FIGURE 1. Natural (1), digital (2), and radiographic images (3) of Nesophontes spp. crania used in this study. 1, these skulls were the source of natural endocasts for Nesophontes micrus (C145) and Nesophontes major (C181) shown in Figures 1 and 2. 2, Digital rendering of N. major skull (C133) from which the digital endocast in Figure 5 was reconstructed. 3, are negative and positive lateral radiographs of Nesophontes spp. endocranial morphology and space.
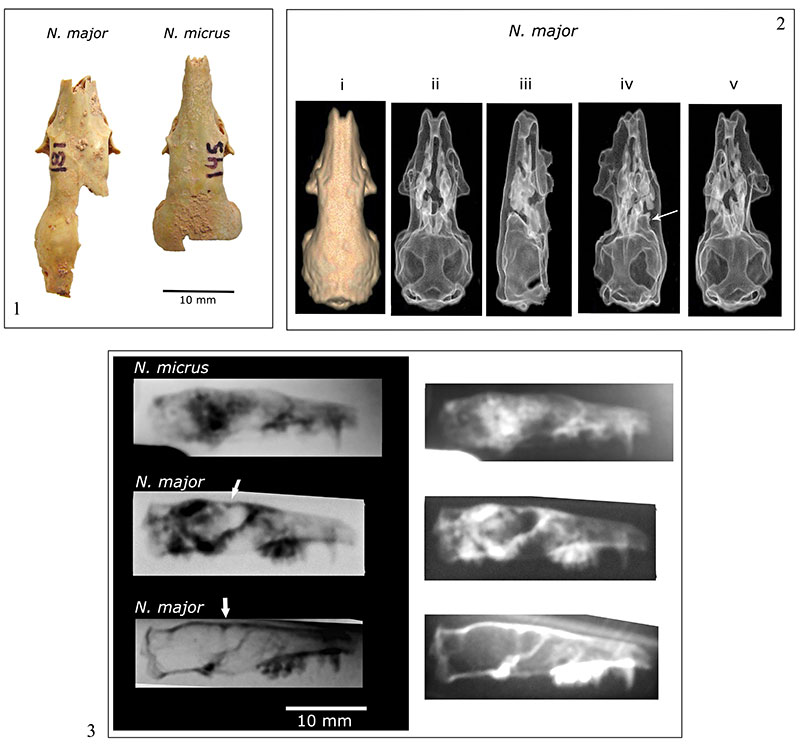
FIGURE 2. Natural endocranial casts of Cuban Nesophontes spp. 1, superior, and right lateral view of Nesophontes major (specimen number C181) endocasts. 2-3, superior and right lateral views of Nesophontes micrus endocasts. 2, Nesophontes micrus (C145); 3-4, are not cataloged.
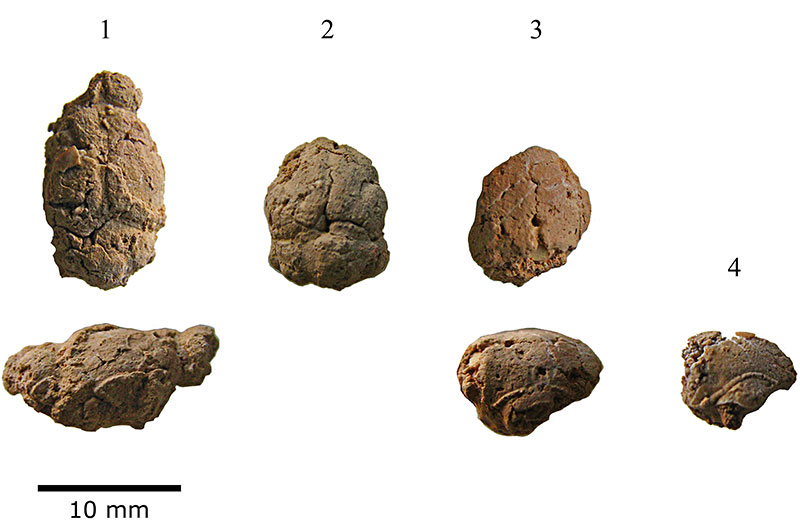

FIGURE 3. Anatomical terminology of Nesophontes endocranial casts. 1, superior and lateral views of Nesophontes major endocranial cast (C181). 2, superior and lateral views of Nesophontes micrus (C145) specimen. 3, single view of partial endocranial cast extracted from an uncataloged N. micrus skull. Abbreviations of anatomical terminology: Cb cerebellum; cs superior colliculi; fan annular or circular fissure; Iar internal auditory region; lal lateral lobe of cerebellum; las lateral transverse sinus; Ncx neocortex; Ob olfactory lobes; otg orbitotemporal groove; Ocx olfactory (=piriform) cortex; Pfl paraflocculus; rhf rhinal fissure; sas sagittal sinus or longitudinal sinus; Sphr sphenorbital region; Sv confluence of the transverse and sagittal sinuses; Vc cerebellar vermis. A and P stand for anterior and posterior.
