C, the maximum opening angle of around 40° (in wider angles, the raised posterolateral margin of the glenoid fossa hits the quadrate). The lower jaw rami spread approx. 8° sideways, producing a pharynx mediolaterally widened around 3 cm per side. Additionally, each lower jaw ramus is rotating around the long axis by approx. 2° (dorsally lateral and ventrally medial). These values are measured from the point of origin for the maximum opening angle in relation to the closed position.