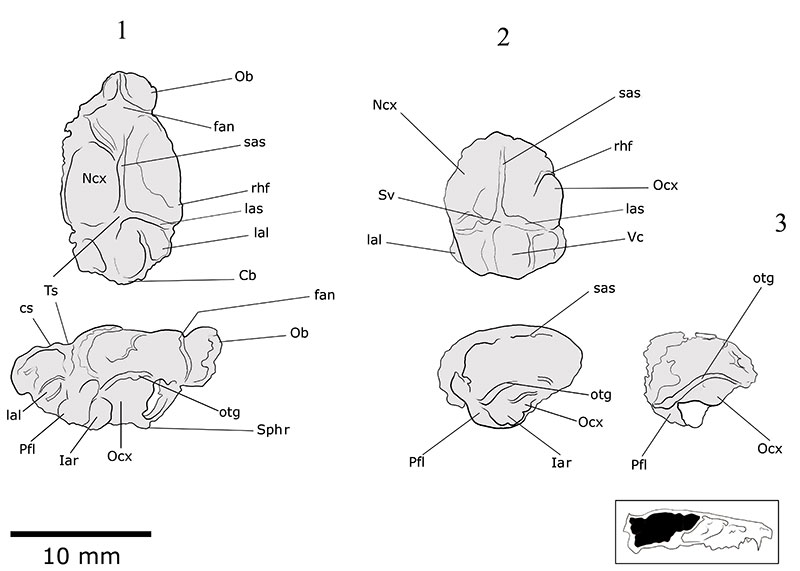
FIGURE 4. Natural endocranial casts extracted from Nesophontes spp. skulls. (4.1) Nesophontes major hindbrain fragment; (4.2) N. major olfactory lobes; (4.3-4.4) Nesophontes micrus superior (4.3) and left lateral (4.5) views of a partial hindbrain. Cb cerebellum; cs superior colliculi; lal lateral lobe of cerebellum; Ob olfactory lobes; op olfactory peduncle; Pfl paraflocculus; Ts transverse sinus canal; Ts-c confluence of the transverse and sagittal sinuses. A and P stand for anterior and posterior.
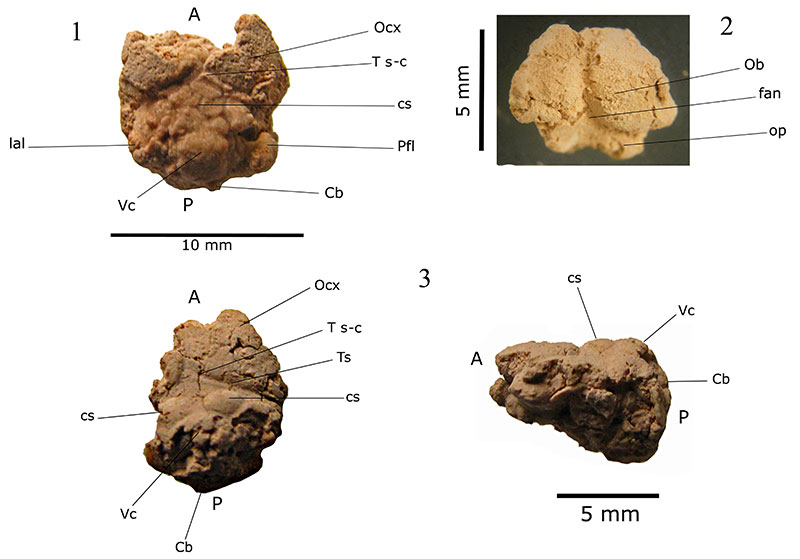
FIGURE 5. Digital endocranial cast of Nesophontes major (C133) in right lateral (1), anterior (2), and inferior (3) views. Abbreviations: Cb cerebellum; cc possible cast of spinal cord space; cs superior colliculi; fan annular or circular fissure; hy hypophyseal fossa; Iar internal auditory region; lal lateral lobe of cerebellum; las lateral transverse sinus; Ncx neocortex; Ob olfactory lobes; Och. optic chiasm; Ocx olfactory (=piriform) cortex; ot olfactory nerve fibers; otg orbitotemporal groove; Pfl paraflocculus; rhf rhinal fissure; sas sagittal sinus or longitudinal sinus; Sphr sphenorbital region; Sv confluence of the transverse and sagittal sinuses; Vc cerebellar vermis. A and P stand for anterior and posterior.
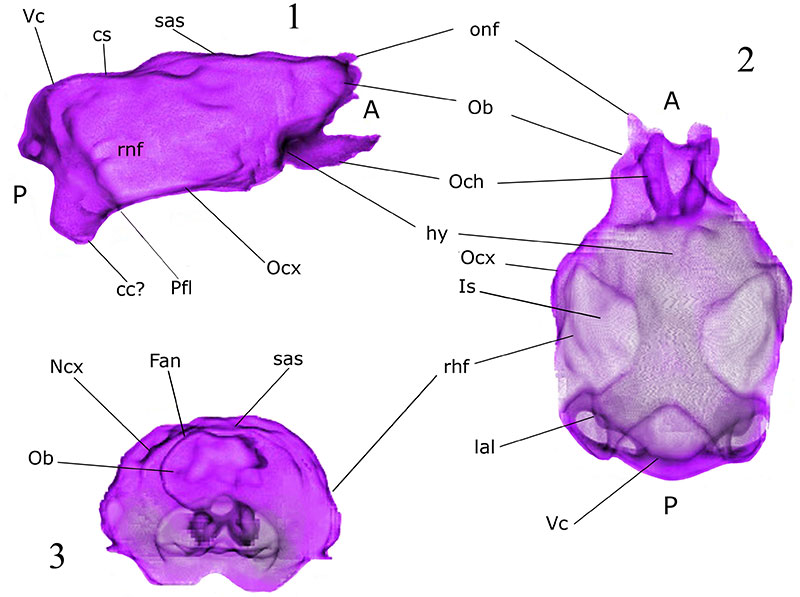
FIGURE 6. Volume rendering of Nesophontes major (C133) endocranial space in lateral (1) and oblique (2) views showing possible olfactory nerve fibers (onf), sylvian fissure (S. f.), and rhinal fissure (rhf). A and P stand for anterior and posterior.
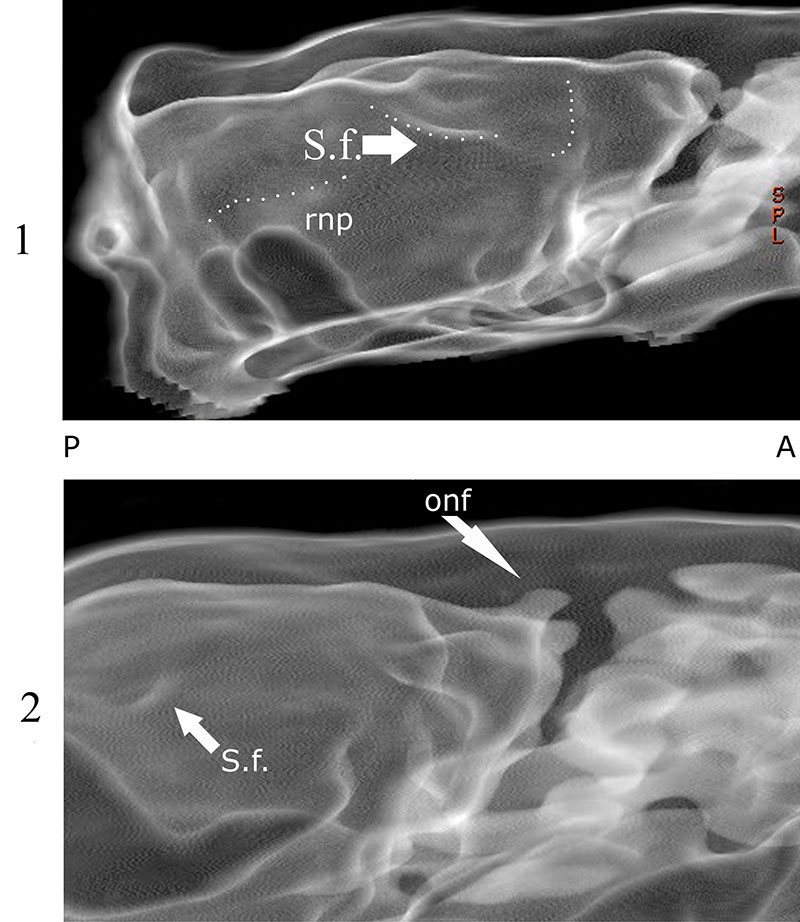
FIGURE 7. Endocranial casts of Cuban Nesophontes spp . Nesophontes micrus (C437) first column. Endocast volume: 0.580 mL, encephalization quotients (EQ 2 and 3): 0.21 and 0.33. Nesophontes micrus (C436), second column. Endocast volume: 1.231 mL, EQ 2 and 3: 0.33 and 0.52. Nesophontes major (270), third column. Endocast volume: 0.729 mL, EQs: 0.27 and 0.43. Nesophontes major (C133), fourth and last column. Endocast volume: 0.888 mL, EQs: 0.36 and 0.57.
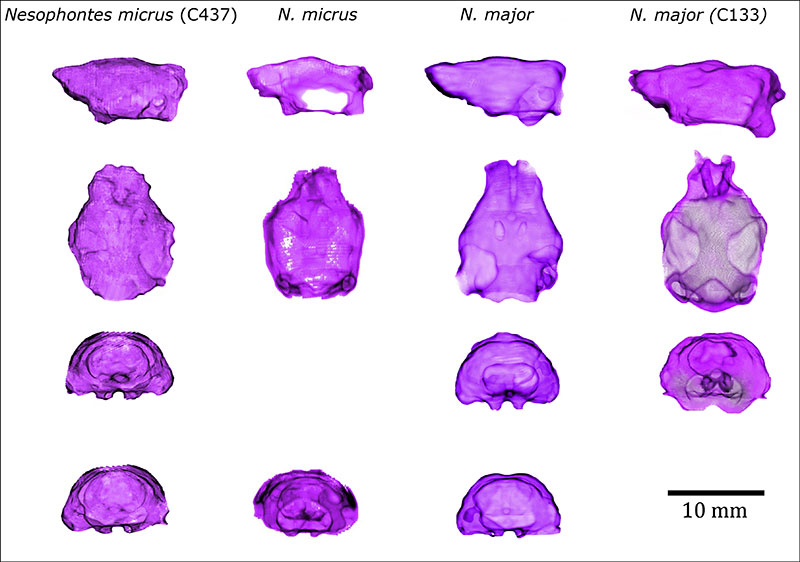
FIGURE 8. Cribriform and olfactory regions in Nesophontes major (1) and Nesophontes micrus (2). Abbreviations: ar annular ridge; As alisphenoid; cef cribroethmoidal foramen; cg crista galli; ec ectoturbinal foramina; etI ethmoturbinal foramina; fo foramen ovalae; hs horizontal sulcus; Js jugun sphenoidalis; nc nasocribriform foramina; ntf nasoturbinal foramina; of optic foramen for optic nerve; off olfactory fossa; otc orbitotemporal canal; psp parasphenoid plate; sof sphenorbital fossa; sor sphenorbital ridge. A and P stand for anterior and posterior.
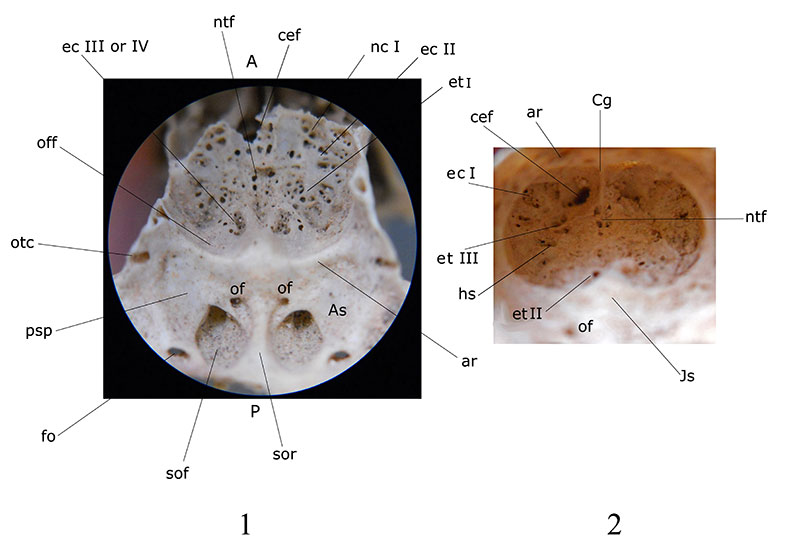
FIGURE 9. Endocranial morphology of Nesophontes micrus and Nesophontes major calotte showing slight differences in tectum and transverse sinus. Top arrows point to the confluence of the transverse sinus and the colliculi fossae. A and P stand for anterior and posterior.
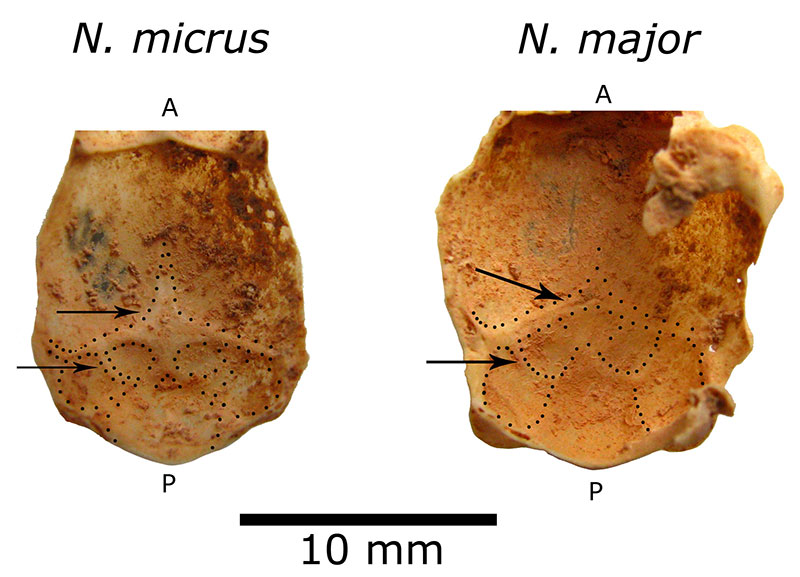
FIGURE 10. Idealized brain reconstruction of Nesophontes spp (1), and Solenodon paradoxus (2) in superior and lateral views. The brain of Nesophontes is a composite reconstruction based on natural and digital casts. Solenodon paradoxus was drawn from photographs of Stephen and Andy (1982:541, figures 20-22). Lines and labels on the lateral views indicate similar morphologic features. Olfactory lobes are in red, neocortex is in blue, and posterior brain (part of midbrain and cerebellum) is in green. Specimens are not to same scale. Abbreviations: Cb cerebellum; cs superior colliculi; Fan annular or circular fissure; Iar internal auditory region; lal lateral lobe of cerebellum; las lateral transverse sinus; Ncx neocortex; Ob olfactory lobes; Och optic chiasm; Ocx olfactory (=piriform) cortex; onf olfactory nerve fiber; otg orbitotemporal groove; Pfl paraflocculus; Pof post-orbital fissure; rhf rhinal fissure; sas sagittal sinus or longitudinal sinus; Sphr sphenorbital region; Sv confluence of the transverse and sagittal sinuses; T tectum; Vc cerebellar vermis. A and P stand for anterior and posterior.
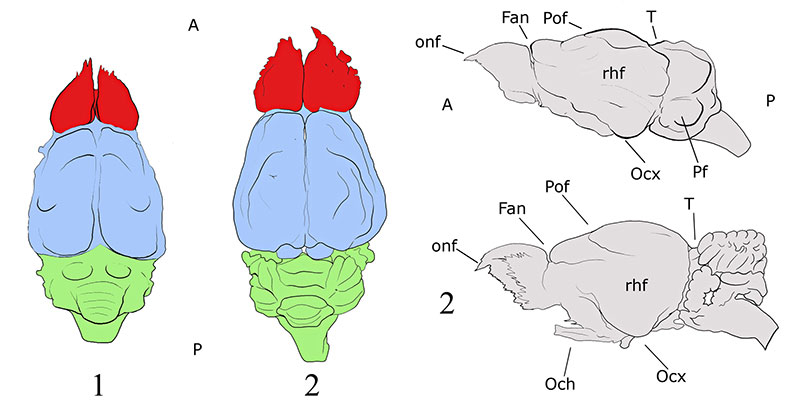
FIGURE 11. Brain morphology of selected extinct and extant mammals, including Nesophontes spp. Upper row contains extant placentals and marsupials. Lower row contains extinct taxa and Nesophontes . Olfactory lobes are in red, neocortex is in blue, and hindbrain is in green. Scale bar equals 10 mm. Sources: Monodelphis domestica drawn from Rowe et al. (2011); Solenodon paradoxus from Allen (1910); Tenrec ecuadatus from Stephan and Andy (1982); Eoryctes melanus from Thewissen and Gingerich (1989); Hyopsodus lepidus from Orliac et al. (2012); Vincelestes neuquenianus from Macrini et al. (2007a) Nesophontes taxa reported here, and the remaining from the Comparative Brain Collection at www.brainmuseum.org. A and P stand for anterior and posterior. Scale bar = 1 cm.
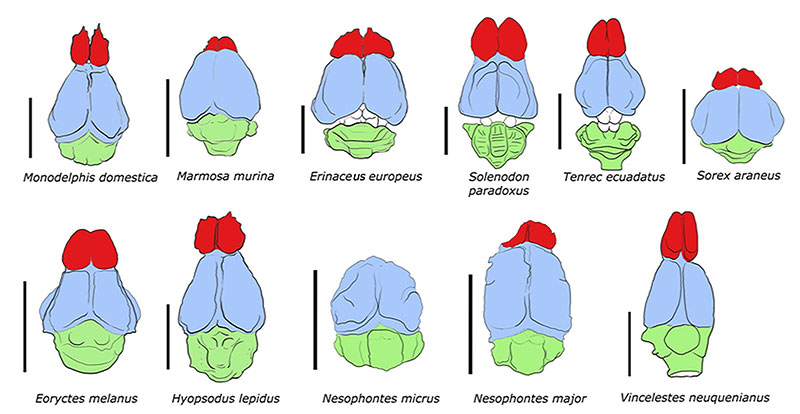
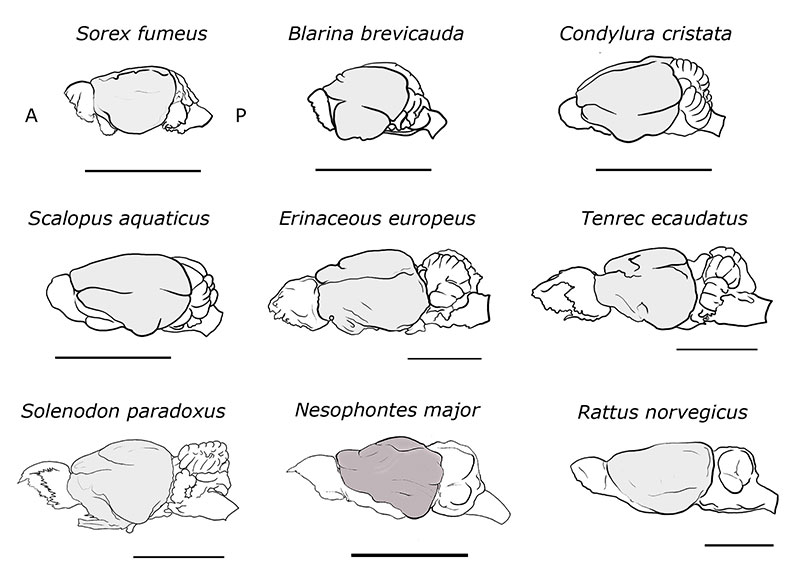
FIGURE 12. Idealized brain reconstruction of Nesophontes major compared to other insectivoran-mammals, plus the Norway rat Rattus norvegicus . Sorex , Blarina , Condylura , Scalopus , and Rattus specimens were redrawn and modified from specimens in the Comparative Brain Collection at www.brainmuseum.org and Sarko et al. (2009). Erinaceous , Tenrec , and Solenodon were drawn from Stephen and Andy (1982). A and P stand for anterior and posterior. Scale bar = 1 cm.